High-yield fermentation method of bacterial cellulose
A technology of bacterial cellulose and fermentation method, which is applied in the field of fermentation of high-yield bacterial cellulose, can solve the problem of low yield and achieve the effect of increasing dry weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
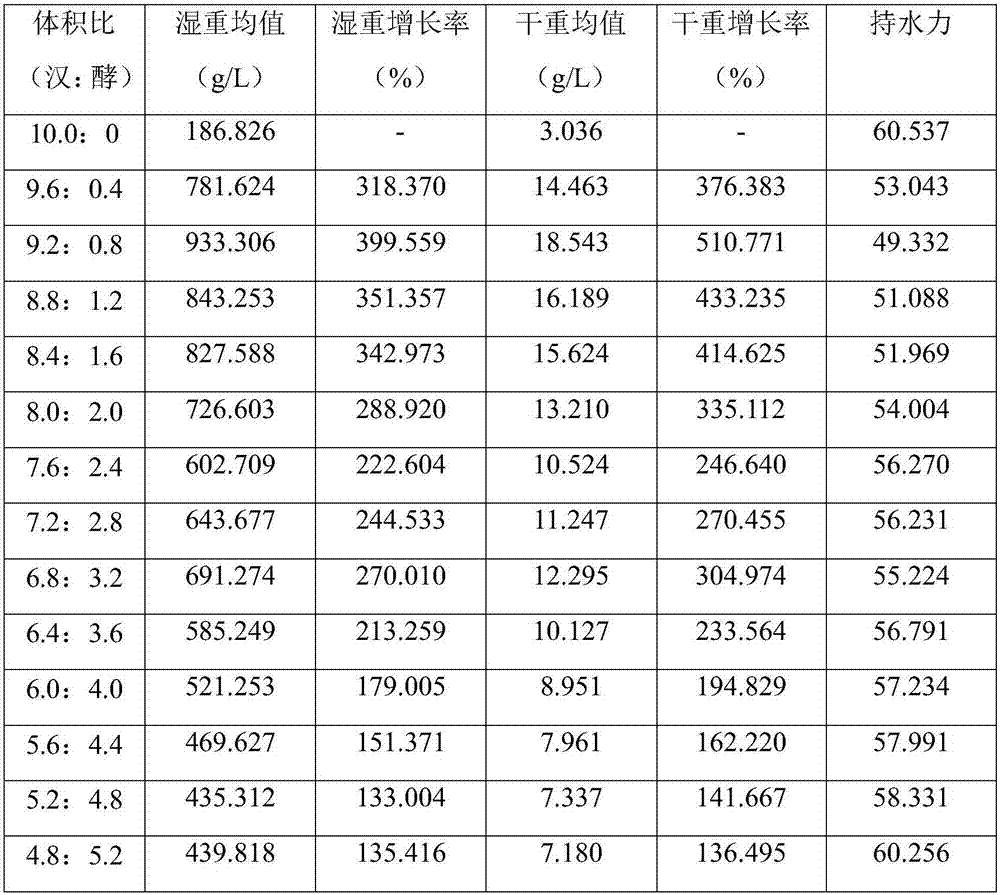
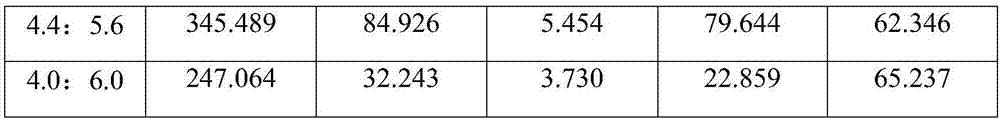
[0025] 1. Activation of acetic acid bacteria strains: Streak inoculation of Gluconacetobacter hansenii stored in a 4°C refrigerator on a BSH plate, culture at 30°C for 5 days for strain activation, and repeat this process twice;
[0026] 2. Yeast strain activation: Saccharomyces cerevisiae stored in a refrigerator at 4°C was streaked and inoculated on a YPD plate, cultured at 30°C for 2-3 days for strain activation, and this process was repeated twice;
[0027] 3. Preparation of acetic acid bacteria seed liquid: pick two activated single colonies of Gluconacetobacter hansenii and put them in a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 100ml of BSH liquid medium, under the conditions of 30°C and 150r / min Cultivate for 24 hours to prepare seed solution, and expand the prepared seed solution twice with 10% inoculation amount;
[0028] 4. Preparation of yeast seed liquid: Pick two single colonies of activated Saccharomyces cerevisiae and place them in a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask filled with ...
Embodiment 2
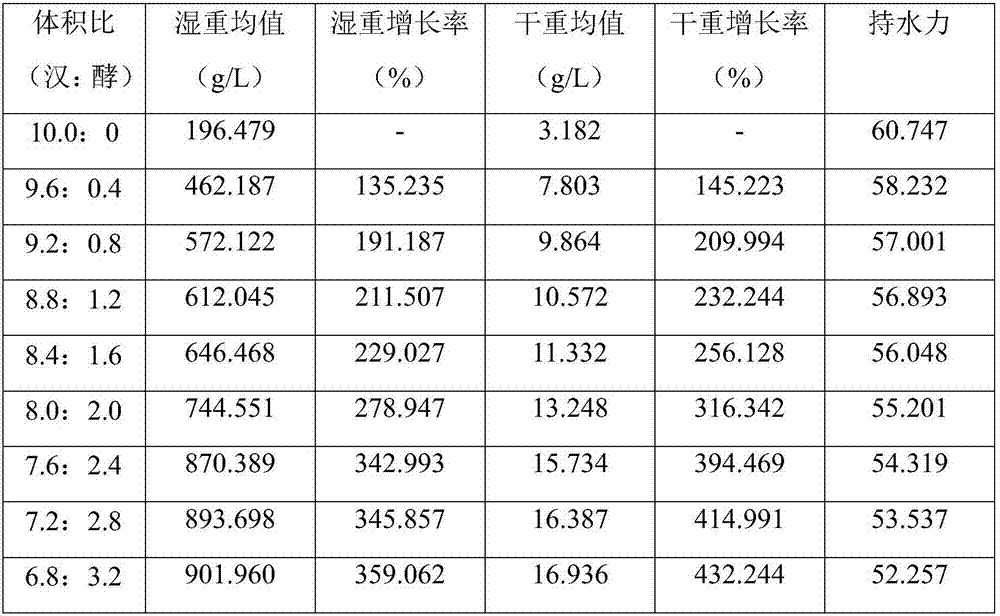
[0043] 1. Activation of acetic acid bacteria strains: Streak inoculation of Gluconacetobacter hansenii stored in a 4°C refrigerator on a BSH plate, culture at 30°C for 5 days for strain activation, and repeat this process twice;
[0044] 2. Yeast strain activation: Streak inoculation of Candida utilis stored in a refrigerator at 4°C on a YPD plate, culture at 30°C for 2-3 days for strain activation, and repeat this process twice;
[0045] 3. Preparation of acetic acid bacteria seed liquid: pick two activated single colonies of Gluconacetobacter hansenii and put them in a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 100ml of BSH liquid medium, under the conditions of 30°C and 150r / min Cultivate for 24 hours to prepare seed solution, and expand the prepared seed solution twice with 10% inoculation amount;
[0046] 4. Preparation of yeast seed solution: pick two single colonies of activated Candida utilis into a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 100ml YPD liquid medium, and cultivate them f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com