Touch control and fingerprint identification module, manufacture method thereof, and electronic terminal
A fingerprint recognition module and fingerprint recognition technology, applied in the field of human-computer interaction, can solve the problem of occupying mobile phone space, and achieve the effects of cost saving, convenient operation, and effective use of screen space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
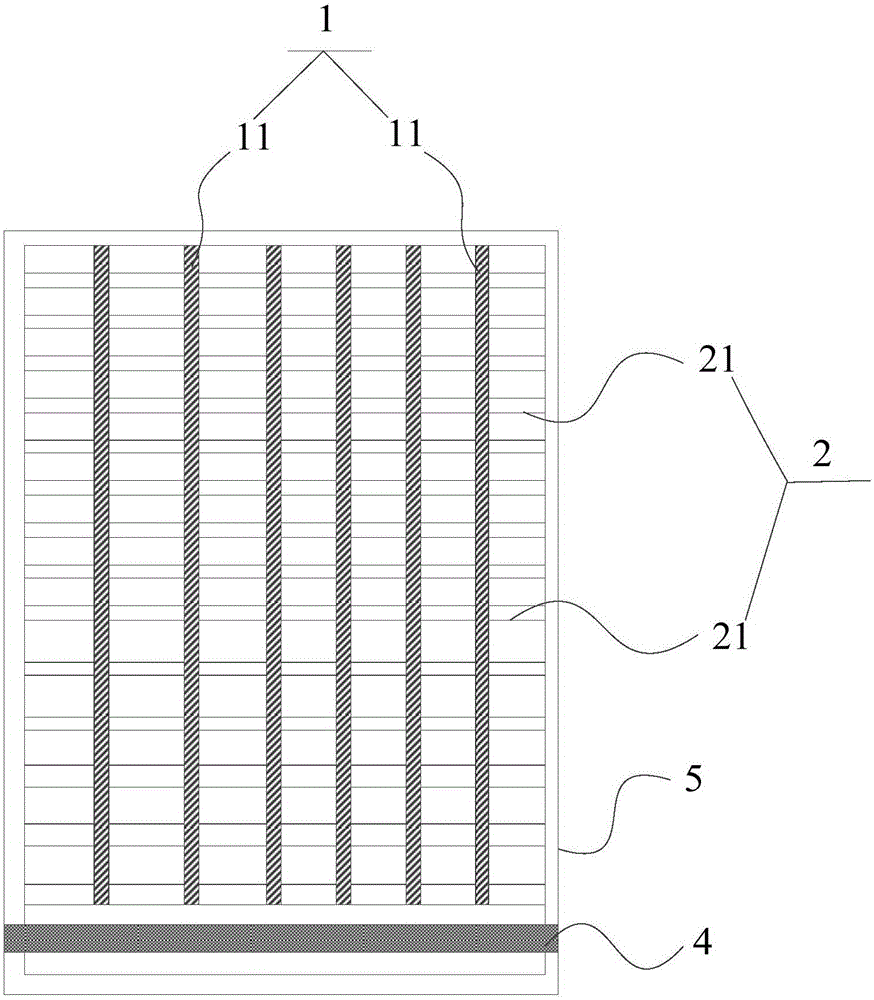
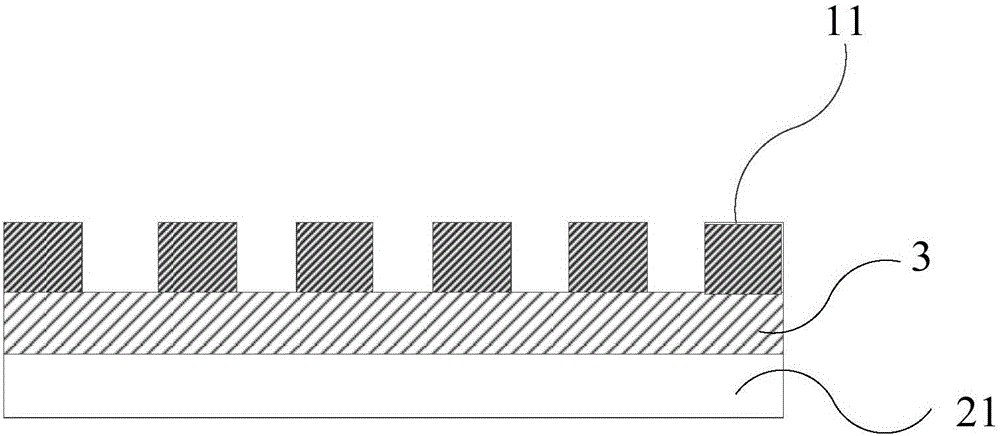
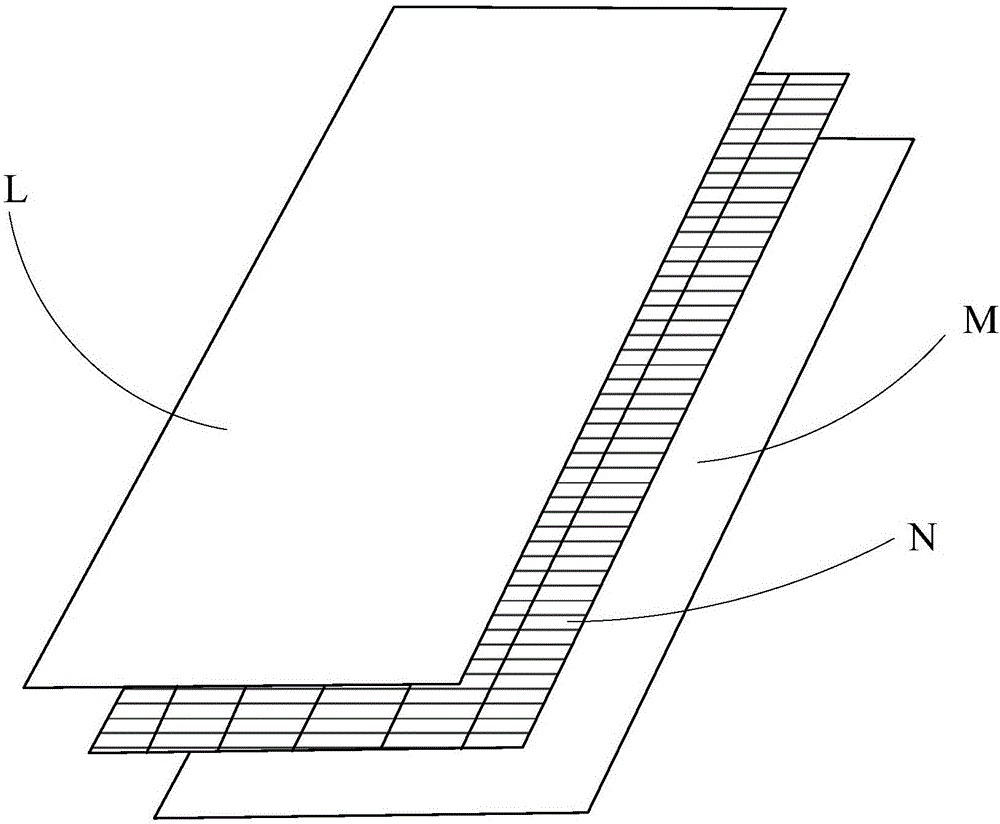
[0106] combine figure 1 and figure 2 , a touch and fingerprint recognition module, including: a first electrode layer 1 as a receiving electrode, a second electrode layer 2 as an emitter, and a spacer layer between the first electrode layer 1 and the second electrode layer 2 The insulating layer 3; the first electrode layer 1, used as the first electrode layer for fingerprint recognition and touch control, includes a plurality of first electrode lines 11 arranged in sequence. The second electrode layer 2, as the second electrode layer for fingerprint identification and touch control, includes a plurality of second electrode lines 21 arranged in sequence; the first electrode lines 11 of the first electrode layer 1 and the second electrode lines of the second electrode layer 2 The electrode lines 21 are arranged in a staggered manner. The first electrode lines 11 and the second electrode lines 21 are made of ITO material. The insulating layer 3 is made of insulating resin. ...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Implementation 1 was repeated, except that the line width of the first electrode lines 11 was 0.01 mm; the line width of the second electrode lines 21 was 0.01 mm. The distance between two adjacent first electrode lines 11 is 0.15 mm; the distance between two adjacent second electrode lines 21 is 0.15 mm. The first electrode lines 11 and the second electrode lines 21 form an angle of 90° with each other, that is, they are perpendicular.
[0110] Taking 5 inches as an example, the size of the viewing area is 62.1mm*110.4mm, the distance between the receiving electrode and the emitting electrode is 0.15*0.15mm, and the width of a single metal wire is 0.01mm. (414) + emitter (736), the sum of the two requires a total of 1150 PADs (pins), and the metal lead is pulled down to the bottom of the glass to connect the processing chip.
Embodiment 3
[0112] Embodiment 1 was repeated, except that the line width of the first electrode lines 11 was 0.005 mm; the line width of the second electrode lines 21 was 0.002 mm. The distance between two adjacent first electrode lines 11 is 0.08 mm; the distance between two adjacent second electrode lines 21 is 0.06 mm. The first electrode lines 11 and the second electrode lines 21 form an angle of 90° with each other, that is, they are perpendicular.
[0113] Taking 5 inches as an example, the size of the visible area is 62.1mm*110.4mm, the distance between the receiving electrode and the emitter electrode is 0.08*0.06mm, the width of a single first electrode metal wire is 0.05mm, and the width of a single second electrode The width of the electrode metal wire is 0.002mm, and the visible area requires a total of receiving electrodes (776) + emitters (1833). The sum of the two requires a total of 2609 PADs (pins). Pull the metal leads down to the bottom of the glass and connect the proc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com