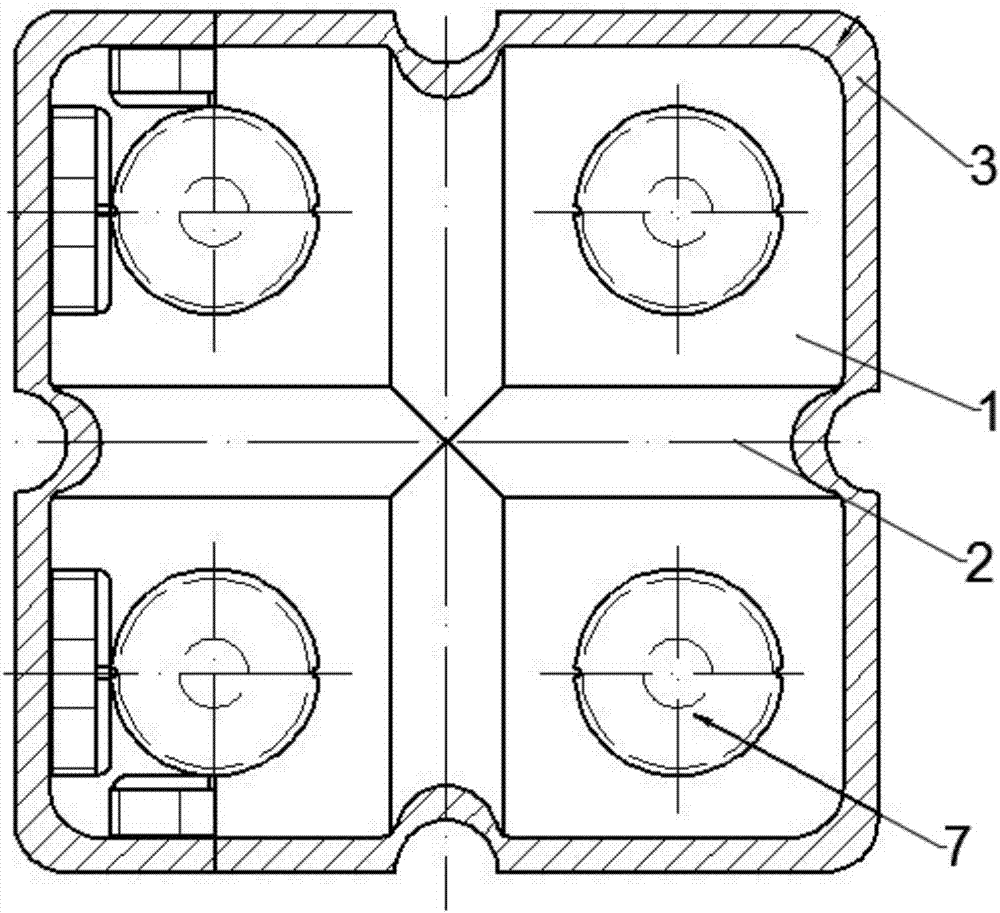
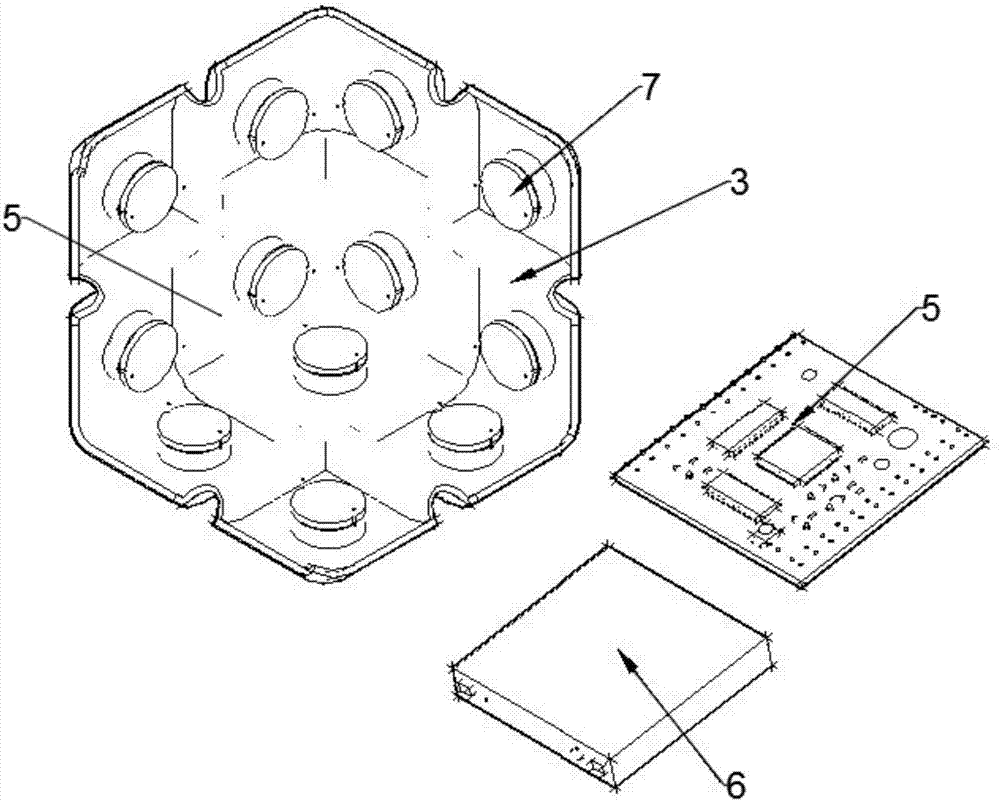
Combined mobile robot
A mobile robot and combined technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve the problems of poor component compatibility and narrow application range, and achieve the effects of saving use costs, great compatibility, and improving operation and maintenance efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] One of the basic movement modes of combined robots, translation:
[0036] Take two modules as an example ( Figure 6 ). The two modules are arranged side by side, and the direction of the intersection line between their contact surface and the ground is the direction in which the combined robot can translate. First a module is needed to fix its position. like Figure 6 ①, Module A turns on the four electromagnets (lower-9, 10, 11, 12) at the bottom of the module to fix it on the metal plate, and module B does not fix it. At the same time, module A turns on the two electromagnets "Up-2" and "Down-2", and B turns on the two electromagnets "Up-5" and "Down-5", so that the two modules enter the initial state of movement. like Figure 6 ②, module B turns on the two electromagnets "Up-6" and "Down-6", and module A turns on the two electromagnets "Up-2" and "Down-2". Under the action of the magnetic force, module B moves along the X-axis Direction produces movement. The...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The second basic movement mode of the combined robot is rotation:
[0039] Take two modules as an example ( Figure 7 ). The main purpose of the rotation is to rotate the direction of the intersection line between the contact surfaces of the two modules and the ground. First a module is needed to fix its position. Such as Figure 7 ①, Module A turns on the four electromagnets (lower-9, 10, 11, 12) at the bottom of the module to fix it on the metal plate, and module B does not fix it. At the same time, module A turns on the two electromagnets "Up-2" and "Down-2", and module B turns on the two electromagnets "Up-5" and "Down-5", so that the two modules enter the initial state of rotation. Such as Figure 7 ②, module B turns on the two electromagnets "Up-6" and "Down-6", and module A turns on the two electromagnets "Up-2" and "Down-2". Under the action of magnetic force, module B moves to the X axis direction to move. The movement distance is half the side length of...
Embodiment 3
[0041] The third basic movement mode of the combined robot is climbing:
[0042] Take two modules as an example ( Figure 8 ). The purpose of climbing is to move one module over another. First a module is needed to fix its position. Such as Figure 8 ①, Module A turns on the four electromagnets (lower-9, 10, 11, 12) at the bottom of the module to fix it on the metal plate, and module B does not fix it. At the same time, individual A turns on the two electromagnets "Shang-1" and "Shang-2", and module B turns on the two electromagnets "Shang-5" and "Shang-6", so that the two modules enter the initial climbing state. Such as Figure 8 ② Module B turns on the two electromagnets "Down-5" and "Down-6", and module A turns on the two electromagnets "Up-1" and "Up-2". Under the action of magnetic force, module B moves towards the Z axis up in the positive direction. The rise distance is half the side length of the module. Such as Figure 8 ③ Module A turns on the two electroma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com