Tree grafting method for Camellia liberofilamenta Chang et C.H.Yang
A golden camellia and large tree technology, applied in the field of forest tree propagation, can solve problems such as unfavorable large-scale production of asexual reproduction of golden camellia lily, low reproduction coefficient, large propagation materials, etc., and achieves improved ornamental quality, low cultivation cost, and high growth and development. strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
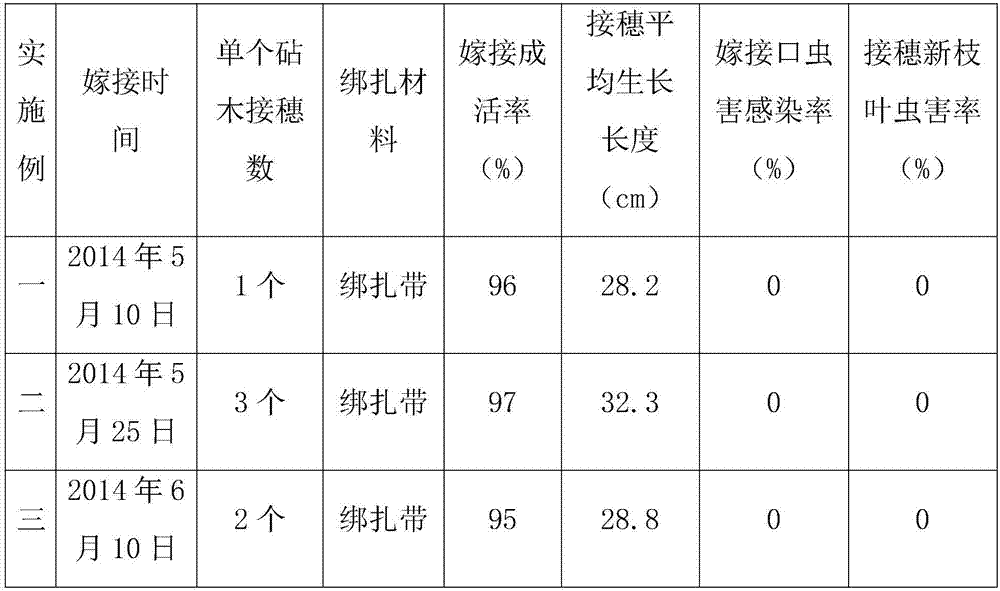
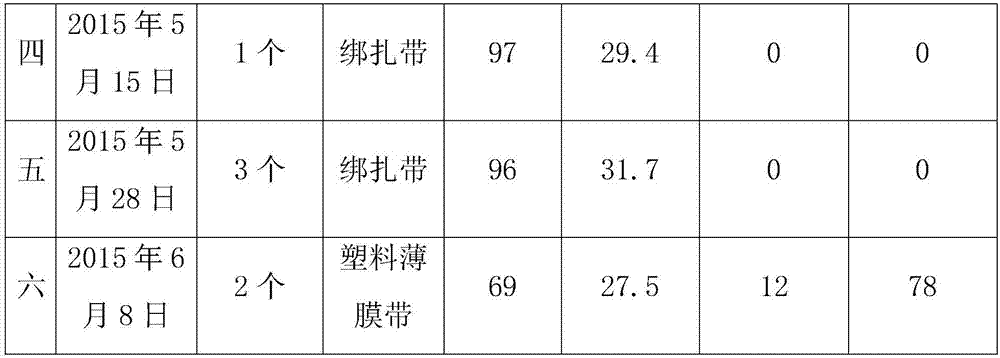
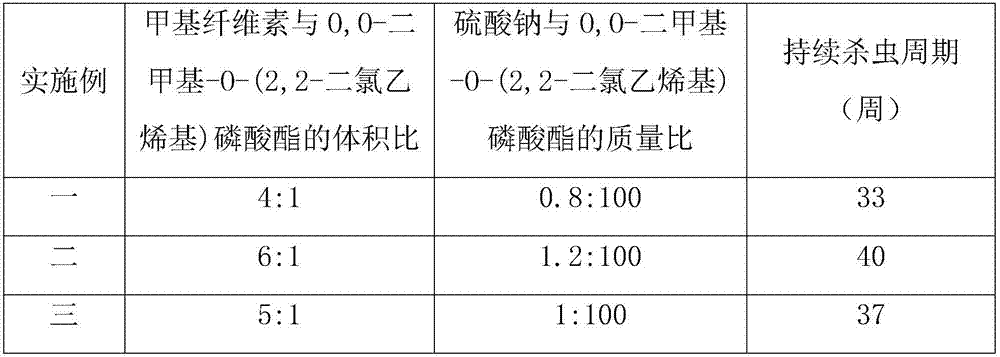
[0039]On May 10, 2014, in the periphery of the upper part of the canopy of C. japonica, the semi-lignified branches of the year that were healthy, free from diseases and insect pests, and full of axillary buds were collected as spikes, and then put into a container with ice cubes and wet towels. In the foam box, on the same day, use a single-sided blade to cut the scion into a length of 2.0cm-2.5cm, keep the scion with one leaf and one bud, cut off 1 / 2 of each leaf, and cut off from the 0.3cm-0.5cm above the leaf bud of the scion , the lower end of the leaf bud remains 1.6cm to 2.0cm long, and then straight down from the 0.3cm to 0.5cm below the bud base to a long section with a length of 1.6 to 2.0cm. The xylem can be seen slightly on the long section, and the pith can be seen at the base. Then cut a horse ear-shaped short section at an angle of 20 to 30 degrees on the back of the long section; select a common Camellia oleifera tree with a smooth surface, no pests and diseases...
Embodiment 2
[0043] On May 25, 2014, in the outer periphery of the upper part of the crown of C. japonica, the semi-lignified branches of the year that were healthy, free from diseases and insect pests, and full of axillary buds were collected as spikes, and then put into a container with ice cubes and wet towels. In the foam box, on the same day, use a single-sided blade to cut the scion into a length of 2.0cm-2.5cm, keep the scion with one leaf and one bud, cut off 1 / 2 of each leaf, and cut off from the 0.3cm-0.5cm above the leaf bud of the scion , the lower end of the leaf bud remains 1.6cm-2.0cm long, and then straightly and obliquely pulls a long section with a length of 1.6cm-2.0cm from the 0.3cm-0.5cm below the bud base. The xylem can be seen slightly on the long section, and the pith can be seen at the base , and then cut a 20-30-degree horse-ear-shaped short section on the back of the long section; select a common Camellia oleifera tree with a smooth surface, no pests and diseases,...
Embodiment 3
[0047] On June 10, 2014, in the periphery of the upper part of the crown of C. japonica C. japonica, we collected semi-lignified branches of the year that were healthy, free from diseases and insect pests, and full of axillary buds as cuttings, and then put them in a container with ice cubes and wet towels. In the foam box, on the same day, use a single-sided blade to cut the scion into a length of 2.0cm-2.5cm, keep the scion with one leaf and one bud, cut off 1 / 2 of each leaf, and cut off from the 0.3cm-0.5cm above the leaf bud of the scion , the lower end of the leaf bud remains 1.6cm-2.0cm long, and then straightly and obliquely pulls a long section with a length of 1.6cm-2.0cm from the 0.3cm-0.5cm below the bud base. The xylem can be seen slightly on the long section, and the pith can be seen at the base , and then cut a 20-30-degree horse-ear-shaped short section on the back of the long section; select a common Camellia oleifera tree with a smooth surface, no pests and dis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com