A quantitative detection method for defects in magnesium and magnesium alloys
A quantitative detection method, magnesium alloy technology, applied in the direction of optical testing flaws/defects, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of poor reproducibility, cumbersome process, and poor versatility, and achieve strong versatility, simple process, and detection The results are accurate
Active Publication Date: 2018-12-07
NEW MATERIAL INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF SCI
View PDF9 Cites 0 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
When these standards are used for defect analysis, they have a certain scope of application. The scope of application is the microscopic evaluation method of non-metallic inclusions in rolled or forged steel with a compression ratio greater than or equal to 3, which is not universal; This method is widely used to evaluate the suitability of steel for a given application. However, due to the influence of the test personnel, it is difficult to reproduce the test results even if a large number of samples are used, and the reproducibility is poor; although the detection of the entire surface to be tested can be realized, but In the detection process, it is necessary to process each image collected and extract the phase of the target to be tested. The process is quite cumbersome; moreover, the method of extracting defects is the same as the conventional quantitative metallographic method based on image processing. The adjustment of hue, saturation, contrast, etc., is extracted by gray threshold segmentation method and clustering technology, and the accuracy needs to be improved
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
[0032] The present invention will be described in further detail below through embodiments and in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
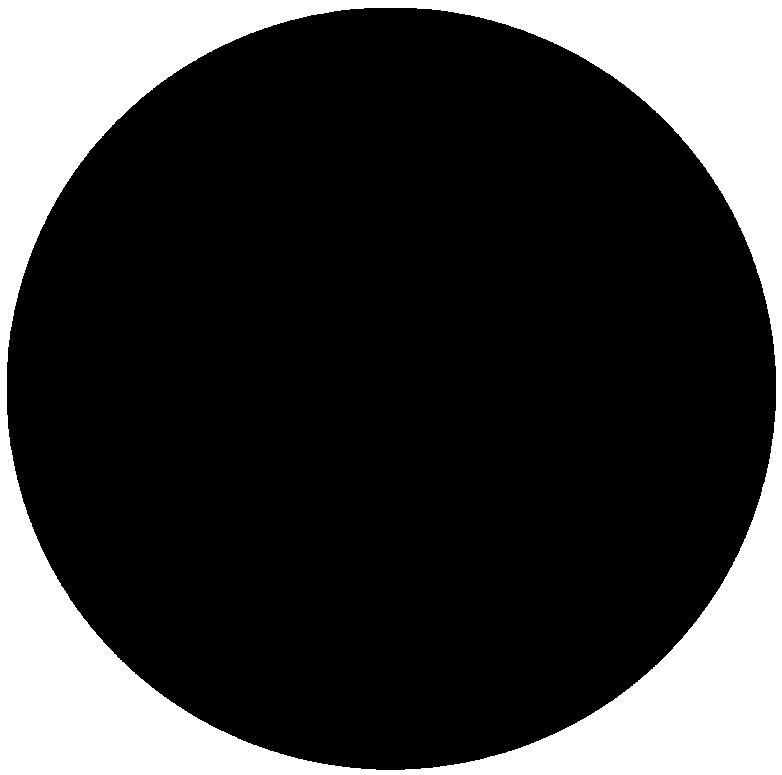
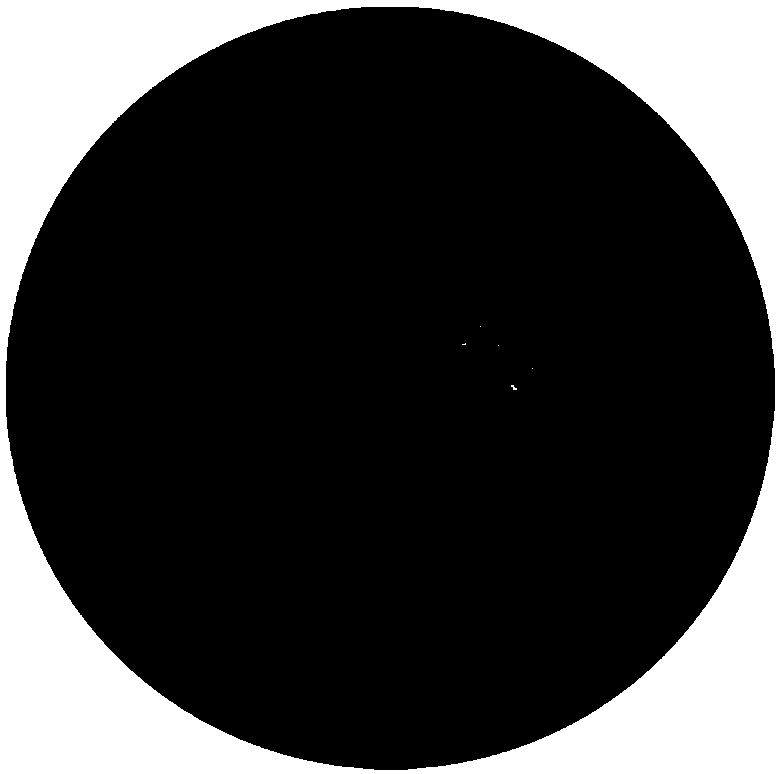
The invention relates to a quantitative detection method for defects in magnesium and a magnesium alloy. The quantitative detection method comprises the following steps: sequentially, continuously and thoroughly collecting images of a whole polished surface in an overlapping manner by virtue of a camera attached to an optical microscope; splicing the images, and processing overlapped parts, so as to obtain a spliced image of a whole to-be-detected cross section; clicking in a newly-built image layer in Photoshop software by virtue of a magic wand tool so as to select each defected region, and saving all defects on the whole cross section into the same image; and analyzing, aggregating and calculating all the defects in the image. The quantitative detection method has the beneficial effects that the processing process is relatively simple and convenient, the defects can be accurately extracted, and the accuracy of a quantitative detection result is improved. The quantitative detection method has reproducibility and relatively strong universality.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention relates to a quantitative detection method for defects in magnesium and magnesium alloys, and belongs to the technical field of quantitative detection of physical properties of materials. Background technique [0002] Magnesium alloy is currently the lightest metal structural material in practical applications in the world. It has the characteristics of abundant reserves, low density, high specific strength and specific stiffness, impact resistance, and easy recycling of products. It is an ideal energy-saving and environmentally friendly material that meets sustainable development. It is the third largest engineering material after steel and aluminum alloy materials, and has important application value and broad application prospects in the fields of aviation, military, automobile and 3C. [0003] During the solidification process of magnesium and magnesium alloys, due to liquid shrinkage and solidification shrinkage, large and concentrat...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Patents(China)
IPC IPC(8): G01N21/88
CPCG01N21/8851G01N2021/8854G01N2021/8887
Inventor 李卫红周吉学马百常吴建华庄海华韩青友杨院生
Owner NEW MATERIAL INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com