Robot autonomous barrier avoiding method and device
A robot and sensor technology, applied in the field of robots, can solve problems such as poor adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
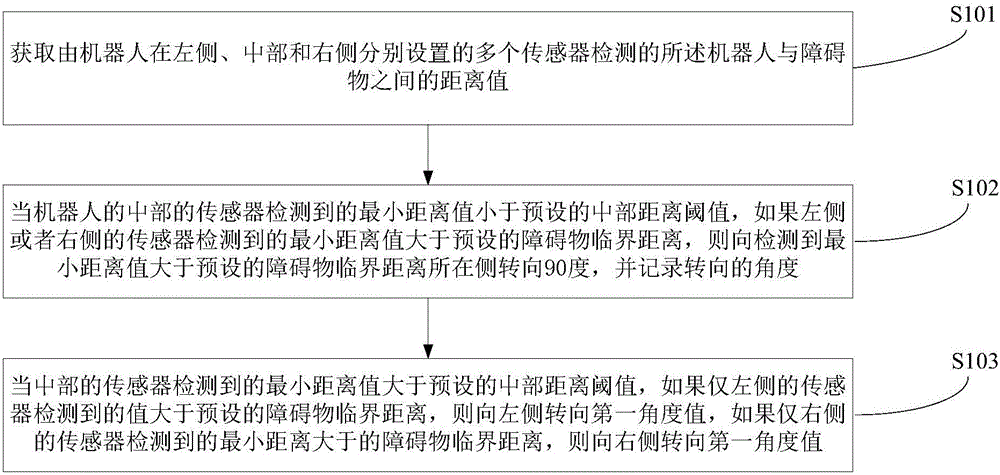
[0039] figure 1 The implementation flow of the robot autonomous obstacle avoidance method provided by the first embodiment of the present invention is shown, and the details are as follows:
[0040] In step S101, the distance values between the robot and obstacles detected by a plurality of sensors respectively arranged on the left side, the middle part and the right side of the robot are obtained. For the sensors of the feet, the right side of the robot includes sensors that are respectively arranged on the right hand and the right foot of the robot, and the middle part of the robot includes sensors that are respectively arranged on the head and the torso of the robot.
[0041] Specifically, the sensor described in the embodiment of the present invention may use an infrared sensor, an ultrasonic sensor, or a depth sensor to detect the distance. In order to better judge obstacles, we can divide the front ranging sensors of the robot into three groups: left, middle, and right,...
Embodiment 2
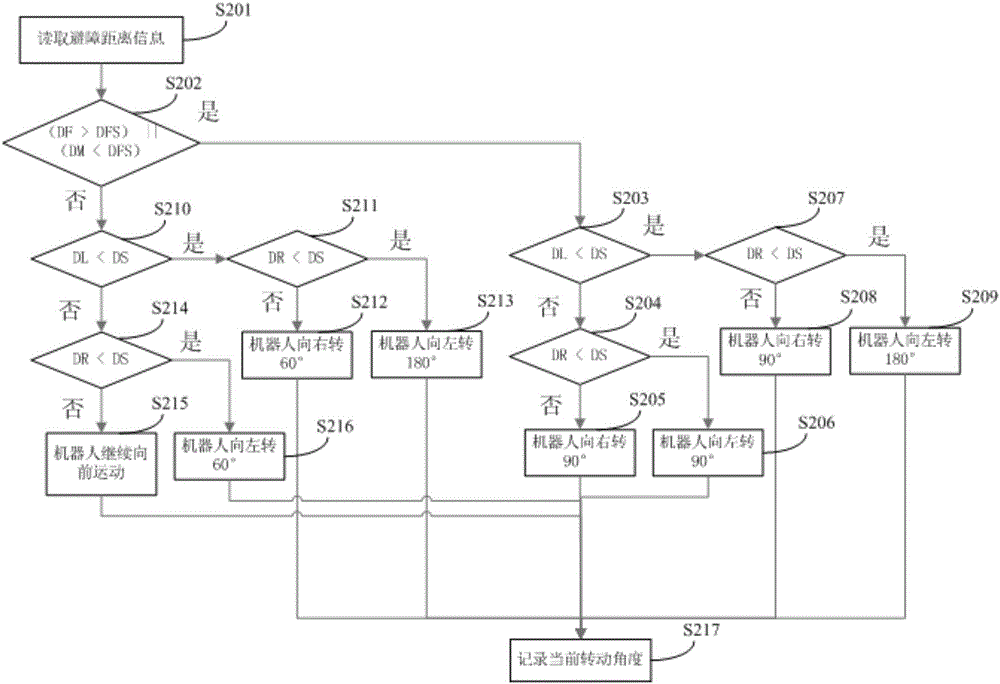
[0065] figure 2 The implementation process of the robot autonomous obstacle avoidance method provided by the second embodiment of the present invention is shown, and the details are as follows:
[0066] In step S201, the robot reads the distance data detected by the sensor, which may include the sensor data detected by the 17 sensors listed in Embodiment 1, and for each group of sensor data, automatically obtains the smallest value as the sensor of the group output value. Among them, DL, DM, DR and DF are used to indicate the minimum distance of the left, middle, right and anti-drop of the robot, and DS is used as the obstacle critical distance of the obstacle confirmation layer. DFS is the obstacle critical distance to prevent falling. Every time you avoid obstacles, you must record the direction of rotation and the distance you move. After avoiding obstacles, perform rotation compensation and continue to walk in the original direction.
[0067] In step S202, it is determ...
Embodiment 3
[0085] image 3 The implementation process of the robot autonomous obstacle avoidance method provided by the third embodiment of the present invention is shown, and the details are as follows:
[0086] In the embodiment of the present invention, we use DS as the critical distance of the obstacle confirmation layer. DFS is the critical distance of obstacles to prevent falling, DRN is the shortest critical distance for walking to the right, DRF is the farthest critical distance for walking to the right, and DRTF is the distance against the wall that is too far away to stop walking along the wall.
[0087] In step S301, the robot reads the distance data detected by the sensor, which may include the sensor data detected by the 17 sensors listed in Embodiment 1, and for each group of sensor data, automatically obtains the smallest value as the sensor of the group output value. Among them, DL, DM, DR and DF are used to represent the left, middle, right and minimum distances of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com