Dual-weight maximum-clique scheduling method for elastic optical multicast switching node structure based on shared frequency spectrum converter
A technology for sharing spectrum and switching nodes, which is applied in the field of double-weighted maximal group scheduling of elastic optical multicast switching node structure, which can solve the problems of complex scheduling scheme, reduce packet loss rate, improve utilization rate, and reduce cost. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] Hereinafter, the preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
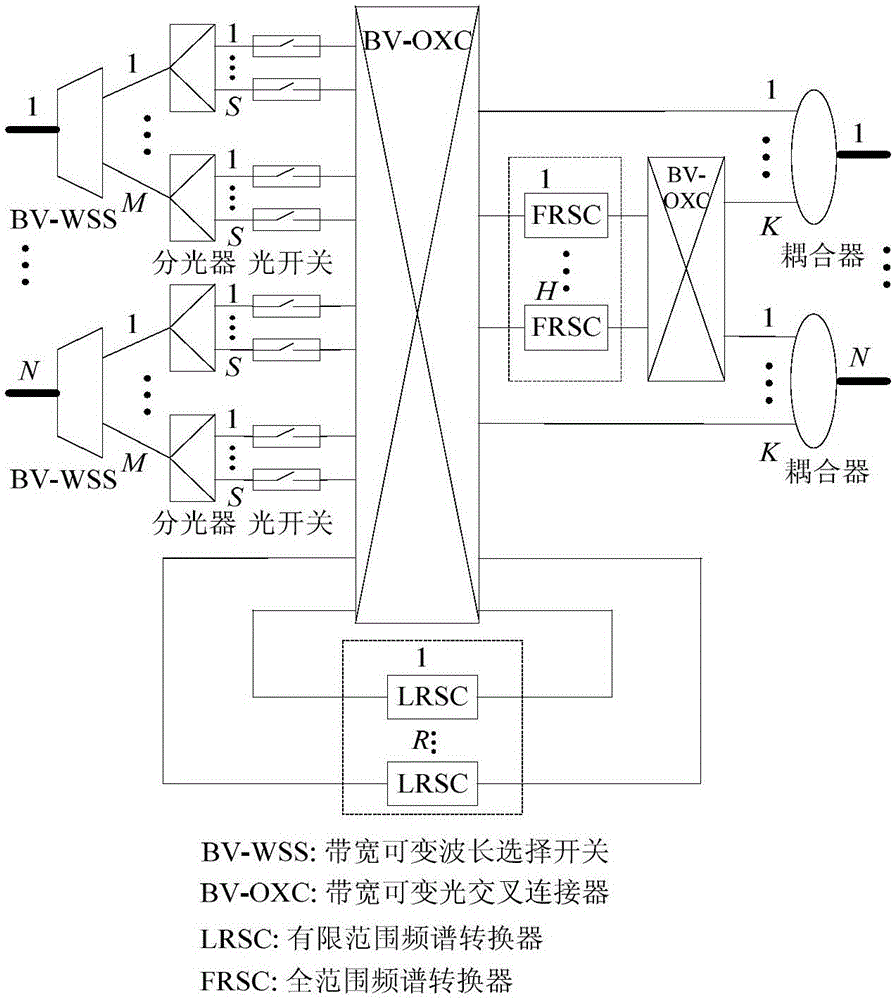
[0035] figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of the structure of a multicast switching node based on a shared spectrum converter suitable for flexible optical networks, including N input / output ports, N 1×M bandwidth variable wavelength selective switches (BV-WSS), N× M splitters, N×M×S optical switches, 2 bandwidth variable optical cross connectors (BV-OXC), R limited range spectrum converters (LRSC), H full range spectrum converters (FRSC) And N couplers. Among them, LRSC adopts the configuration mode of feedback sharing, and FRSC adopts the configuration mode of output sharing.
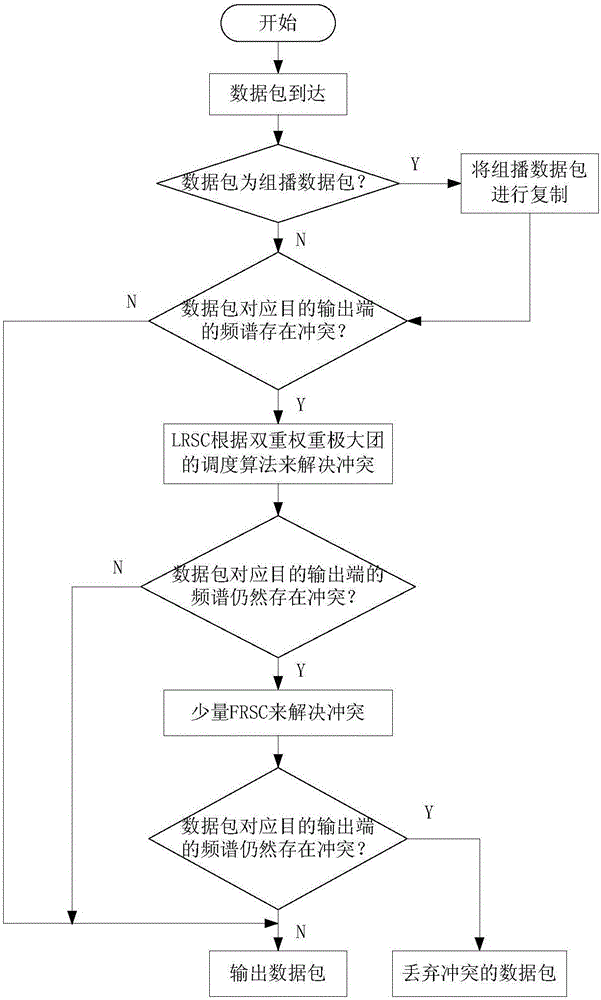
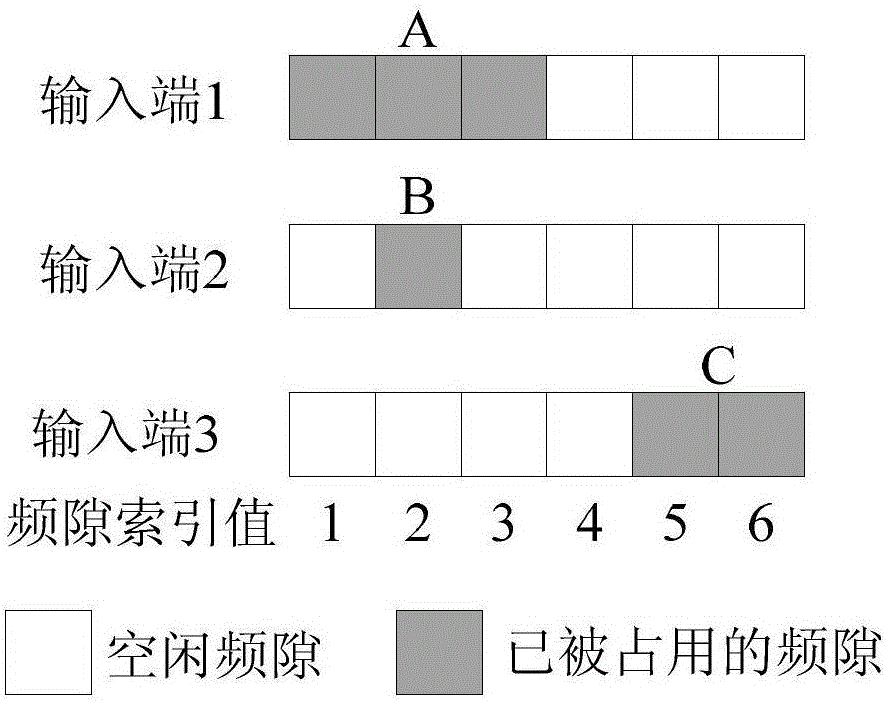
[0036] The working principle of the shared spectrum converter-based multicast switching node structure for flexible optical networks is as follows: First, data packets arrive at the input end of the switching node structure, and the arriving data packets occ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com