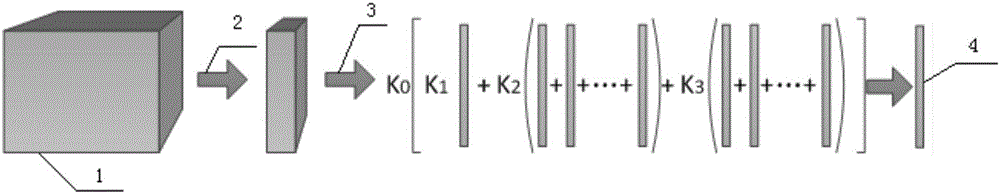Depth belief network-based neighborhood weighted averaging hyperspectral image classification method
A deep belief network, hyperspectral image technology, applied in instrument, character and pattern recognition, scene recognition and other directions, can solve the problem of increasing pre-training and fine-tuning computing time, achieve low computer performance requirements, fast running speed, and optimize data The effect of dimension
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
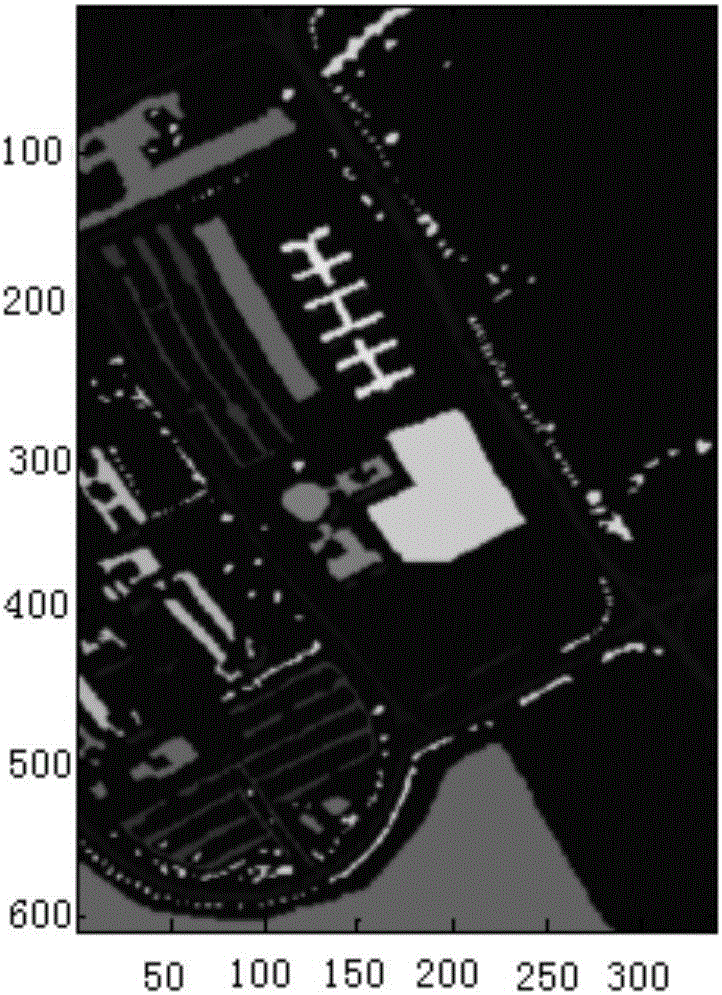
[0023] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, a specific process of a neighborhood weighted average hyperspectral image classification method based on a depth belief network (Depth Belief Networks, DBN) in this embodiment is as follows:
[0024] Step 1, extracting the spatial information of the hyperspectral raw data to obtain the spatial information of the hyperspectral raw data;
[0025] Step 2: Neighborhood weighting is performed on the spatial information of the hyperspectral raw data to obtain the processed hyperspectral data, namely the matrix M;
[0026] Step 3. Using the matrix M as the training set, the deep belief network is used for classification training.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0027] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in the first step, the hyperspectral raw data is extracted with spatial information to obtain the spatial information of the hyperspectral raw data; the specific process is:
[0028] First of all, because the PCA transformation will lose part of the nonlinear information, the PCA transformation is not performed on the hyperspectral image here, and the small square neighborhood is directly extracted for each pixel.
[0029] When the pixels to be classified in the hyperspectral raw data are not located at the edge of the hyperspectral remote sensing image, that is, there is a 5*5 square neighborhood around the pixels to be classified in the hyperspectral raw data, the pixels to be classified in the hyperspectral raw data Extract the spatial information of the pixels in the neighborhood of a 5*5 square, and obtain the spatial information of the original hyperspectral data;
[0030] When the pixel...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0032] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiments 1 or 2 is that in the step 2, the spatial information of the hyperspectral raw data is subjected to neighborhood weighting to obtain the processed hyperspectral data, namely the matrix M; specifically The process is:
[0033] The so-called neighborhood weighting method takes the pixel to be classified as the center point, and performs weighted average according to the distance between the pixel in the square neighborhood and the center point and the number of pixels;
[0034] Step 21, grouping pixels in a square neighborhood of a size of 5*5 around the pixel to be classified according to the pixel distance from the center point in a square neighborhood of a size of 5*5 around the pixel to be classified;
[0035] Step 22, determining the weight coefficient and the overall weight coefficient of each group of pixels;
[0036] Step two and three, after summing the internal pixels of each...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com