Cerebral functional magnetic resonance imaging blind source separation method based on grouping SIM algorithm
A functional magnetic resonance and blind source separation technology, applied in computing, computer components, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as undersampling, and achieve the effect of suppressing overfitting problems, accurate analysis results, and accurate and reliable separation results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
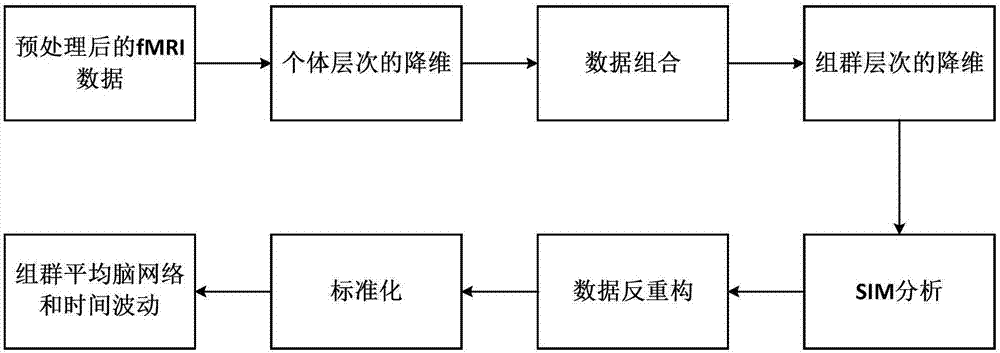
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, the implementation steps of the brain functional magnetic resonance imaging blind source separation method based on the group SIM algorithm in this embodiment include:
[0032]1) For the preprocessed functional magnetic resonance imaging of each subject, the dimensionality reduction at the individual level is first performed by the PCA method, and then the dimensionality reduction data of all subjects are combined to obtain a group data set , and then perform group-level dimensionality reduction on the group data set through the PCA method;
[0033] 2) Analyze and process the data set of the group after dimensionality reduction through the SIM algorithm to obtain the brain source network at the group level;
[0034] 3) The brain source network at the group level is de-reconstructed and then standardized to obtain the brain source network and corresponding time fluctuations of each subject;
[0035] 4) The brain source network and time fluctu...
Embodiment 2
[0047] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and its main difference is that step 1.3) converts all matrices subpcaM i The detailed steps of grouping into a new data matrix groupM are different. In this embodiment, the matrix subpcaM i A row of can be regarded as a spatial component, step 1.3) will all matrix subpcaM i The detailed steps of combining into a new data matrix groupM include: each matrix subpcaM i Each row of is used as a row of groupM, and a new data matrix groupM is formed according to the combination of rows.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com