Modeling method of conducted electromagnetic interference receiver
A technology of conducted electromagnetic interference and modeling method, which is applied in the field of modeling conducted electromagnetic interference receivers, can solve problems such as increasing design costs, and achieve the effects of reducing the amount of calculation, reducing costs, and shortening the time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
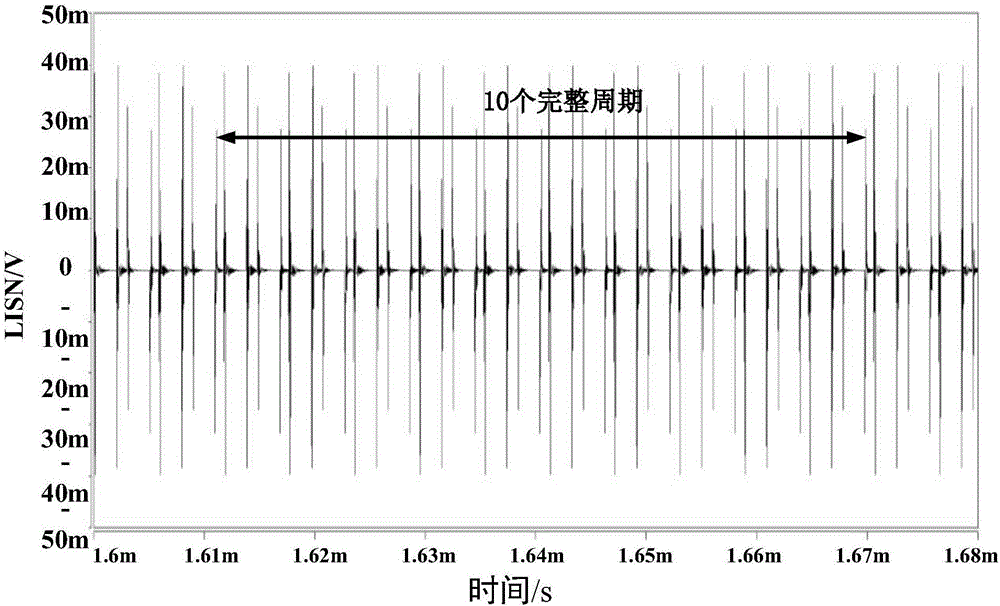
[0029] Example: The frequency range of conducted electromagnetic interference [150kHz~30MHz] is divided into 7463 frequency points with a step size of 4kHz, and the frequency component corresponding to each frequency point is multiplied by the window function corresponding to the frequency to obtain 7463 window passing functions The following frequency points and their frequency components. Such as Figure 5 , is a schematic diagram of the window function specified in the international standard CISPR16-1-1. In the figure, the dotted line indicates the maximum bandwidth specified by CISPR16-1-1, and the solid line indicates the minimum bandwidth specified by the international standard CISPR16-1-1. The designed window function needs to be between the maximum bandwidth and the minimum bandwidth. 7463 frequency points correspond to 7463 window functions. Each window function is different only in the center frequency and has the same shape. The window function corresponding to th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com