A Smoothing Method for RSS Data Based on Multidimensional Scaling Analysis Algorithm
A multi-dimensional scale analysis and data smoothing technology, applied in wireless communication, network topology, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of increased influence of environmental noise and acquisition error RadioMap, reduction of RadioMap accuracy and positioning accuracy, etc., to eliminate noise and measurement errors , The effect of high-precision online positioning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0031] Specific implementation mode one: a kind of RSS data smoothing method based on multi-dimensional scale analysis algorithm in this implementation mode The specific process is as follows:
[0032] The multi-dimensional dimension is a positive integer;
[0033] 1. Create an offline Radio Map after RSS data smoothing processing, the specific process is:
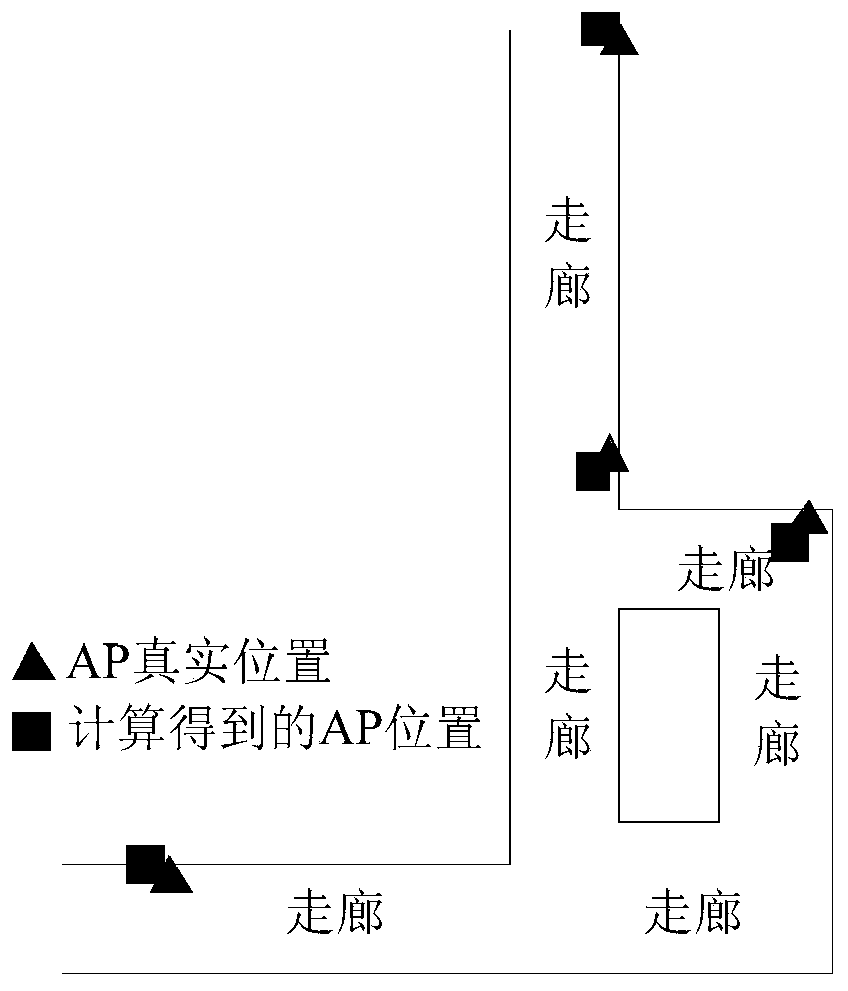
[0034] Step 1. Arrange m APs in the indoor area to be located, and calibrate the AP positions, such as figure 1 The experimental scene is shown, so that the wireless signal covers the entire indoor area to be positioned, and the WLAN network construction is completed;
[0035] The handheld mobile terminal moves in the indoor area to be positioned. During the movement, the mobile terminal (smart phone, tablet computer, etc.) is used to measure the inertial navigation data and RSS data. Inertial navigation data (such as acceleration data, direction data, etc.) calculates the relative coordinates between the corresponding ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0051] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in the first step, m APs are arranged in the indoor area to be positioned, and the positions of the APs are calibrated, such as figure 1 The experimental scene is shown, so that the wireless signal covers the entire indoor area to be positioned, and the construction of the WLAN network is completed; the specific process is as follows:
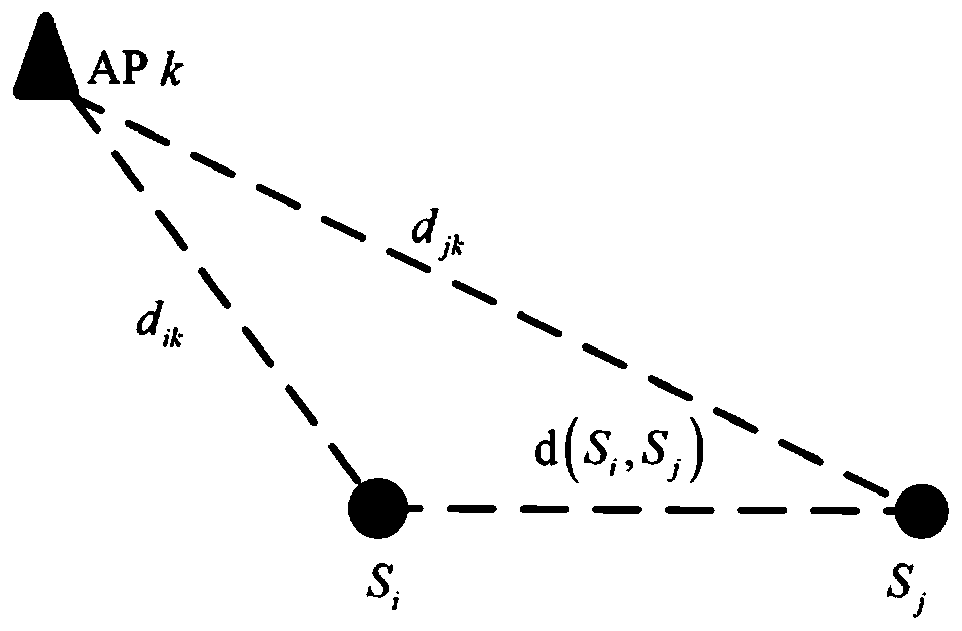
[0052] Calibrate the position coordinate of the kth AP as c APk =(x k ,y k ),k=1,2,...,m;
[0053] where x k is the abscissa of the kth AP position; y k is the ordinate of the kth AP position.
[0054] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0055] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: in the step one, the handheld mobile terminal moves in the indoor area to be positioned, and the mobile terminal (smart phone, tablet computer, etc.) ) to measure the inertial navigation data and RSS data, in order to determine the collection position of the RSS data, that is, the position coordinates of the RP, use the inertial navigation data (such as acceleration data, direction data, etc.,) to calculate the relative coordinates between the corresponding positions of each RSS data, that is, the RP The relative coordinates; the specific process is:
[0056] Use the mobile terminal to measure the inertial navigation data and RSS data, and obtain the relative position coordinates of n RPs according to the measured inertial navigation data and the set starting point coordinates, c RPi =(x i ,y i ), i=1,2,...,n,c RPj =(x j ,y j ),j=1,2,...,n
[0057] where x i i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com