Leg and foot structure of hydraulic-driven robot
A robot and driving technology, applied in the field of robot leg and foot structure, hydraulically driven robot leg and foot structure, can solve the problems of poor coordination performance of mechanical legs, uncoordinated movement, unfavorable motion control of biped mechanical legs, etc., to achieve Stable synergistic performance, stable driving mode, increased movement space and flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
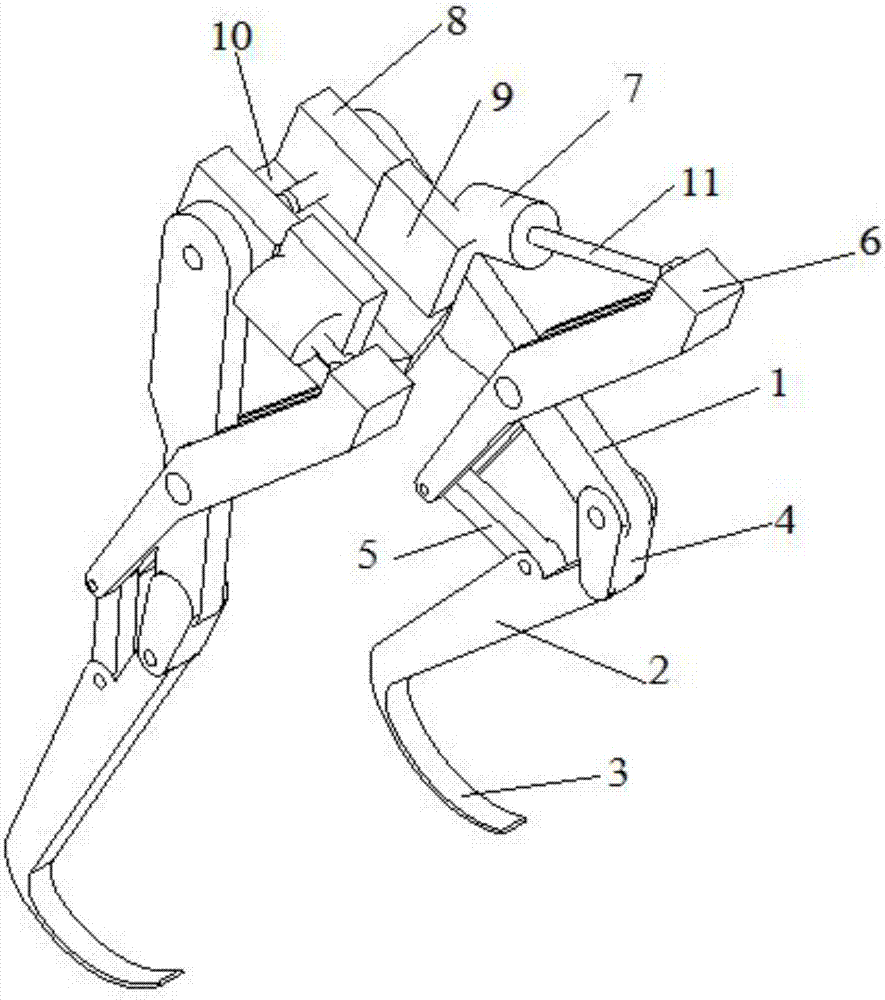
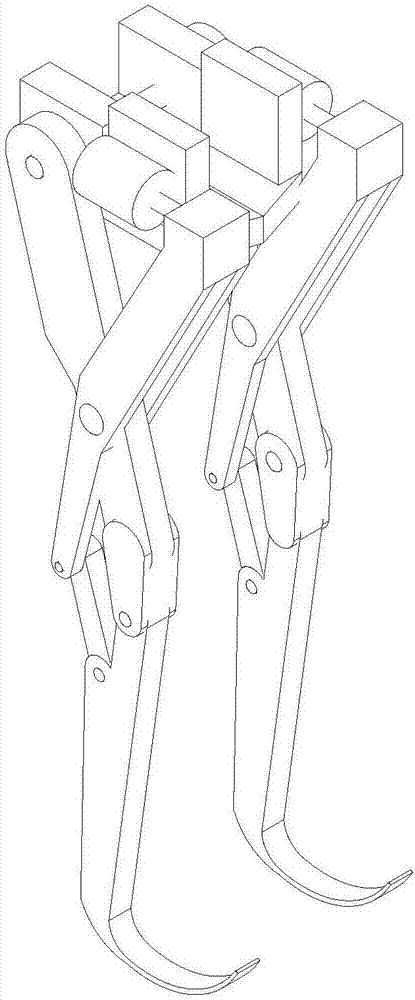
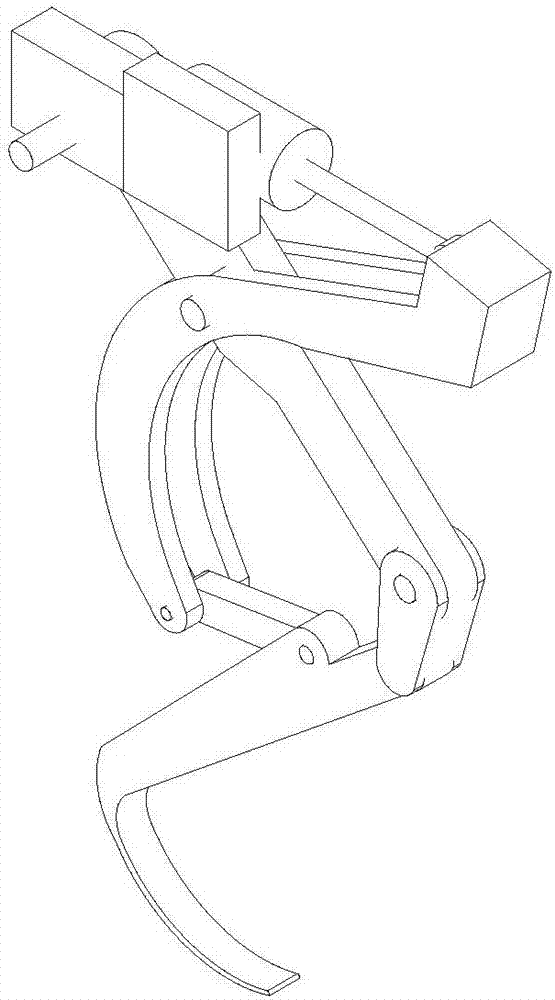
[0023] like figure 1 Shown is the overall structure of the leg and foot structure. The thigh piece 1 and the calf piece 2 are connected by the knee piece 4, and the bottom of the calf piece 2 is connected with a foot piece 3, and the foot piece 3 is welded on the bottom of the calf piece 2; between the thigh piece 1 and the knee piece 4 and between the knee piece 4 and the calf Parts 2 are all connected by pin shafts, and calf part 2 is connected with thigh part 1, calf part 2, foot part 3 and knee part 4 to form the main moving component of the robot; the main connecting part 6 and the receiving part 5 are auxiliary connections of the robot Adjusting piece; the main connecting piece 6 is provided with two pin holes, the first pin hole is set at the middle position of the main connecting piece 6, and the second pin hole is set at the bottom position of the main connecting piece 6; the main connecting piece 6 The top is connected with the hydraulic rod 11, the first pin hole o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com