Deviation rectifying and strengthening structure for shallow-foundation building and construction method of deviation rectifying and strengthening structure
A technology for strengthening structures and construction methods, applied in basic structure engineering, basic structure repair, construction, etc., can solve problems such as complex construction technology, limited scope of use, damage to the original structure of buildings, etc., to ensure the quality of the project and the scope of application Widespread, low-cost-to-manufacture effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
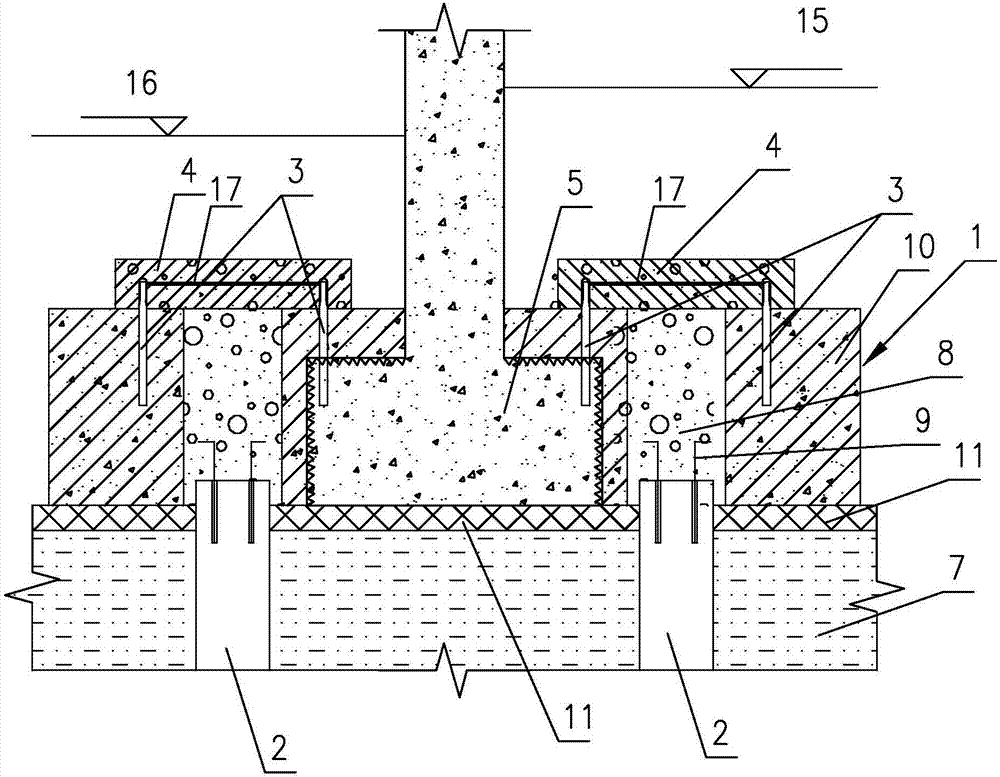
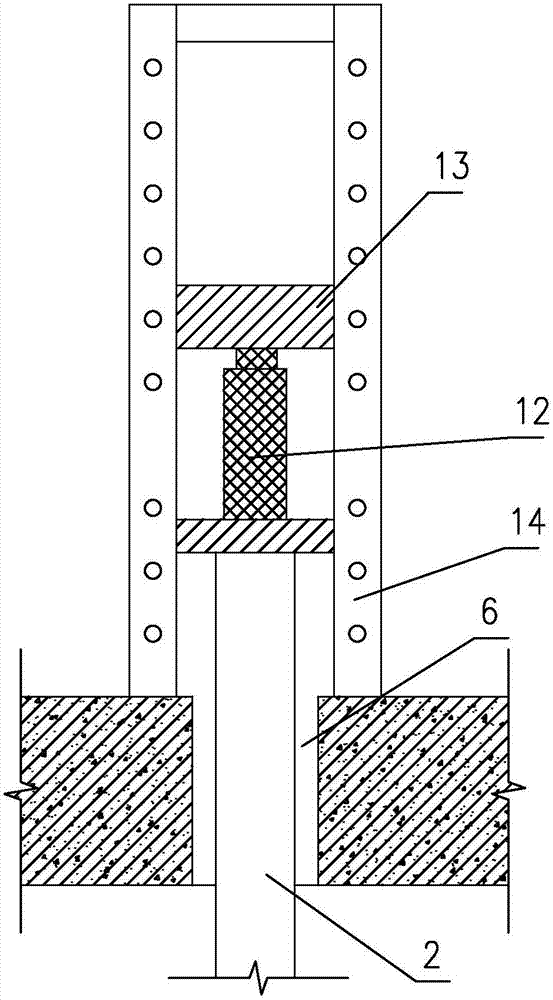
[0038] Such as figure 1As shown, it is a deflection correction and reinforcement structure for a shallow foundation building of the present invention, which includes a pile cap 1, an anchor static pressure pile, a concrete cushion 11, a pile sealing plate 4, pouring in the pile cap 1 and the underground soil layer 7 The filling layer (not shown in the figure) in the gap between them, the filling layer adopts cement mortar with good fluidity, which can ensure that the gap between the foundation and the underground soil layer is filled tightly. The anchor static pressure pile includes a static pressure pile 2, a pressure pile anchor 3 and a steel bar 17 for welding the pressure pile anchor 3. The outdoor floor elevation is 15, and the indoor floor elevation is 16. In this embodiment, the pile cap 1 is an additional foundation part added on the shallow foundation 5 of the original building, and the additional foundation part is combined with the shallow foundation 5 of the origi...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: when the shallow foundation of the original building meets the specification requirements, the pile cap can be the shallow foundation of the original building. On the shallow foundation of the original building, the pressure pile hole is excavated or core-pulled to form a hole on the shallow foundation of the original building, and the pressure pile anchor rod adopts the post-implantation method.
[0053] The difference between the construction method of this embodiment and the construction method of Embodiment 1 is that the step of constructing the additional foundation part is omitted, and the rest of the steps are the same.
Embodiment 3
[0055] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the additional foundation part is an enlarged foundation part, which is a concrete block, and the enlarged foundation part is connected with the edge of the shallow foundation of the original building and integrated with it. The pile pressure hole is located in the enlarged foundation part, and the pile pressure hole is reserved, or the pile pressure hole is located in the shallow foundation of the original building, which is excavated on the shallow foundation of the original building or cored to form a hole, correspondingly , the pressure pile anchor on the enlarged foundation part adopts the pre-embedded method, while the pressure pile anchor on the shallow foundation of the original building adopts the post-implantation method.
[0056] The construction method of this embodiment is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com