Near-in-situ Complementation Method for Site-directed Insertion Mutation of Fungal Genes
A gene and mutant technology, applied in the field of near-in-situ complementation of fungal gene-directed insertion mutation, can solve problems such as impact, inability to verify gene complementation, and inability to achieve accurate recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
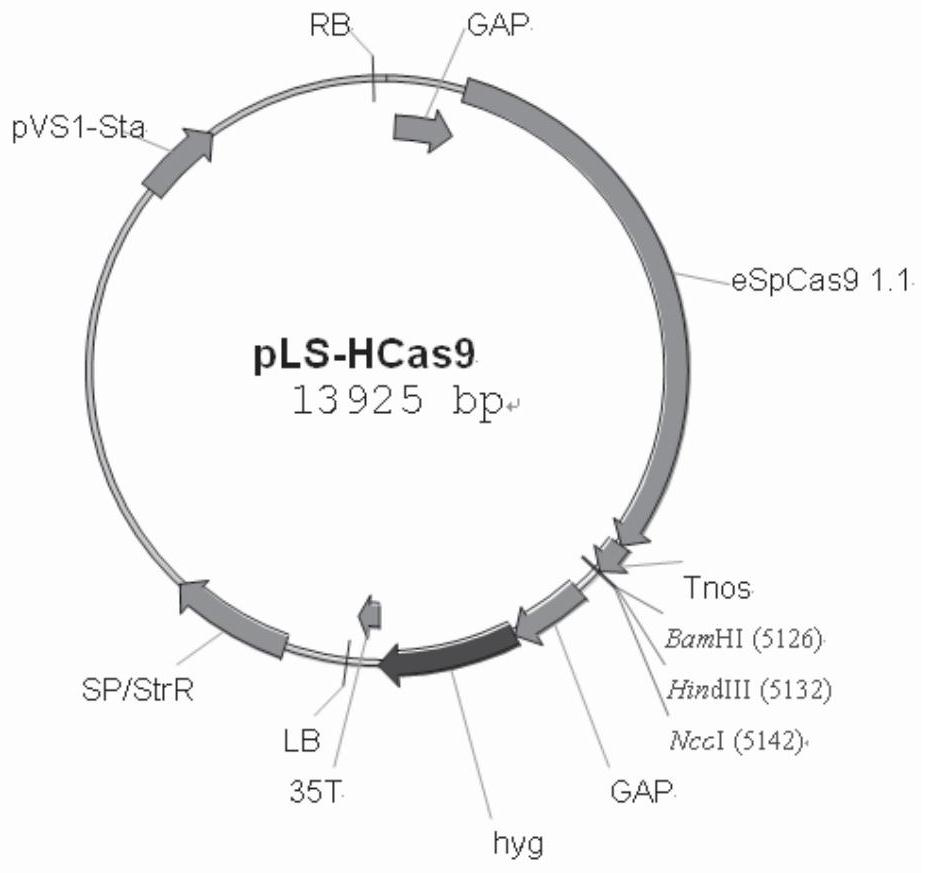
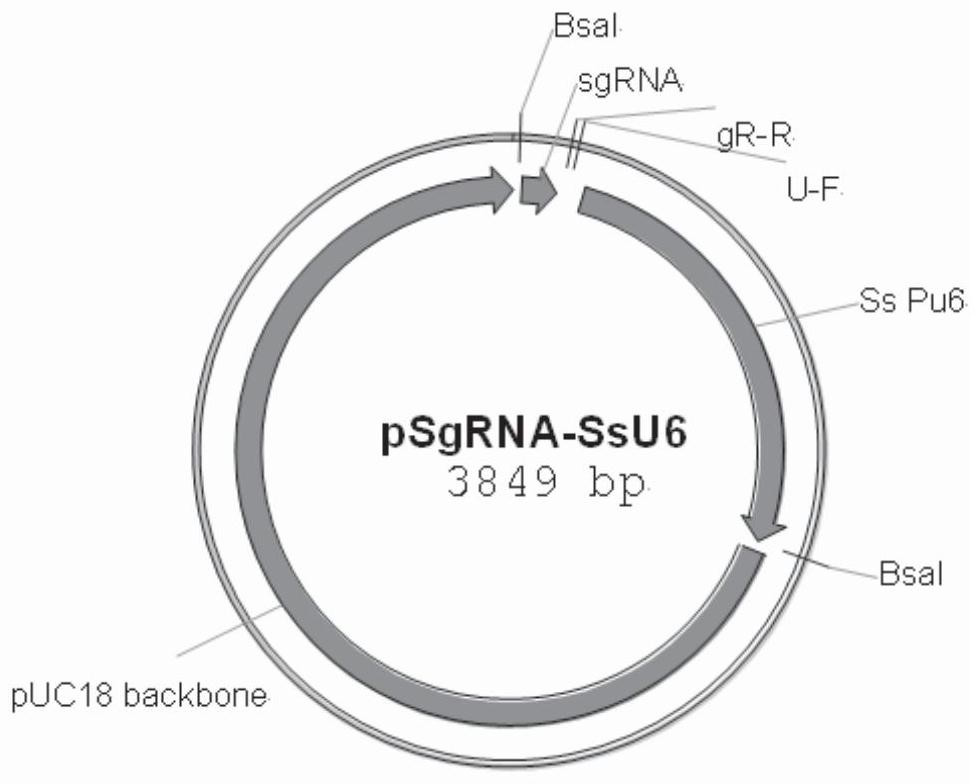
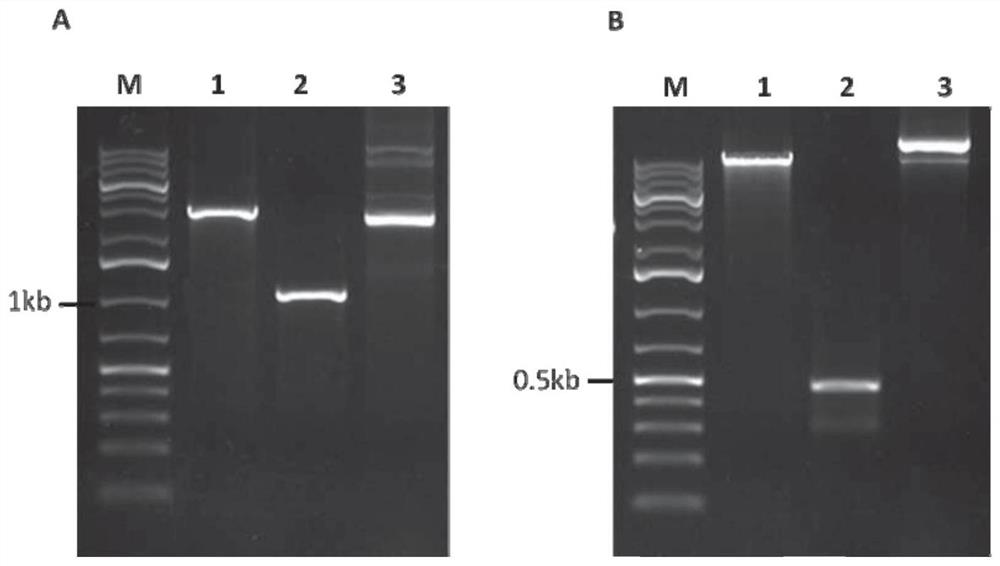
[0034] The near-in-situ complementation method of fungal gene site-directed insertion mutation of the present invention is to express the complementary gene fragment and the U6 promoter that drive the expression of sgRNA carrying the specific recognition sequence of the resistance gene after the base has been changed at the target site but the amino acid sequence is unchanged The cassette is integrated with the T-plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and the Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated site-directed complementation vector of pathogenic fungal genes is constructed with nourthricin as a resistance selection marker; the complementary vector is used to transform the insertional inactivation mutant of pathogenic fungal genes The spores rely on the Cas9 carried in the gene insertion inactivation mutant to cut the target site, so as to realize the accurate insertion of the complementary gene fragment into the resistance gene target sequence of the mutant. Among them, the comple...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com