Feature-based factory manufacturing process difference detection method
A manufacturing process and detection method technology, applied in the field of feature-based factory manufacturing process difference detection, can solve the problems of inability to find the difference of the whole process model, unreasonable process model, etc., and achieve the effect of flexible design, improved efficiency, and flexible methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
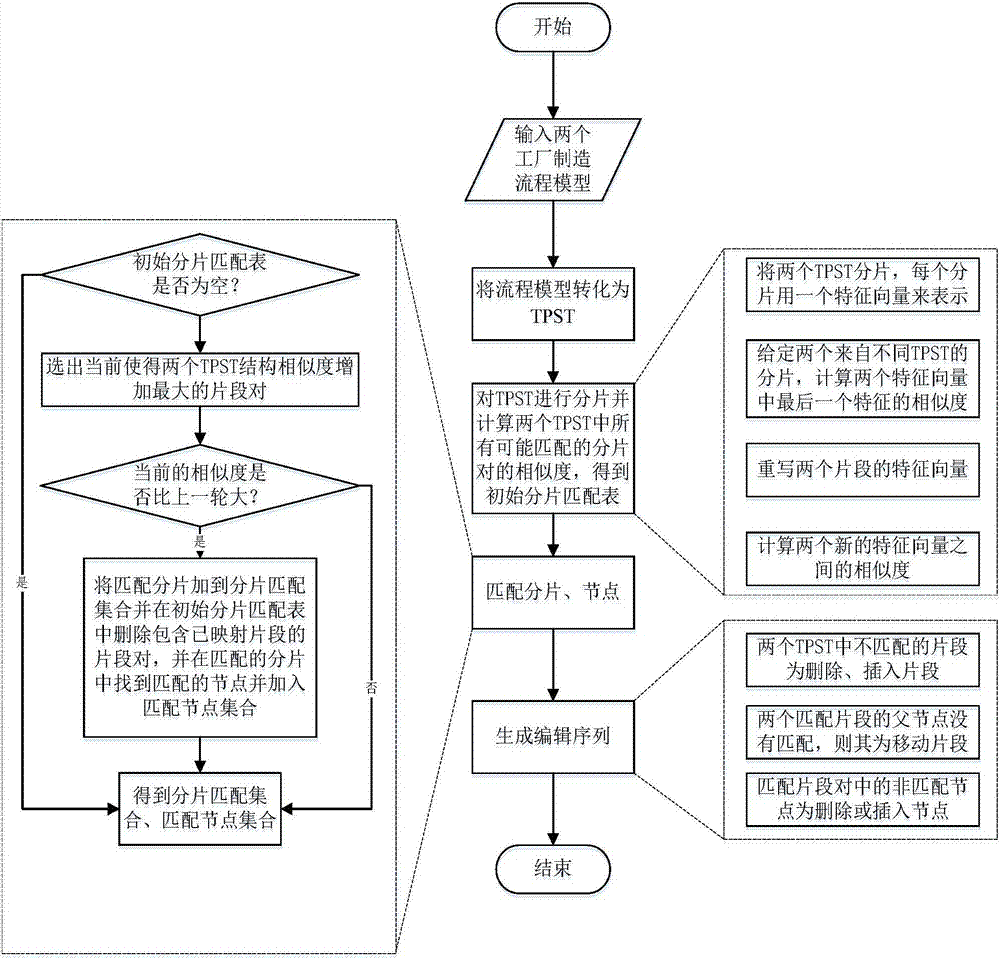
[0043] Reference attached figure 1
[0044] A feature-based method for detecting differences in factory manufacturing processes includes the following steps:
[0045] (1) Input the factory manufacturing process model of two differences to be detected;
[0046] (2) Transform the manufacturing process models of the two factories into their corresponding task-based process structure trees (task-based process structure tree, TPST);
[0047] (3) Fragment the two TPSTs respectively, and calculate the similarity of all possible matching fragment pairs in the two TPSTs, and obtain the initial fragment matching table F={(f 1 ,f 1 ’, sim 1 ),(f 2 ,f 2 ’, sim 2 ),…,(f i ,f i ’, sim i )}, only fragments of the same type can match, including:
[0048] (3.1) Fragment the two TPSTs separately, where each fragment is represented by a feature vector composed of multiple features;
[0049] (3.2) Given slices from two different TPSTs, calculate the similarity between the last features ...
Embodiment 2
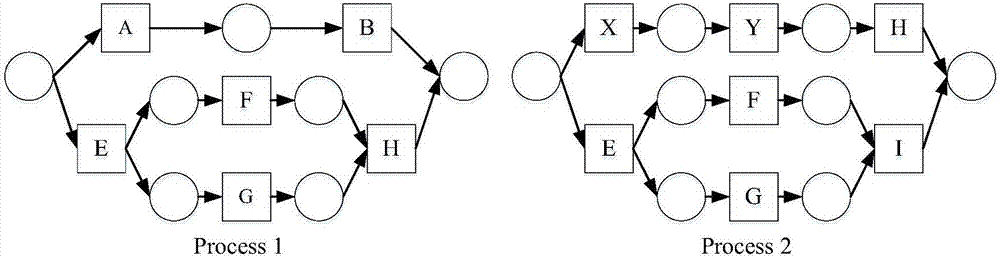
[0063] Reference attached figure 2 ,3,4,5
[0064] figure 2 Indicates two examples of factory auxiliary material processing flow model diagrams: Process 1 and Process 2. Due to the limitation of the page, letters are used to represent the meaning of task nodes: A means "finished product acceptance", B means "packaging", E means "ingredient processing", F means "cutting", G means "surface treatment", H means " Subpackage", I means "delivery to packaging department", X means "finished product inspection", Y means "coloring".
[0065] In order to get the difference between Process 1 and Process 2, we need to perform the following steps:
[0066] (1) Input two processing flow models of auxiliary materials to be detected: Process 1 and Process 2, which are modeled by Petri nets, such as figure 2 shown;
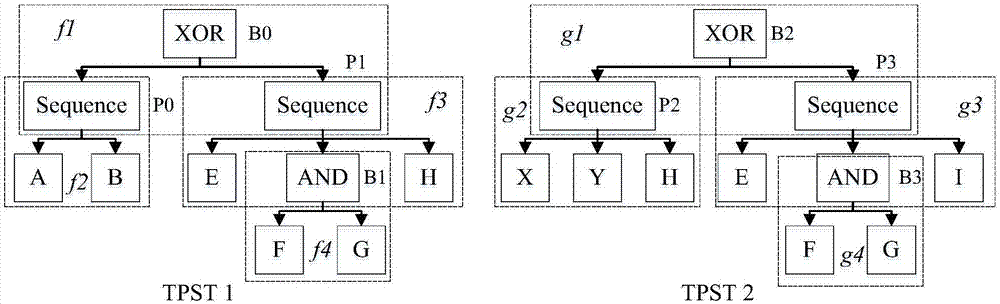
[0067] (2) Transform Process 1 and Process 2 into their corresponding task node-based process structure tree (TPST): TPST 1 、TPST 2 ,Such as image 3 As shown, each rout...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com