Biological information acquisition device, smart garment and smart gloves
A technology of biological information and collection device, applied in the field of textiles, can solve the problems of the influence of biological movements, the large diameter, the inconvenience of carrying equipment for measuring biological information, etc., so as to improve practicability and comfort, improve the effect of fixing, reduce The effect of manufacturing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
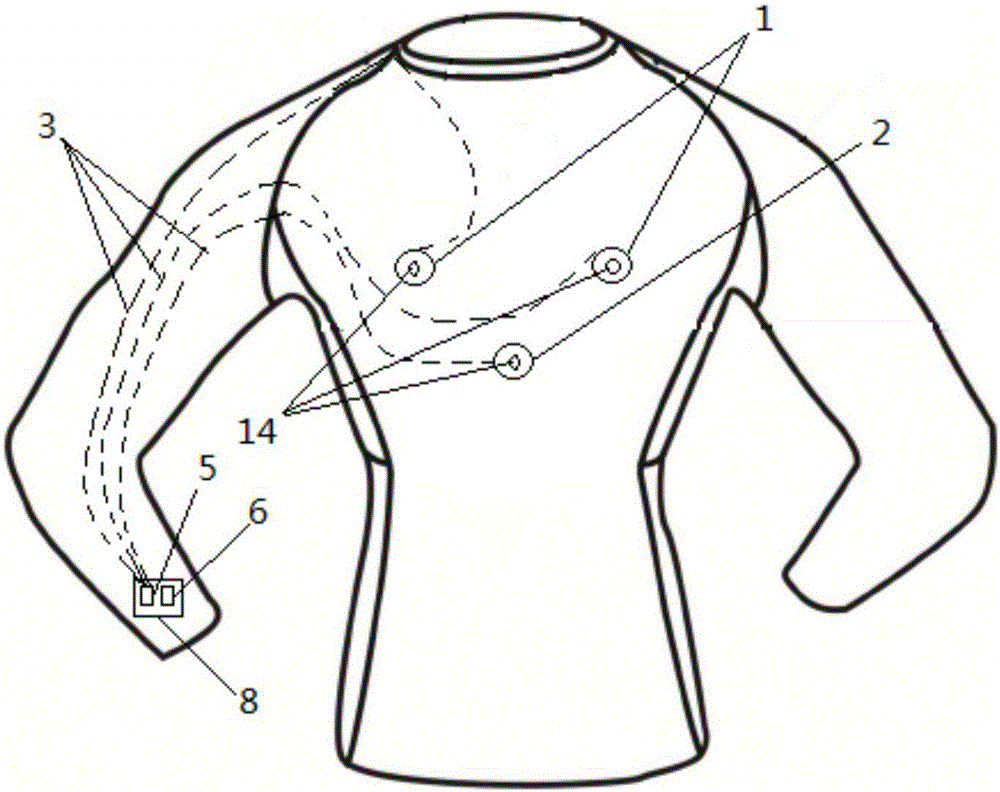
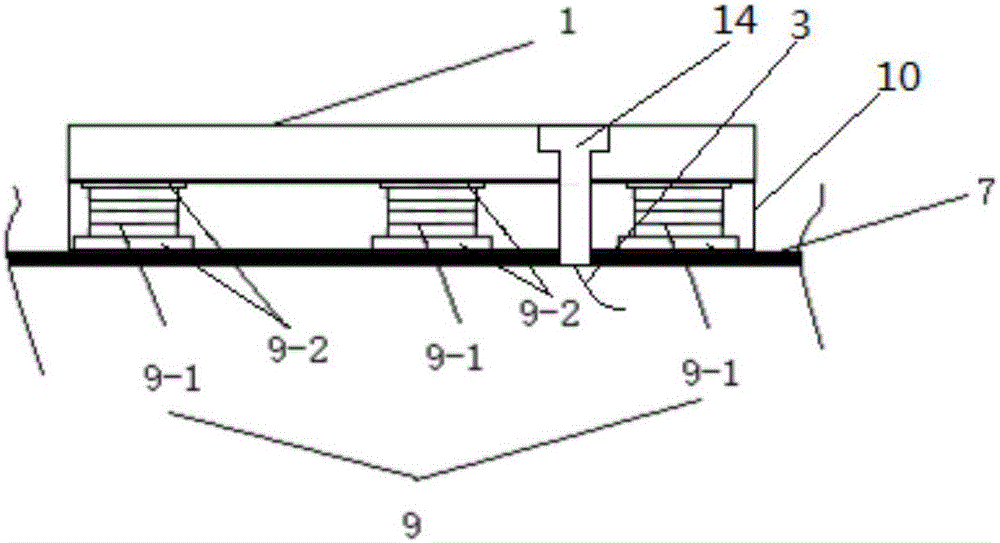
[0042] The first embodiment of the present invention provides a biological information collection device, which is applied to wearable products 3, such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, it includes a biological information collection component arranged on a wearable product 3, a main control unit, and a conductive yarn 4 for connecting the biological information collection component and the main control unit.
[0043] Wherein, at least part of the biological information collection component is fixed on the position of the wearable product 3 corresponding to the part of the biological body to be monitored. After the main control unit is electrically connected with the biological information collection component through the conductive yarn 4 , at least a part of the conductive yarn 4 is threaded in the wearable article 3 . In addition, in this embodiment, it is preferable to take the clothing body as the wearable article 3 as an example for description.
[0044] It is not di...
Embodiment approach 2
[0073] The second embodiment of the present invention relates to a biological information collection device. This embodiment is substantially the same as the above-mentioned first embodiment. The difference is that in this embodiment, the conductive yarn includes several intertwined fibers. Yarns, and each fiber yarn has at least one outer surface of the fiber yarn coated with a metal layer. Moreover, as a preference, this embodiment only uses 20 fiber yarns, of which 10 fiber yarns are coated with a conductive metal layer as an example for illustration.
[0074] From the above, it can be known that since the conductive yarn 4 is composed of several intertwined fiber yarns, and at least one of the fiber yarns in each fiber yarn is coated with a metal layer on the outer surface, thus the conductive function of the conductive yarn 4 can be realized. In the case of the conductive yarn, by intertwining the fiber yarn coated with the metal layer and several fiber yarns not coated w...
Embodiment approach 3
[0079] The third embodiment of the present invention relates to a biological information collection device. This embodiment is substantially the same as the above-mentioned first embodiment. The difference is that in this embodiment, the conductive yarn 4 includes a Yarn body, several conducting metal wires arranged in a hollow structure.
[0080]From the above, it can be seen that since the conductive yarn 4 is composed of a hollow yarn body and a number of wires arranged in the hollow structure, it can be realized that the yarn has a conductive function through the wire wire. , through the yarn body, the hollow structure of the yarn body plays a role of protection and insulation, so as to avoid the wear and tear of the wire wire during use and cause breakage. In addition, since the conductive metal wire is located in the yarn body, and the conductive wire itself has good shrinkage and crimp properties, it can follow the hollow structure of the yarn body to make appropriate c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com