Steady state calculating method of ground fault of undercurrent grounding electric power system
A small current grounding and grounding fault technology, which is applied to the fault location, detects faults according to the conductor type, and measures electricity. It can solve the problems of fire, inability to quantitatively analyze, and difficult effective calculation of ground fault current, etc., to achieve accurate calculation and convenient programming. Calculation, the effect of improving calculation accuracy and practicality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
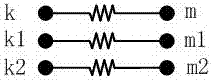
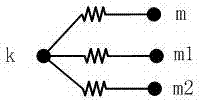
[0058] Embodiment 1: A ground fault steady-state calculation method for a small-current grounded power system. When a ground fault occurs in a small-current grounded system, the node admittance equations are decomposed according to the symmetrical component method, and the positive sequence, negative sequence and The zero-sequence component is then composed into a group of equations for calculation to obtain the steady-state voltage of each node and the steady-state current of each branch in the small-current grounded power system when the ground fault occurs.
[0059] When sorting out branches, the actual branches are treated as two branches, which are the inductive branch and the resistive branch.
[0060] Inductance and capacitance components are divided into three-phase components and single-phase components: the sequence impedance and zero-sequence impedance of three-phase components are different, and the positive sequence, negative sequence and zero sequence impedance ar...
Embodiment 2
[0126] Embodiment 2: This embodiment provides a ground fault steady-state calculation method for a small-current grounded power system. When a ground fault occurs in a small-current grounded system, the node admittance equations are decomposed according to the symmetrical component method, and the positive Sequence, negative sequence and zero sequence components, and then form a group of equations for calculation to obtain the steady-state voltage of each node and the steady-state current of each branch in the small current grounding power system when the ground fault occurs.
[0127] 1. Inductance and capacitance components are divided into three-phase components and single-phase components according to their meanings: the sequence impedance and zero-sequence impedance of three-phase components are different, and the positive sequence, negative sequence and zero sequence are calculated respectively; the sequence impedance and zero sequence impedance of single-phase components ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com