A mimic security method and device for dns recursive server
A technology of DNS server and recursive server, which is applied in the field of network security, can solve the security threats of DNS recursive server and other problems, and achieve the effect of solving cache poisoning and ensuring reliability and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
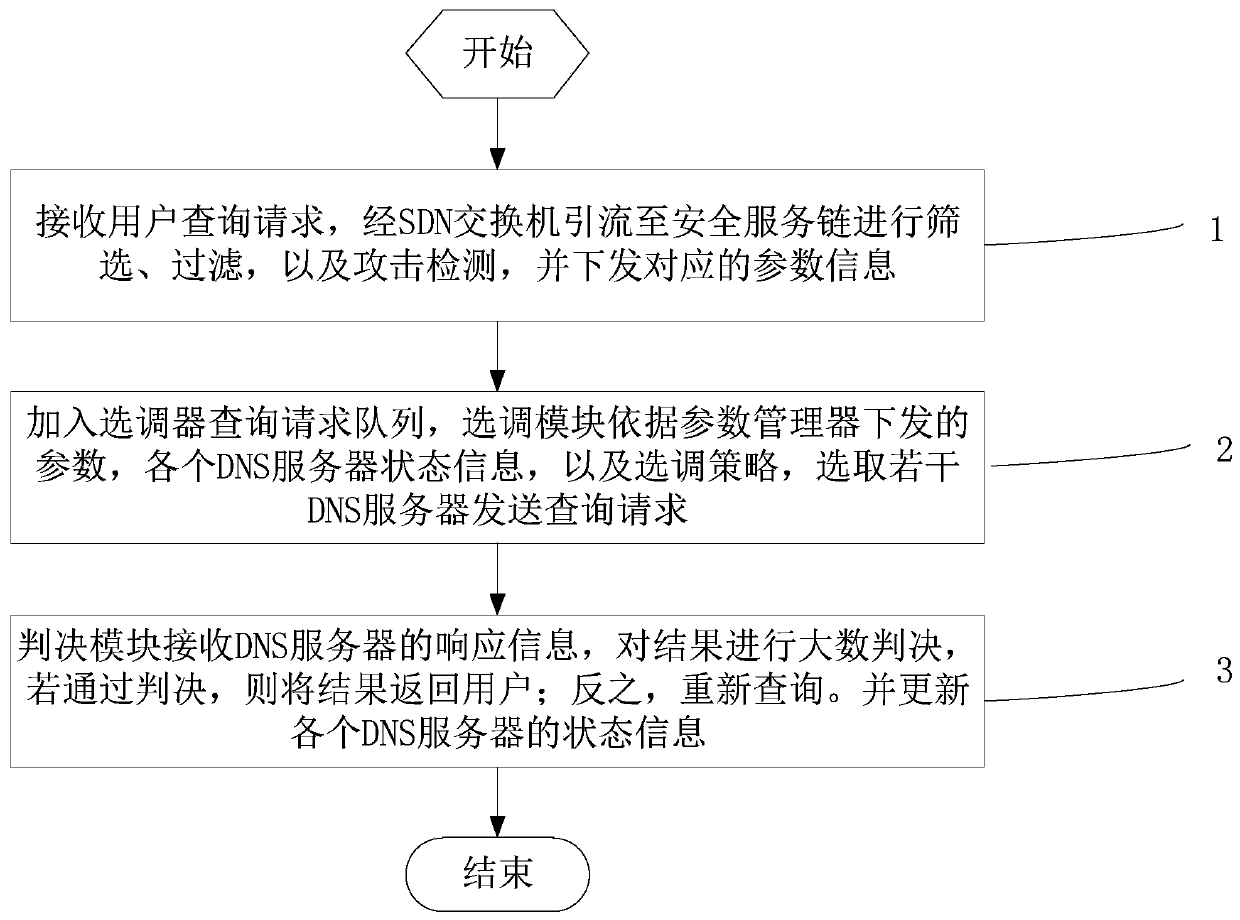
[0033] Embodiment one, see figure 1 As shown, a mimic security method and device for a DNS recursive server, comprising the following steps:
[0034] Step 1: Receive the user query request, divert it to the security service chain through the SDN switch for screening, filtering, and attack detection, and the parameter manager obtains the attack detection data and sends the corresponding parameter information to the tuner;
[0035] Step 2: For each query request in the selector query request queue, the selection module selects several DNS servers to send query requests according to the parameters issued by the parameter manager, the status information of each DNS server, and the selection strategy;
[0036] Step 3: The judging module receives the response information from the DNS server and makes a large number judgment on the result. If the judgment is passed, the result is returned to the user; otherwise, the query is re-queried. And update the status information of each DNS ...
Embodiment 2
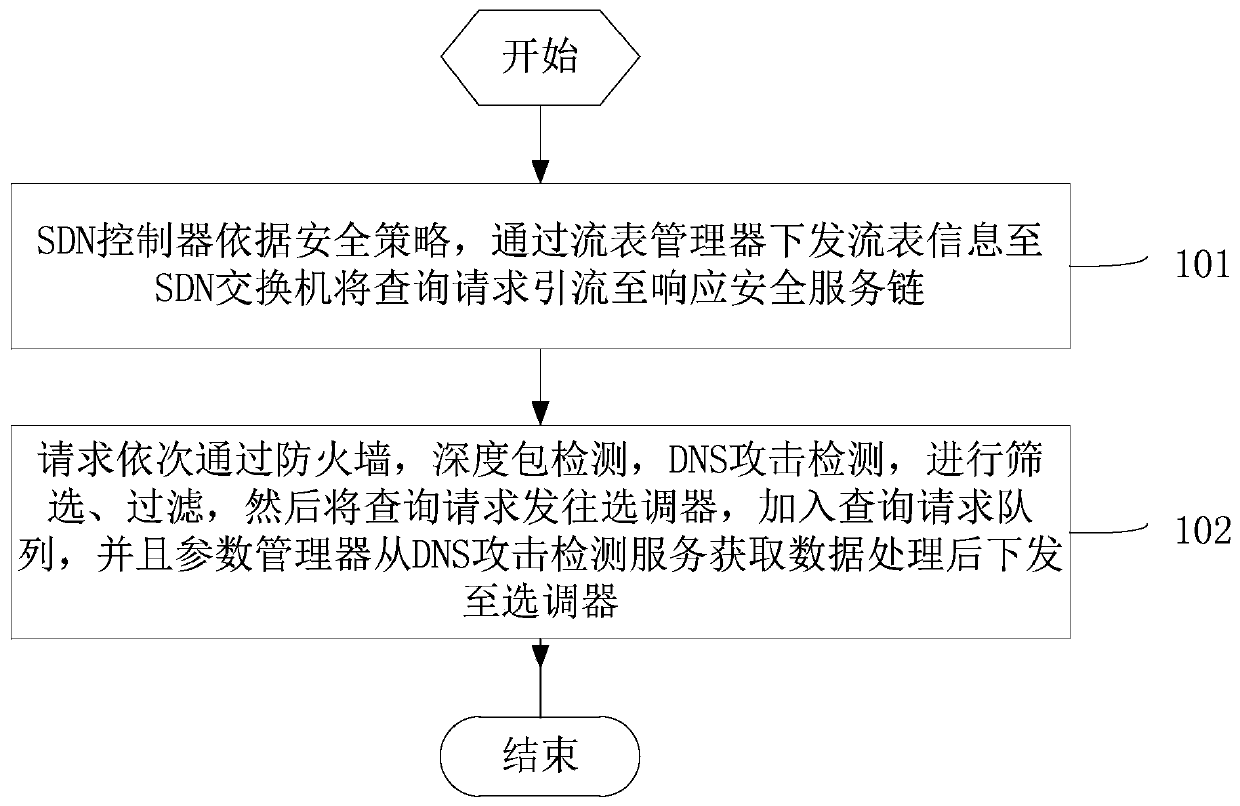
[0037] Embodiment two, step 1 in embodiment one can be realized in the following manner:
[0038] see figure 2 as shown, figure 2 It is a flow diagram of the security service chain module, including the following steps:
[0039] Step 101: According to the security policy, the SDN controller sends the flow table information to the SDN switch through the flow table manager to divert the query request to the response security service chain;
[0040] Step 102: The request passes through the firewall, deep packet inspection, and DNS attack detection in order to screen and filter, and then sends the query request to the selector, joins the query request queue, and the parameter manager obtains data from the DNS attack detection service for processing and sends it out to the tuner;
[0041] Specifically, the parameter information is the coefficient of the DNS server status information (that is, the coefficient of the reliability and load when calculating the selection factor), a...
Embodiment 3
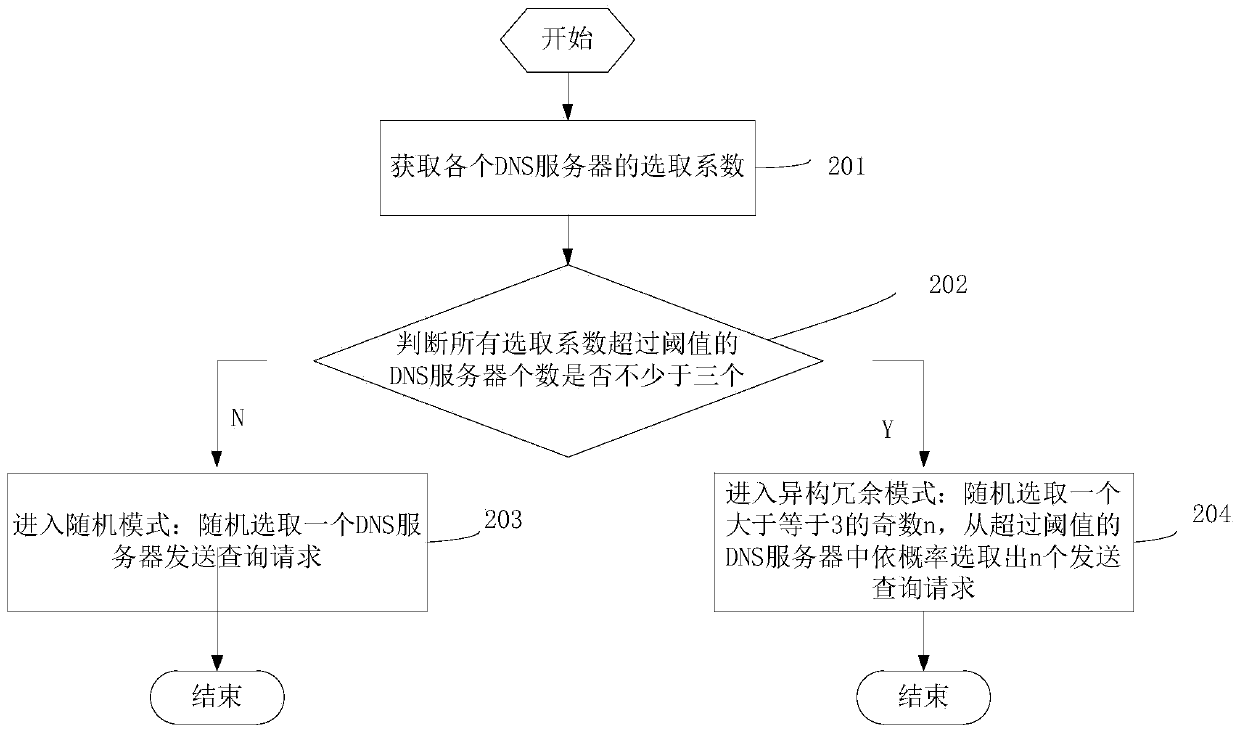
[0042] Embodiment three, step 2 in embodiment one can be realized in the following manner:
[0043] see image 3 as shown, image 3 It is a flow diagram of the selection module, including the following steps:
[0044] Step 201: Obtain selection factors of each DNS server;
[0045] Specifically, the selection factor is determined by multiplying the reliability, load and the coefficient issued by the parameter manager;
[0046] Step 202: Determine that the number of DNS servers whose selection factor exceeds the threshold is greater than or equal to 3: if it is less than 3, enter step 203: random mode, randomly select a DNS server to send a query request; otherwise, enter step 204: different To construct a redundant mode, randomly select an odd number n greater than or equal to 3, and select n query requests from the DNS servers exceeding the threshold according to the probability of the selection factor.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com