Waste heat isothermal normalizing treatment method for medium carbon steel forging
A processing method and forging waste heat technology, applied in the field of warm normalizing treatment, can solve the problems of reducing the strength and plasticity of medium carbon steel, increasing brittleness, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Material: S55C car wheel bearing forging billet, final forging temperature: 900°C (±50°C), the standard requires that the metallographic structure after normalizing is 1-4, and the grain size is ≧4.
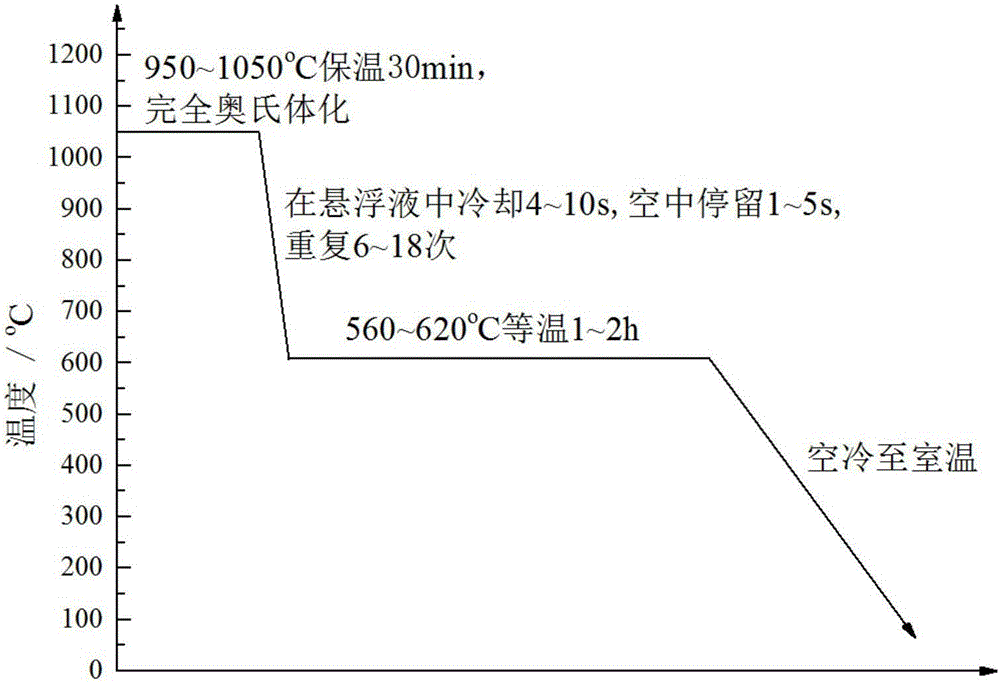
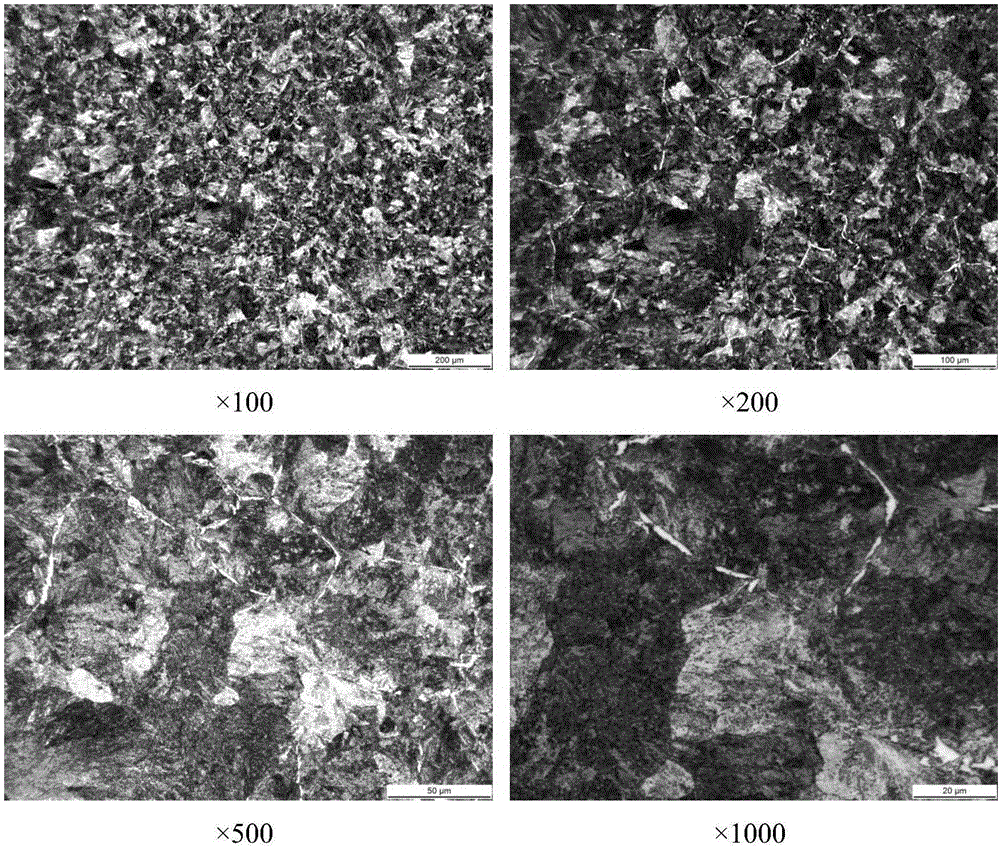
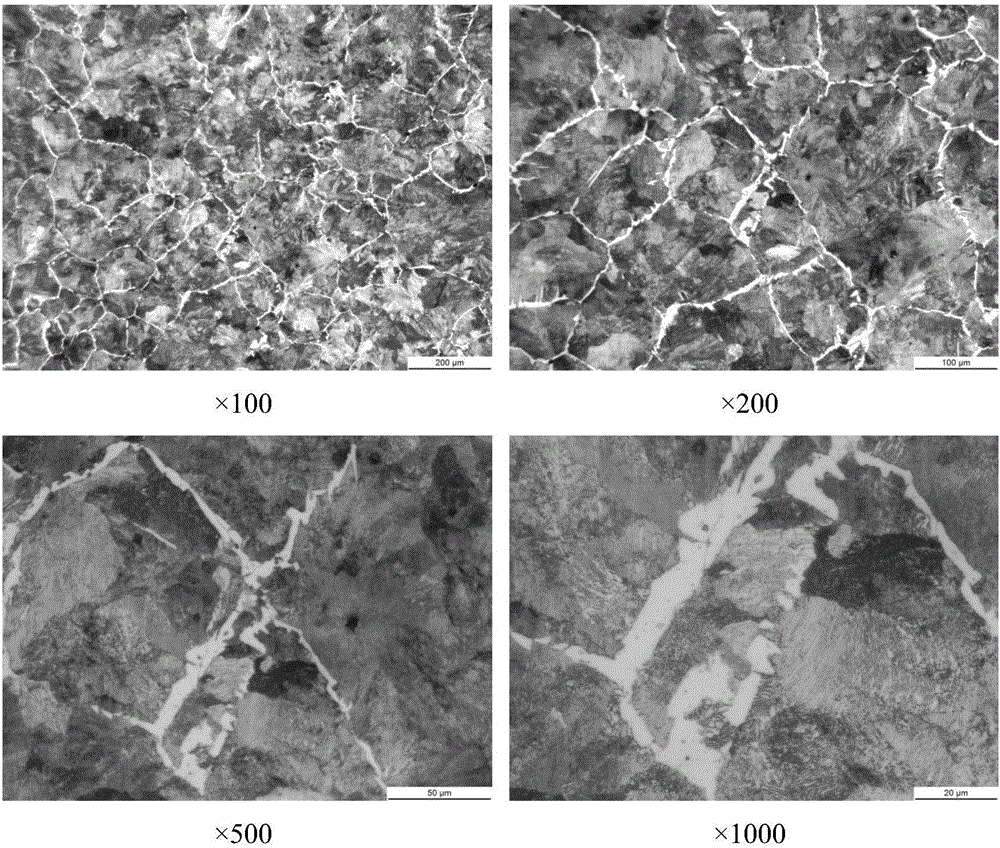
[0029] The process of the present invention is as follows: heat preservation at 950°C for 30 minutes, complete austenitization; then take out the sample, cool it in the quenching water-based suspension medium for 8s, and stay in the air for 3s, repeat the above process 12 times; 2 h in an electric resistance furnace, and then cooled to room temperature in air. figure 2 It is the microstructure obtained after the process of the above-mentioned invention is processed. Below the figure is the magnification. image 3 It is the microstructure after direct isothermal normalizing treatment after forging. Below the figure is the magnification. By comparison, it can be seen that figure 2 In the middle, no network ferrite was found at low magnification, and fine and disjointed...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Material: 55 steel hub bearing forging billet, final forging temperature: 900°C (±50°C), performance requirements, hardness after normalizing: HB220-250.
[0032] The process of the present invention is as follows: heat preservation at 950°C for 40 minutes, complete austenitization; then take out the sample, cool it in the quenching water-based suspension medium for 4s, and stay in the air for 4s, repeat the above process 13 times; 1 h in a resistance furnace, and then cooled to room temperature in air. Figure 4 It is the hardness value obtained after the process of the above invention. It can be seen that the hardness values of the five groups of parts are all within the required range, and the fluctuations are not large. The hardness value after the direct isothermal normalizing treatment after the prior art forging is shown in Figure 5 middle. It can be seen that the Brinell hardness of process 1 and process 2 is as follows Figure 4 , 5 As shown, the averag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com