Method and device for microscopic examination of a sample
A technology for microscopes and samples, applied in microscopes, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to flexibly and accurately set the precise position of sample irradiation, laborious layout and preparation, and impossible implementation of microscope inspection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
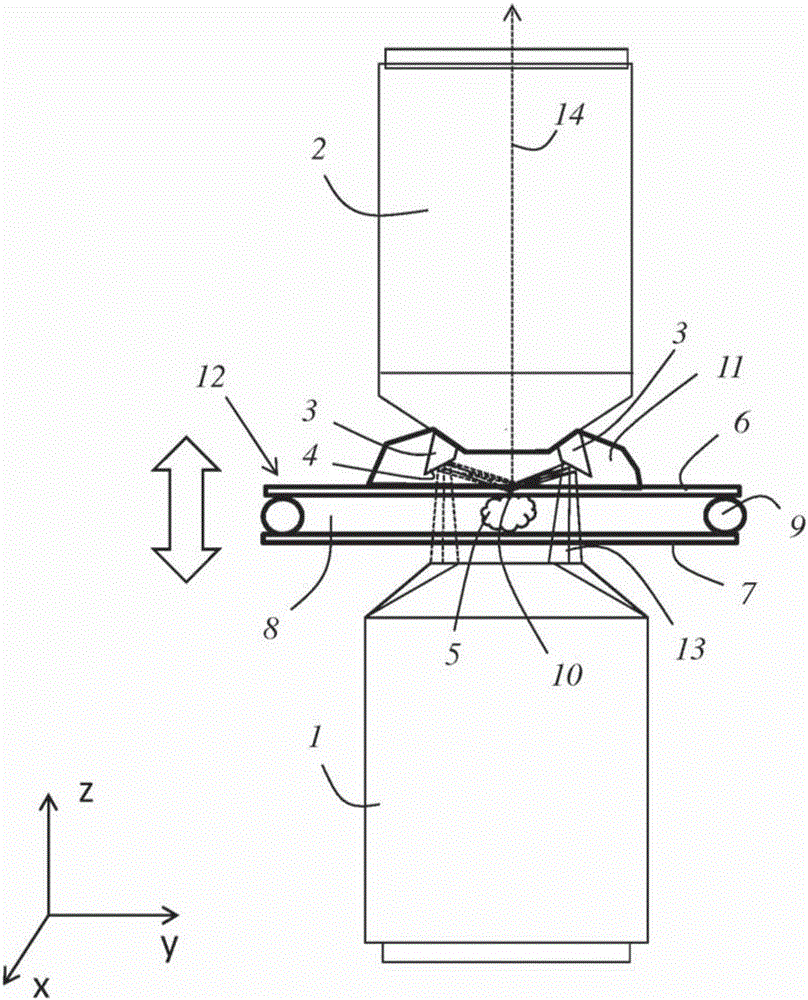
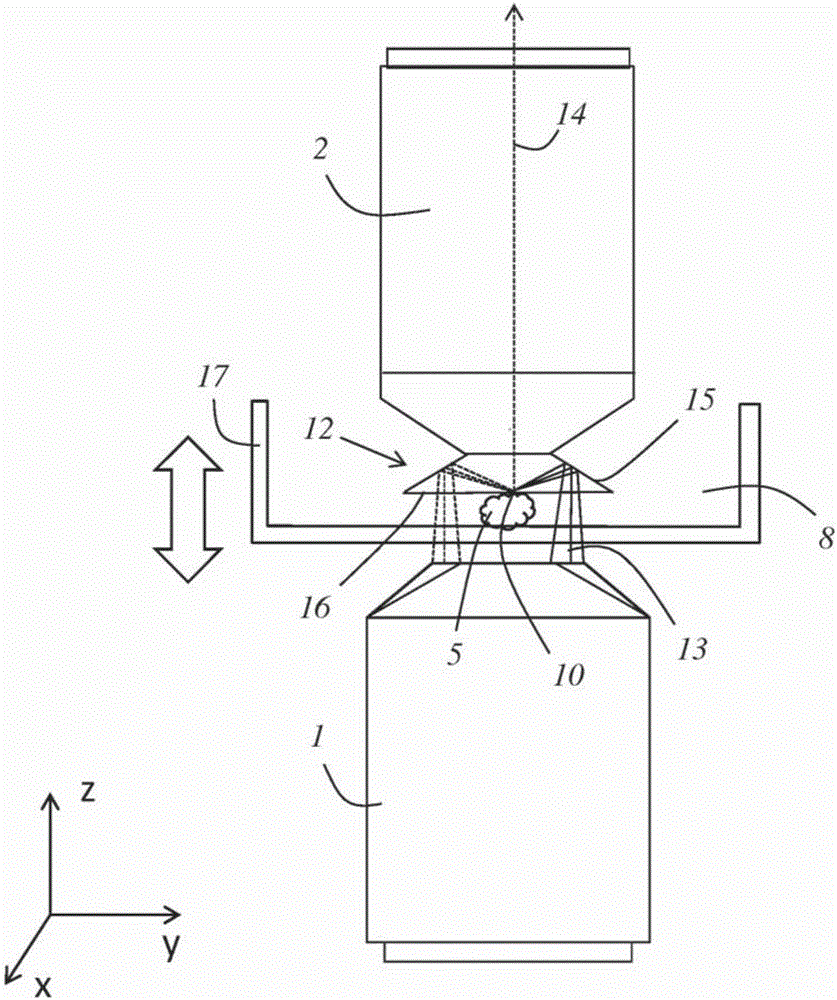
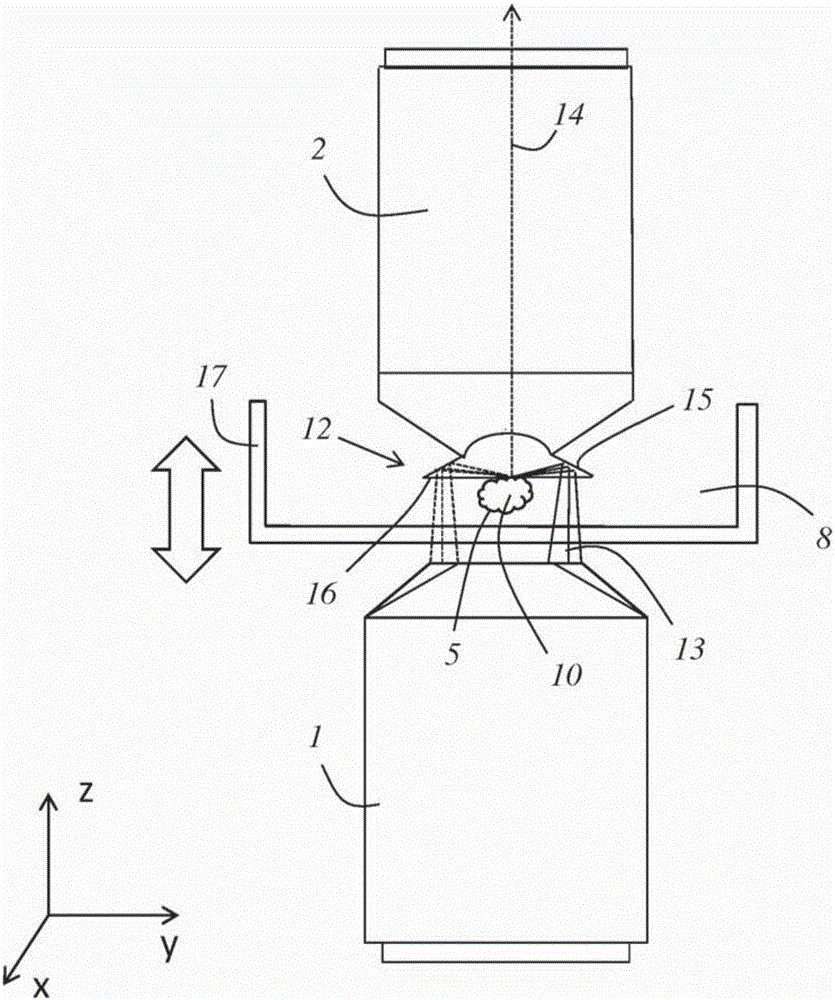
[0070] figure 1 A detailed view of a first embodiment of the device is shown, on the basis of which view a conceivable embodiment of the method according to the invention will be explained below.
[0071] The device has an irradiation objective 1 and a detection objective 2 configured as an oil objective. The optical axes of the irradiation objective 1 and the detection objective 2 are coaxial with each other, and they face in opposite directions. The deflection member 3 is attached to the detection objective 2 and has a frusto-conical mirror surface 4 .
[0072] The sample 5 to be examined is arranged in an aqueous nutrient medium between a first cover glass 6 and a second cover glass 7 . The coverslips 6 , 7 are sealed relative to each other by a surrounding gasket 9 so that the aqueous nutrient medium 8 cannot escape.
[0073] Between the cover glass 6 facing the detection objective 2 and the detection objective 2 there is immersion oil 11 in which the deflection member ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com