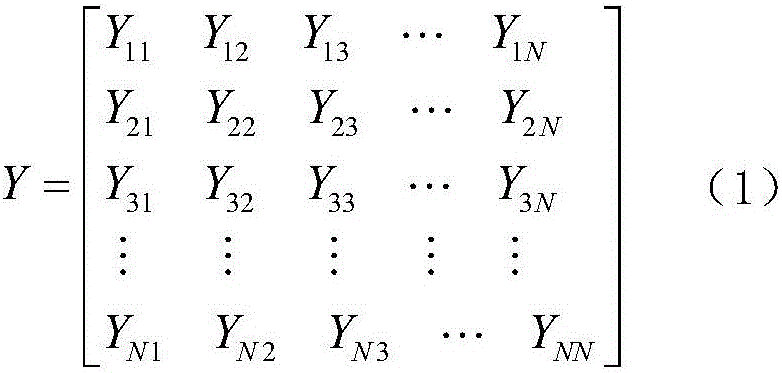Method for rapidly calculating parameters of multi-port equivalent network element with embedded electromechanical transient simulation
An equivalent network, fast computing technology, applied in computing, data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as discrepancy, slow computing speed, and inability to strictly guarantee equivalent potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
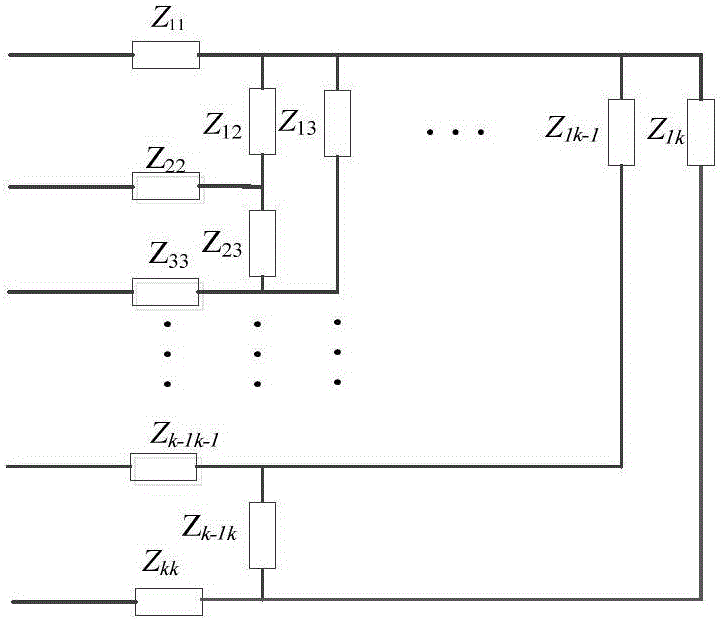
[0035] The invention proposes a fast calculation method for multi-port equivalent network element parameters of embedded electromechanical transient simulation, which will be described in detail below with reference to the drawings and specific embodiments:
[0036] The invention proposes a fast calculation method for multi-port equivalent network element parameters of embedded electromechanical transient simulation, and its flow chart is as follows figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0037] 1) Denote the number of nodes in the entire network as N, the number of electromechanical-electromagnetic transient hybrid simulation interfaces of the power system as n, and the number of N nodes in the entire network as {i 1 ,i 2 ,...,I n }, n≤N;
[0038] 2) Determine the grid topology for a certain normal operating state or fault state of the power grid to form the network node voltage equation matrix-the admittance matrix, denoted as Y, as shown in equation (1):...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com