A method for determining the content of lignocellulosic plant chemical components using a thermogravimetric analyzer
A technology of lignocellulose and thermogravimetric analysis, applied in measuring devices, analytical materials, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as affecting factory production, inability to analyze a small amount of samples, and untimely analysis results, achieving less labor and high work efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Taking wood raw materials as an example
[0064] 60 parts of wood raw materials were selected, among which: 25 parts came from Linyi, Shandong, 15 parts came from Guiyang, Guizhou, and 20 parts came from Changsha, Hunan; samples were made respectively, and the weight of each sample was 50g.
[0065] All the samples were dried at 105°C and pulverized, passed through a 40-mesh sieve to obtain sample powder, each sample was about 30g, and then divided into two parts, one part (20mg) for thermogravimetric analysis, and the other part (30g) for wet chemical analysis ;
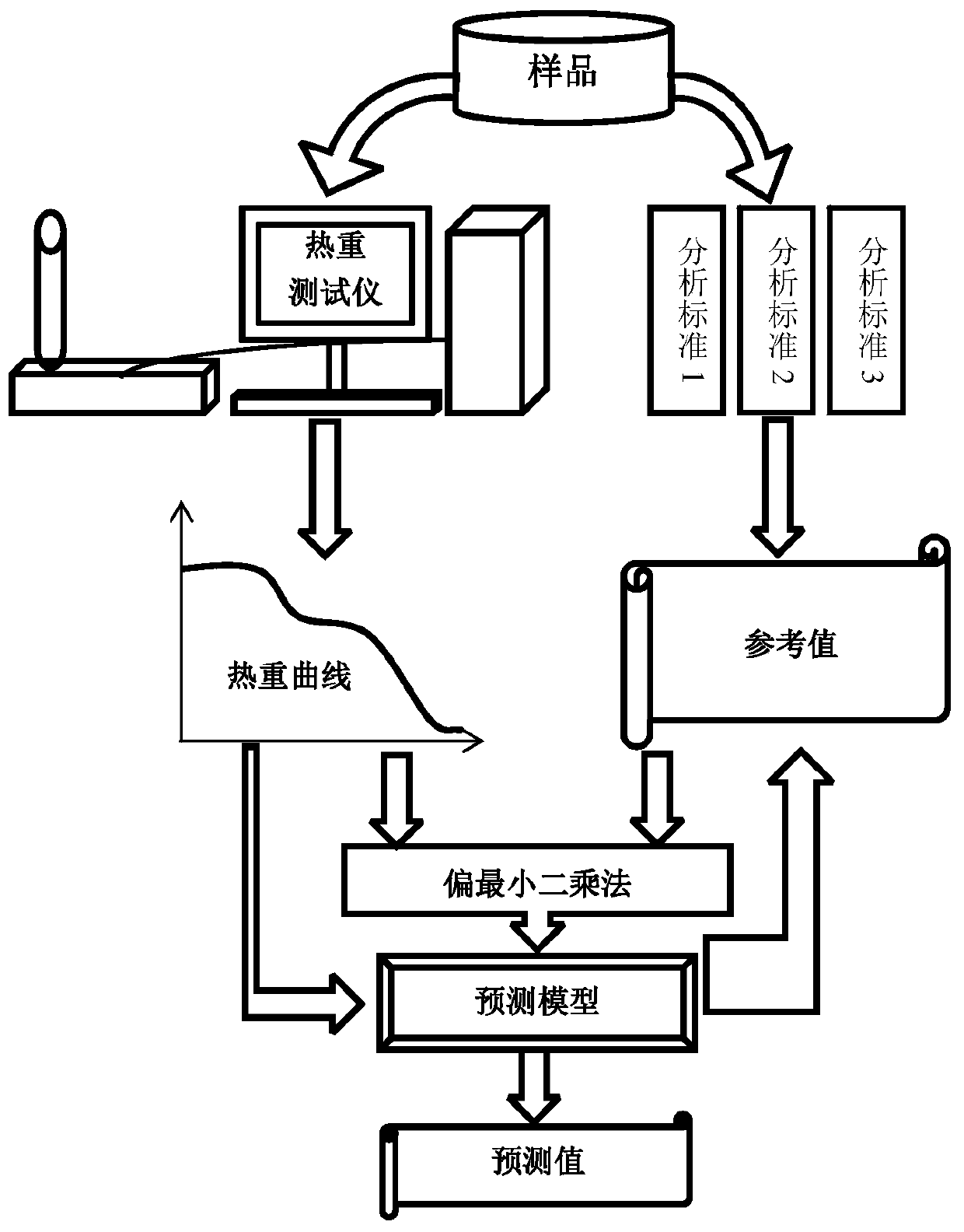
[0066] Such as figure 1 As shown, the calibration sample set and the collection of the thermogravimetric curve of the sample to be tested: Weigh about 20 mg of the sample, put it into the thermogravimetric analyzer for thermogravimetric analysis, and collect the thermogravimetric curve. , the temperature is raised at 5°C / min, the temperature rises to 900°C, the temperature is stopped, and the temperature is...
Embodiment 2
[0081]Taking the kenaf plant as an example, 80 parts of kenaf raw materials were selected, of which 40 parts were produced in Hunan, 20 parts were produced in Shandong, and 20 parts were produced in Xinjiang; samples were made respectively, and the weight of each sample was 50g.
[0082] All the samples were dried at 105°C and pulverized, passed through a 40-mesh sieve to obtain sample powder, each sample was about 30g, and then divided into two parts, one part (20mg) for thermogravimetric analysis, and the other part (30g) for wet chemical analysis ;
[0083] Such as figure 1 As shown, the calibration sample set and the collection of the thermogravimetric curve of the sample to be tested: Weigh about 20 mg of the sample, put it into the thermogravimetric analyzer for thermogravimetric analysis, and collect the thermogravimetric curve. , the temperature is raised at 5°C / min, the temperature rises to 900°C, the temperature is stopped, and the temperature is lowered with liquid...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Taking corn plants as an example, 120 parts of corn stalk raw materials were selected, of which 40 parts were produced in Gaomi, Shandong, 40 parts were produced in Liaocheng, Shandong, and 40 parts were produced in Dezhou, Shandong; samples were made respectively, and the weight of each sample was 50g.
[0090] All the samples were dried at 105°C and pulverized, passed through a 40-mesh sieve to obtain sample powder, each sample was about 30g, and then divided into two parts, one part (20mg) for thermogravimetric analysis, and the other part (30g) for wet chemical analysis ;
[0091] Such as figure 1 As shown, the calibration sample set and the collection of the thermogravimetric curve of the sample to be tested: Weigh about 20 mg of the sample, put it into the thermogravimetric analyzer for thermogravimetric analysis, and collect the thermogravimetric curve. , the temperature is raised at 5°C / min, the temperature rises to 900°C, the temperature is stopped, and the t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com