High-efficiency liquid cooling heat conduction structure and LED lamp
A technology of heat conduction structure and LED lamp, which is applied in cooling/heating devices of lighting devices, cooling/ventilation/heating transformation, semiconductor devices of light-emitting elements, etc. The problem of limited contact surface between coolant and radiator can achieve the effect of increasing contact surface, improving heat exchange efficiency and reducing processing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
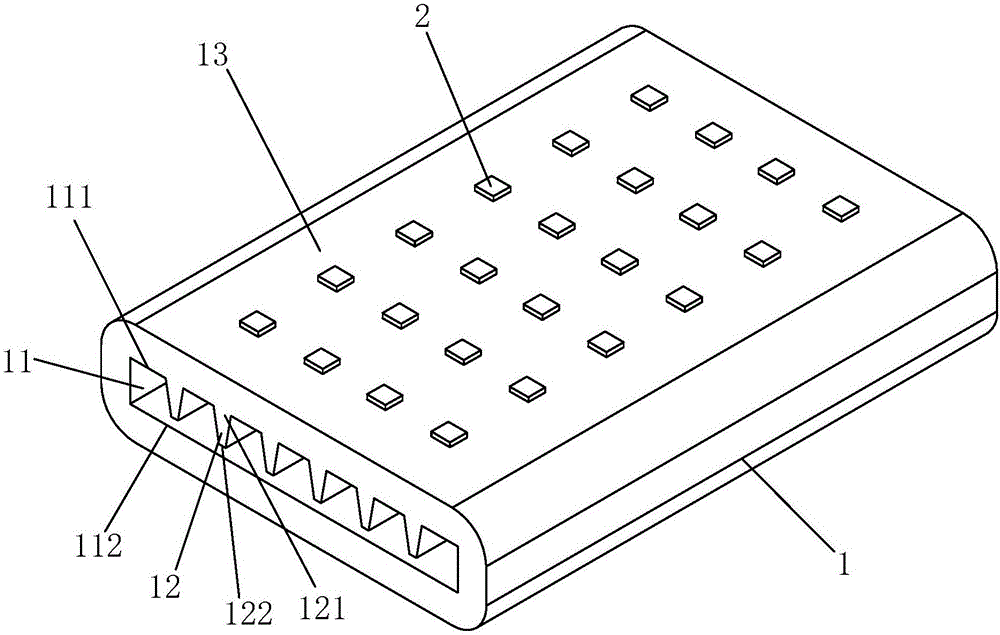
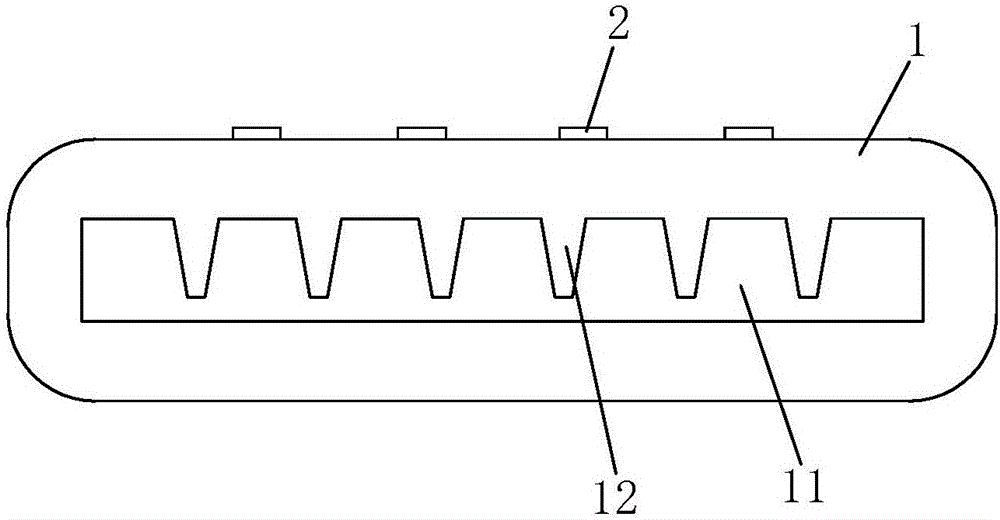
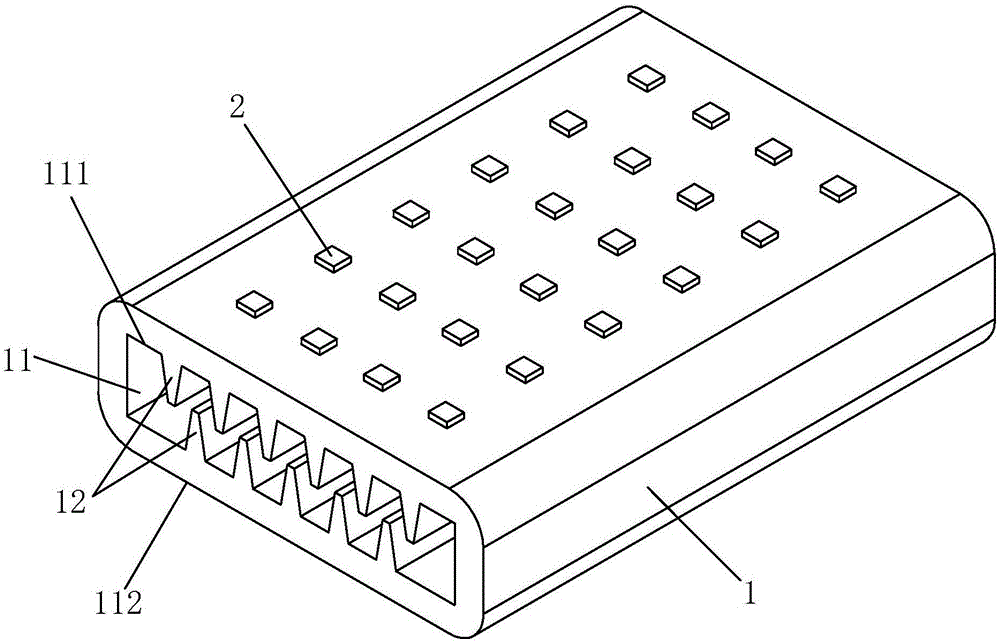
[0027] See figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, a high-efficiency liquid-cooled heat-conducting structure of the present invention includes an integrated radiator 1, which is made of aluminum alloy and has a plate-like structure. The radiator 1 is provided with a liquid flow channel 11 connected at both ends, and the wall surface of the liquid flow channel 11 is provided with a plurality of heat conducting fins 12 at intervals along the direction perpendicular to the flow of the liquid (ie cooling liquid). Each heat conducting fin 12 They are respectively elongated and arranged along the liquid flow direction (that is, the flow direction of the cooling liquid), and the root 121 of each heat conduction fin 12 is integrally formed with the radiator 1, and the tail 122 of each heat conduction fin 12 and the corresponding liquid There is a gap between the wall surface of the flow channel 11 or the opposite heat conducting fins, that is, the tails 122 of each heat conducting fin 12 are ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] See image 3 , Figure 4 As shown, the difference between it and Embodiment 1 is that: the two opposite wall surfaces of the liquid flow channel 11 are respectively distributed with the plurality of heat conduction fins 12 at intervals, and the heat conduction fins 12 on the two opposite wall surfaces of the liquid flow channel 11 are in the form of dislocation distribution.
[0036] In this embodiment, the upper wall surface 111 and the lower wall surface 112 of the liquid flow channel 11 are respectively distributed with the plurality of heat conduction fins 12 at intervals, and the heat conduction fins 12 on the upper wall surface 111 and the lower wall surface 112 of the liquid flow channel 11 are misaligned up and down. . Both the upper surface 13 and the lower surface 14 of the heat sink 1 are heat source contact surfaces, and a plurality of LED patch lamps 2 are attached to them respectively. There is a gap between the tails of the heat conducting fins 12 on t...
Embodiment 3
[0039] See Figure 5 , Figure 6 As shown, the difference between it and Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 is that the cross section of the liquid flow channel 11 is circular, and the wall surface of the liquid flow channel is distributed with the plurality of heat conduction fins 12 at intervals along the circumference.
[0040] In this embodiment, the heat sink 1 is a strip structure with a square cross-section, and chamfering is done at the four corners. The upper and lower surfaces 13, 14, left and right surfaces 15, 16 of the heat sink 1 are heat source contact surfaces, and a plurality of LED patch lamps 2 are pasted thereon respectively. The direction of the liquid flow channel 11 is along the length direction of the radiator 1 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com