Virtual scanning and ranging matching-based AGV laser SLAM method
A virtual scanning and laser technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, non-electric variable control, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of filtering, estimation stability and positioning accuracy cannot be absolutely guaranteed, and it is difficult to meet the application requirements of industrial AGV robots, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Embodiment 1: The SLAM method based on virtual scanning and ranging matching in the present invention is used for offline mapping, and the specific implementation process is as follows.
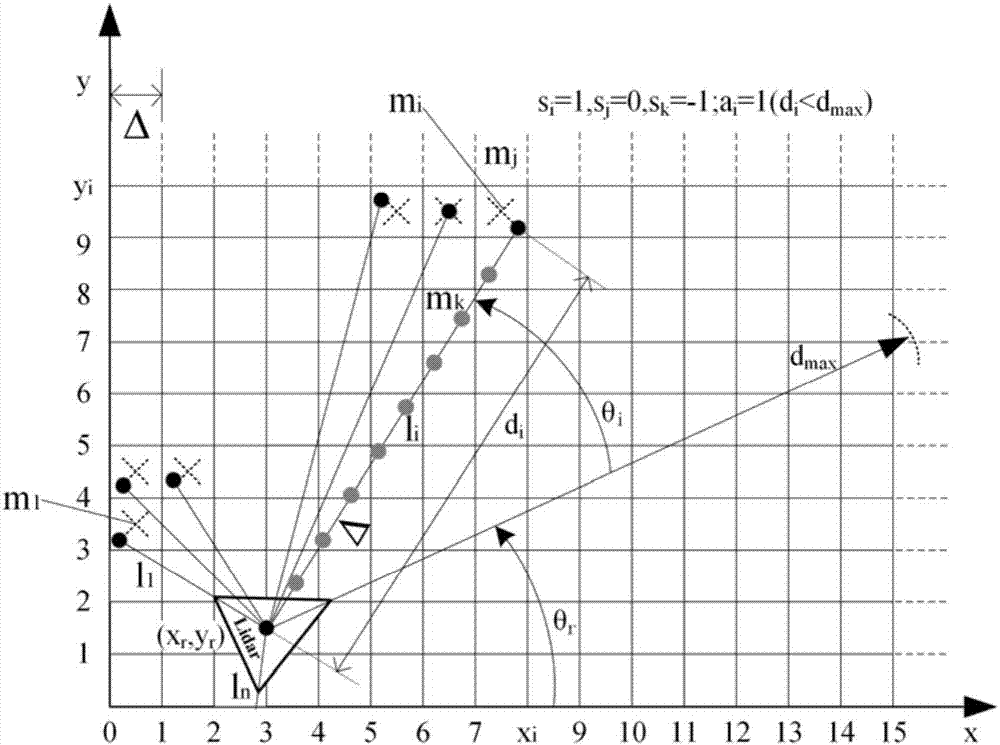
[0051] Step 1: Use remote control or other manual operation methods to control the AGV robot to walk in the working environment, and the laser radar collects and saves all moments (t 0 to t end ) ranging information {d 1 , d 2 ,...,d n}|t 0 、{d 1 , d 2 ,...,d n}|t 1 ,...,{d 1 , d 2 ,...,d n}|t end .
[0052] Step 2: Using appropriate data format and files, define the grid map M shown in formula (1), and initialize it.
[0053] Step 3: From t 0 start time to t end At the end moment, use the ranging information to build a map, the steps are as follows.
[0054] Step 3.1: For the initial time t 0 , the initial pose of the lidar is known, according to formula (2) {d 1 , d 2 ,...,d n}|t 0 Convert to L t0 , and then according to formula (3) L t0 Mapped to the grid map ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Embodiment 2: After offline mapping, the present invention is used for real-time positioning of an AGV robot with a map, and the specific implementation process is as follows.
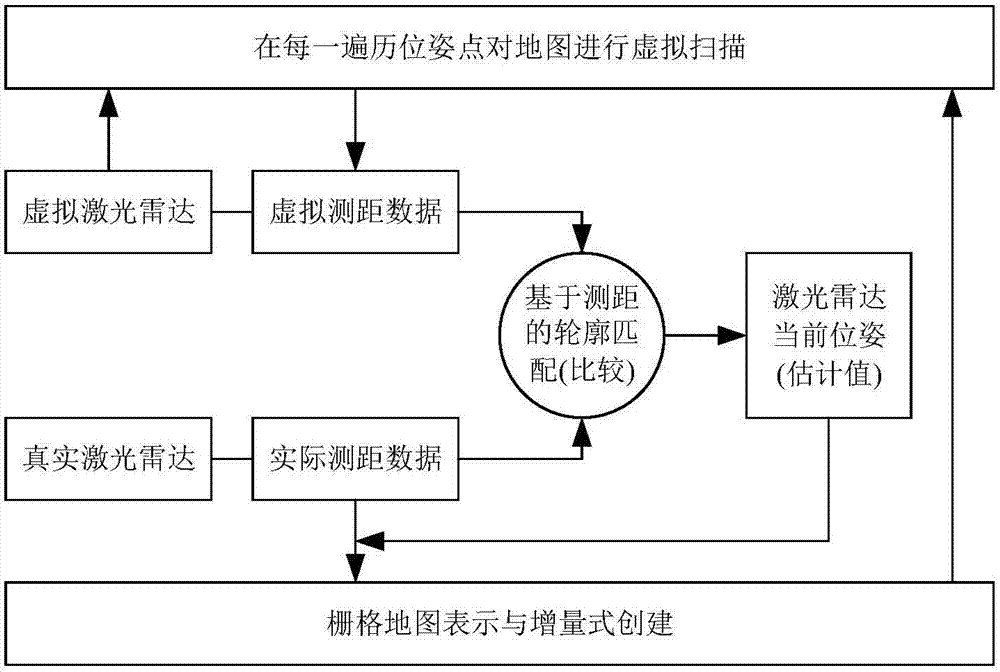
[0059] Step 1: At the current moment, the lidar obtains the ranging information {d 1 , d 2 ,...,d n}, according to formula (2) put {d 1 , d 2 ,...,d n} is converted to L.
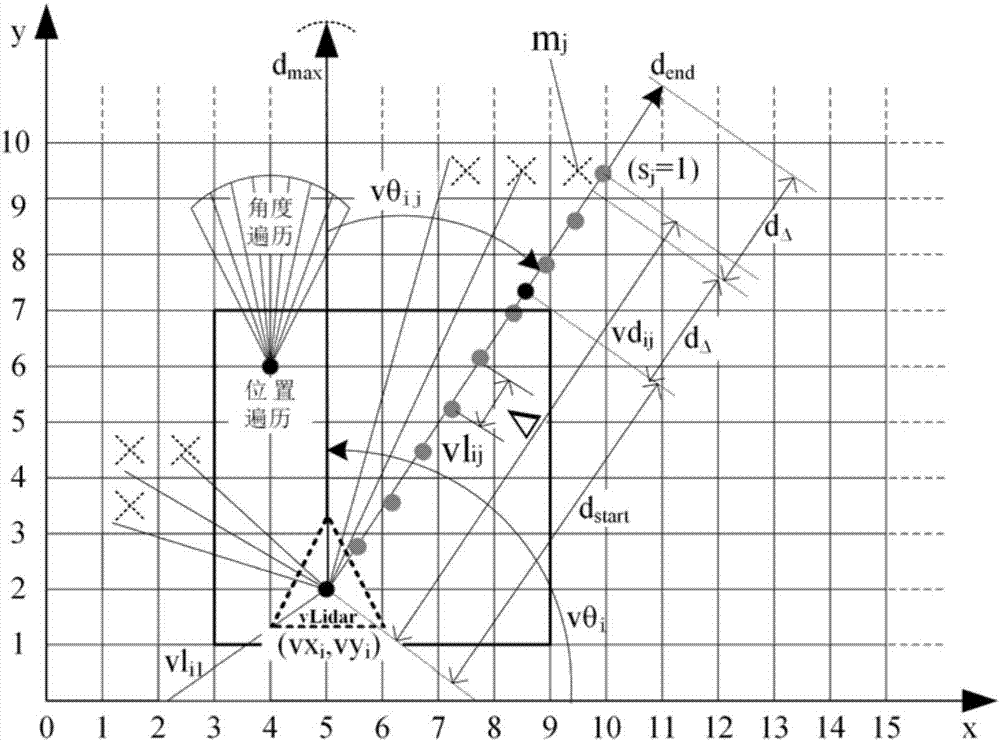
[0060] Step 2: For each pose in the traversal range Ω, simulate the laser radar to scan the map M (using multi-GPU parallel processing and advancing ranging algorithm, each GPU corresponds to a laser scanning direction), and obtain virtual scanning data VSs( Ω)={L 1 , L 2 ,...,L i ,...,L K}.
[0061] Step 3: Put the data VSs(Ω)={L 1 , L 2 ,...,L i ,...,L K} is compared with L, find out the virtual scanning data L* closest to L according to formula (5);
[0062] Step 4: According to L* and formula (6), obtain the estimated value of the current position and orientation of the lidar (that is, positioning).
Embodiment 3
[0063] Embodiment 3: The SLAM method based on virtual scanning and ranging matching in the present invention is directly used for real-time concurrent mapping and positioning, and the specific implementation process is as follows.
[0064] Step 1: Adopt the appropriate data format and file, define the grid map M shown in formula (1), and initialize it.
[0065] Step 2: For the initial time t 0 , the initial pose of the lidar is known, according to formula (2) the ranging {d 1 , d 2 ,...,d n}|t 0 Convert to L t0 , and then according to formula (3) L t0Mapped to the grid map M;
[0066] Step 3: At the next current moment, the lidar obtains the ranging information {d 1 , d 2 ,...,d n}, according to formula (2) put {d 1 , d 2 ,...,d n} is converted to L.
[0067] Step 4: For each pose in the traversal range Ω, simulate the lidar to scan the map M (using multi-GPU parallel processing and advancing ranging algorithm, each GPU corresponds to a laser scanning direction), ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com