A process for advanced treatment of organic wastewater using multiple micro-electrolytic fillers
A technology for organic wastewater and advanced treatment, which is applied in water/sewage multi-stage treatment, filtration treatment, precipitation treatment, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient contact between fillers and water, general treatment effect, hardening and passivation, etc., and achieves the preparation method. Simple and fast, good processing effect, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The process for advanced treatment of organic wastewater by using multiple micro-electrolytic fillers includes the following steps:
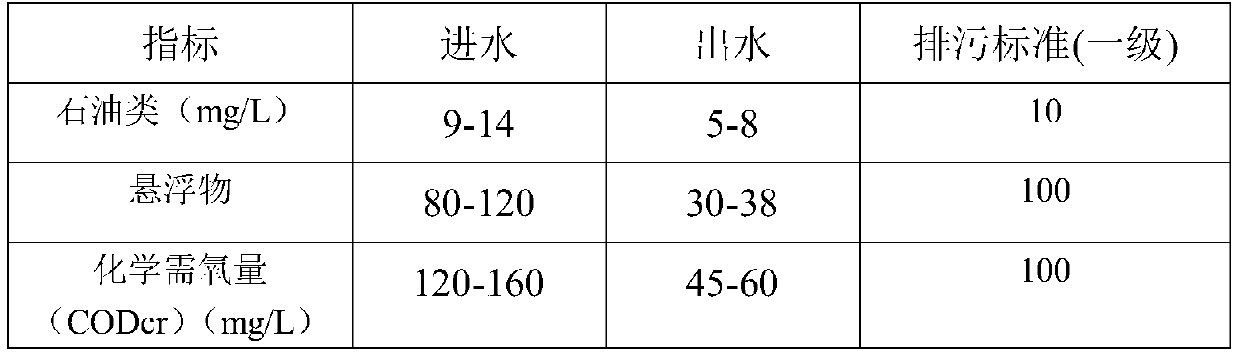
[0033] (1) The organic waste water enters the adjustment tank through the secondary sedimentation tank effluent to adjust the pH to acidity;
[0034] (2) After being adjusted to acidity, the organic waste water enters the quicksand filter, and the organic matter in the organic waste water is oxidatively degraded with the sand-like multi-component alloy structure filler as the micro-electrolysis filler; and the suspended matter is filtered out;
[0035] (3) Enter the flocculation tank with the wastewater effluent treated in step (2), and add NaOH solution in the flocculation tank to generate synergistic flocculation;
[0036] (4) The effluent of the treated wastewater in the flocculation tank enters the inclined tube high-efficiency sedimentation tank to remove the sediment and then effluent to complete the advanced treatment of organic wa...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The process for advanced treatment of organic wastewater by using multiple micro-electrolytic fillers includes the following steps:
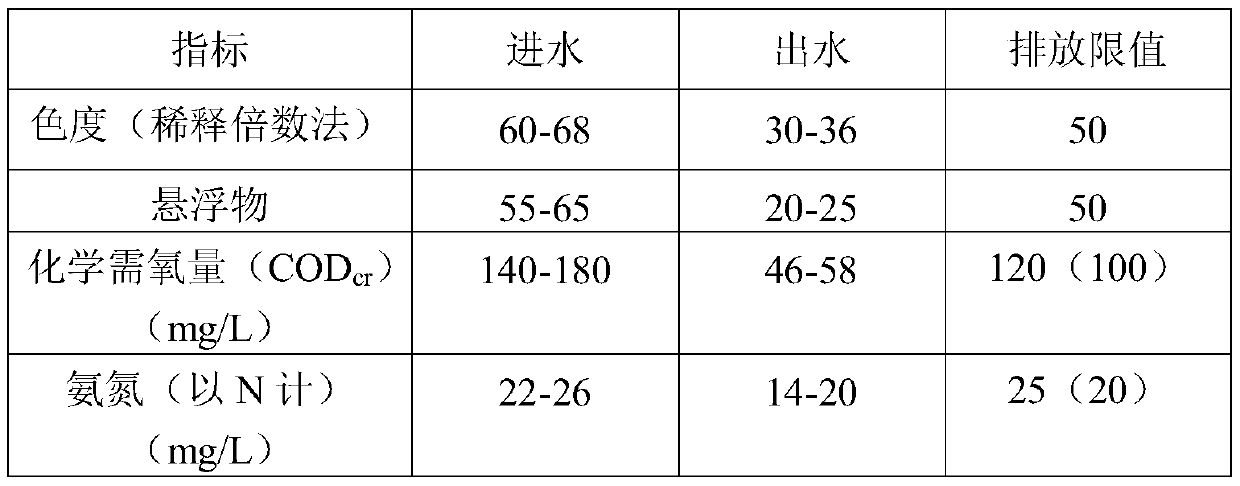
[0046] (1) The organic waste water enters the adjustment tank through the secondary sedimentation tank effluent to adjust the pH to acidity;
[0047] (2) After being adjusted to acidity, the organic waste water enters the quicksand filter, and the organic matter in the organic waste water is oxidatively degraded with the sand-like multi-component alloy structure filler as the micro-electrolysis filler; and the suspended matter is filtered out;
[0048] (3) Enter the flocculation tank with the wastewater effluent treated in step (2), and add KOH solution in the flocculation tank to generate synergistic flocculation;
[0049] (4) The effluent of the treated wastewater in the flocculation tank enters the inclined tube high-efficiency sedimentation tank to remove the sediment and then effluent to complete the advanced treatment of organic was...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The process for advanced treatment of organic wastewater by using multiple micro-electrolytic fillers includes the following steps:
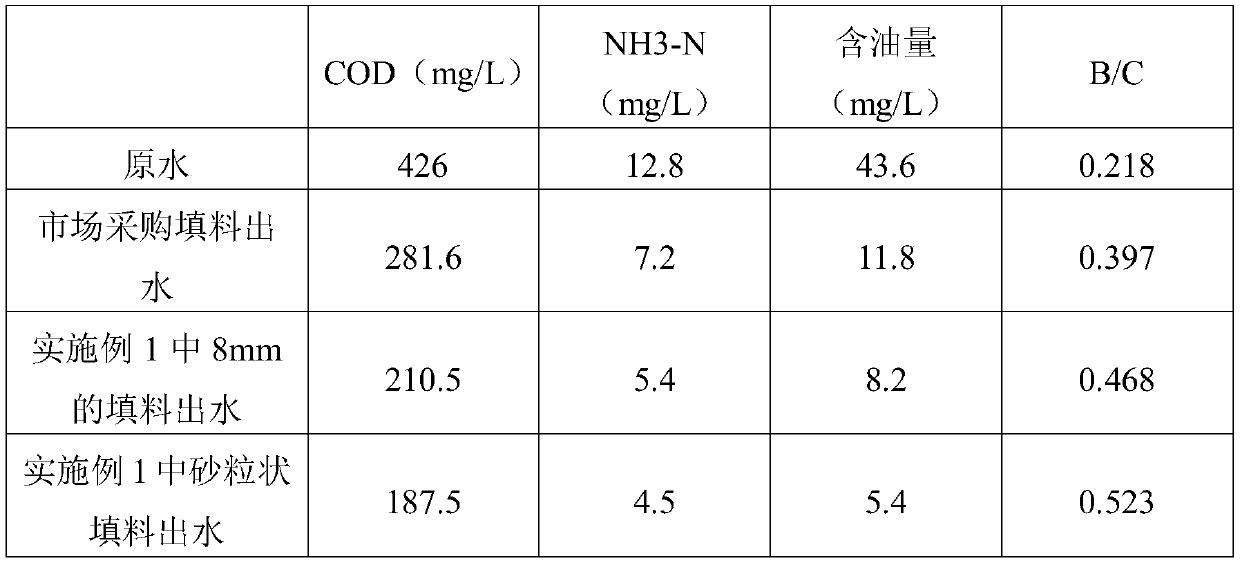
[0059] (1) The organic waste water enters the adjustment tank through the secondary sedimentation tank effluent to adjust the pH to acidity;
[0060] (2) After being adjusted to acidity, the organic waste water enters the quicksand filter, and the organic matter in the organic waste water is oxidatively degraded with the sand-like multi-component alloy structure filler as the micro-electrolysis filler; and the suspended matter is filtered out;
[0061] (3) Enter the flocculation tank with the wastewater effluent treated in step (2), and add KOH solution in the flocculation tank to generate synergistic flocculation;
[0062] (4) The effluent of the treated wastewater in the flocculation tank enters the inclined tube high-efficiency sedimentation tank to remove the sediment and then effluent to complete the advanced treatment of organic was...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com