Remote sensing monitoring method of light use efficiency and gross primary production of phyllostachys pubescens forest ecological system
A total primary productivity and ecological system technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of deviation between model simulated values and measured values, LUE time and space differences, etc., to improve estimation accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] Below in conjunction with embodiment and with reference to accompanying drawing, the present invention will be described in further detail:
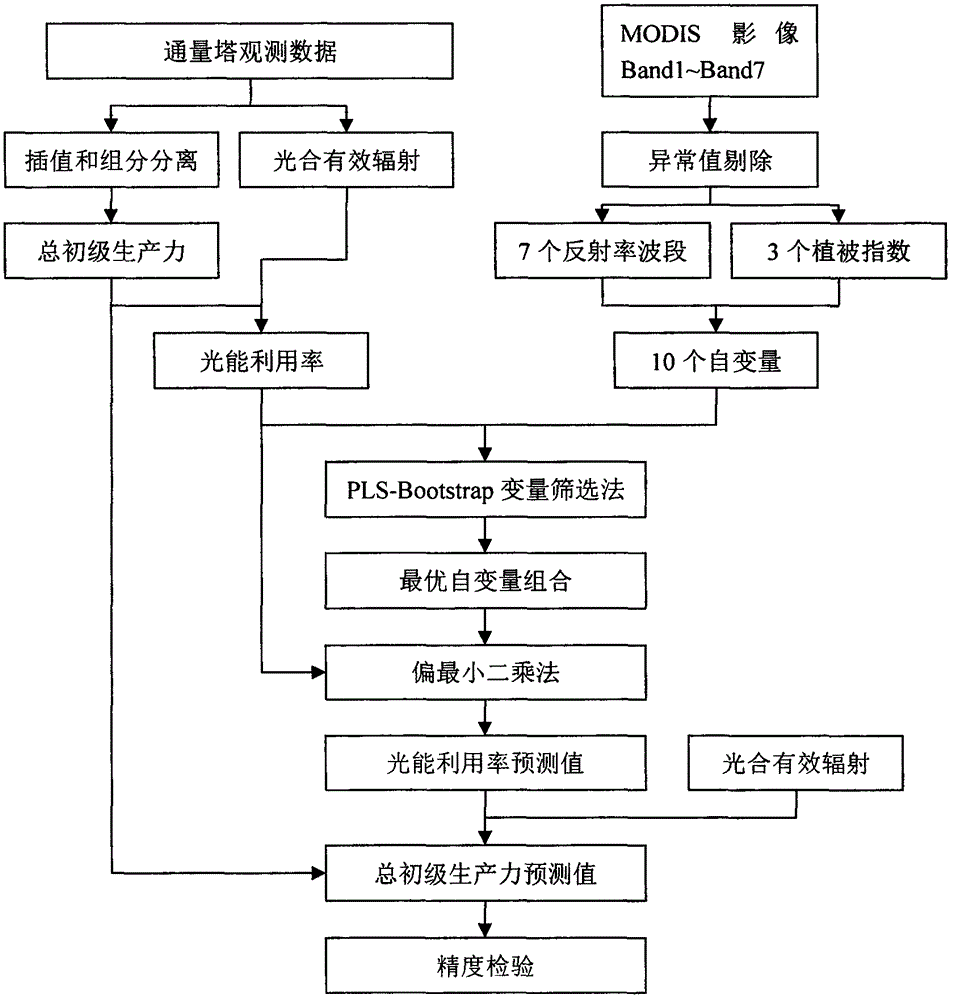
[0026] It should be noted that the present invention takes the 2011-2013 moso bamboo forest LUE and GPP estimation within the range of 500 meters × 500 meters around the moso bamboo forest flux observation tower in Shanchuan Township, Anji County as an example, and the process of the present invention is as follows figure 1 shown. Specific steps are as follows:
[0027] (1) Calculate GPP and LUE according to the observation data of the flux tower:
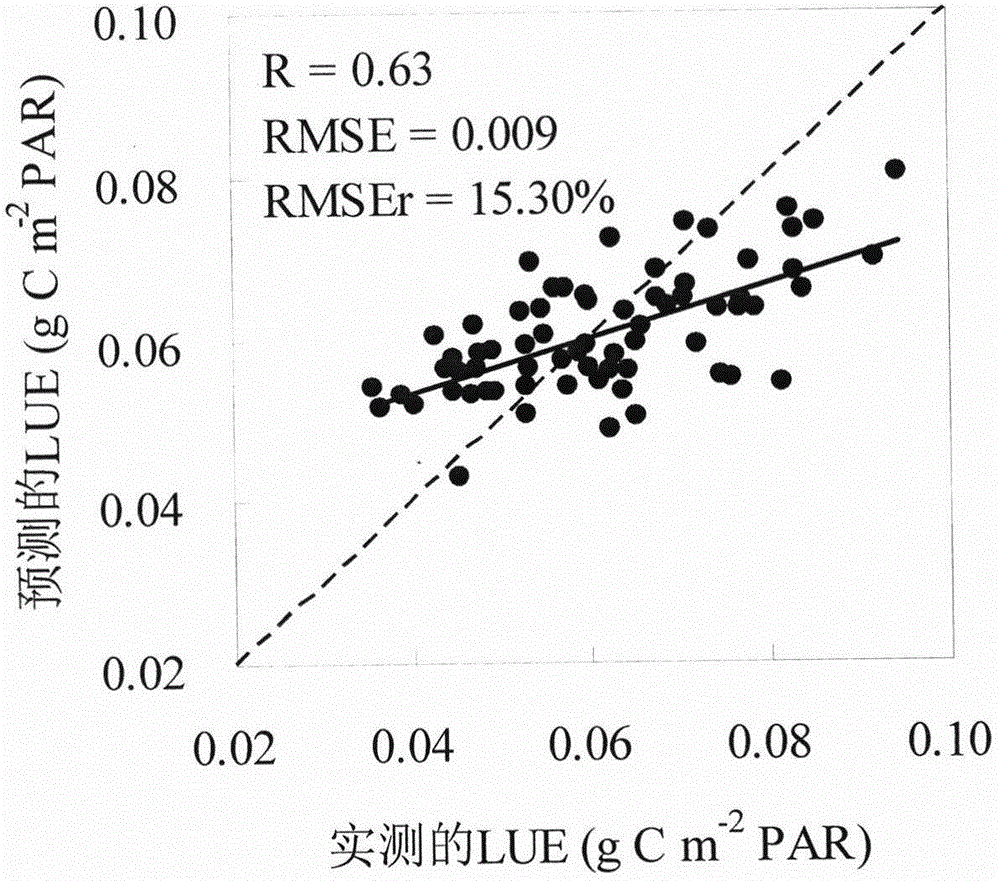
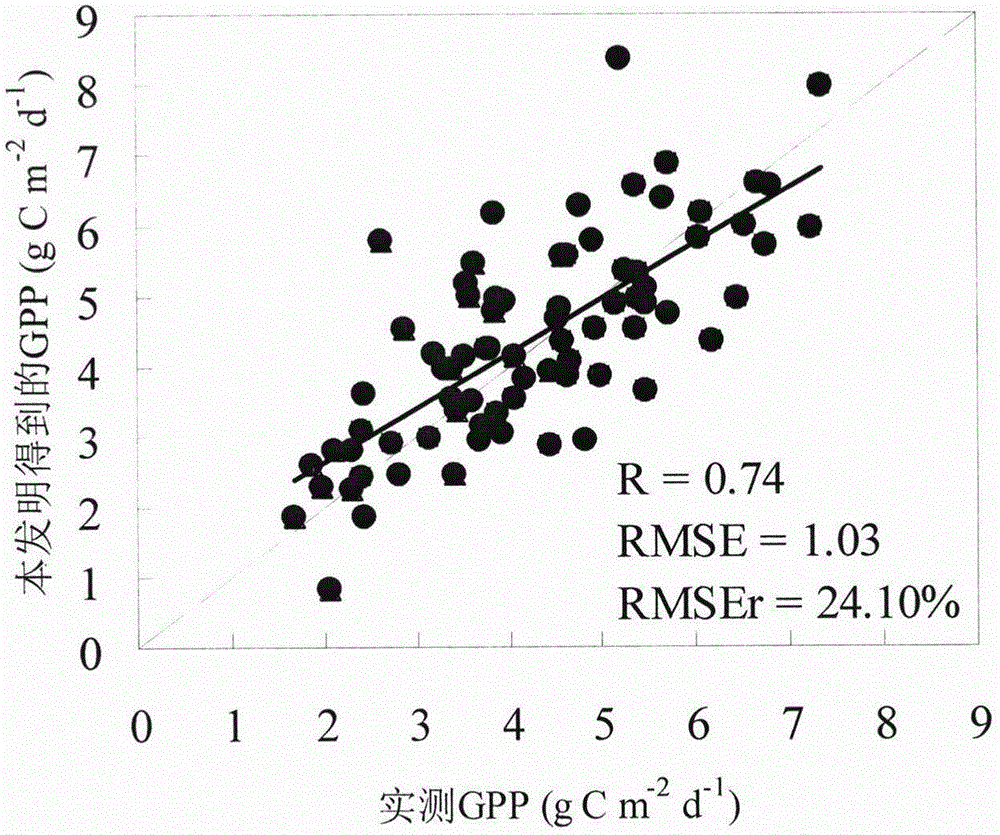
[0028] According to the net ecosystem carbon flux, air temperature, soil temperature and PAR observed by the flux tower, the Arrhenius respiration and Michaelis-Menten photosynthetic response curve models were used to interpolate missing data, and to separate the components of carbon flux, Obtain the measured GPP, and then divide the GPP by the PAR to calculate the LUE;
[0029] The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com