Method for identifying maize haploids
A haploid, corn technology, applied in the directions of botanical equipment and methods, applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as applicability limitations, and achieve the effect of simplifying the identification steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Embodiment 1, the preparation of hybrid population
[0046] 1. Preparation of DH series
[0047] 1. Maize inbred line Qi 319 (female parent) was crossed with corn inbred line Chang 7-2 (male parent) to obtain hybrid offspring (grain).
[0048] 2. The hybrid progeny (plant) obtained in step 1 is used as the female parent, and is crossed with the induced line CAU5 as the male parent to obtain the hybrid progeny (grain).
[0049] 3. Select pseudo-haploids from the hybrid offspring (grains) obtained in step 2, and perform haploid doubling to obtain 107 DH lines. Named successively as DH series 1 to DH series 107.
[0050] 2. Preparation of Hybrid Population A
[0051] Each DH line obtained in step 1 is used as the female parent, and the induced line CHOI3 is used as the male parent to perform hybridization to obtain hybrid offspring (grains). 30-40 pseudo-haploids and n1 (n1=10 or 0) pseudo-diploids were randomly selected from the hybrid offspring (grain) obtained from ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2, establishing a model to identify haploids by collecting infrared spectra
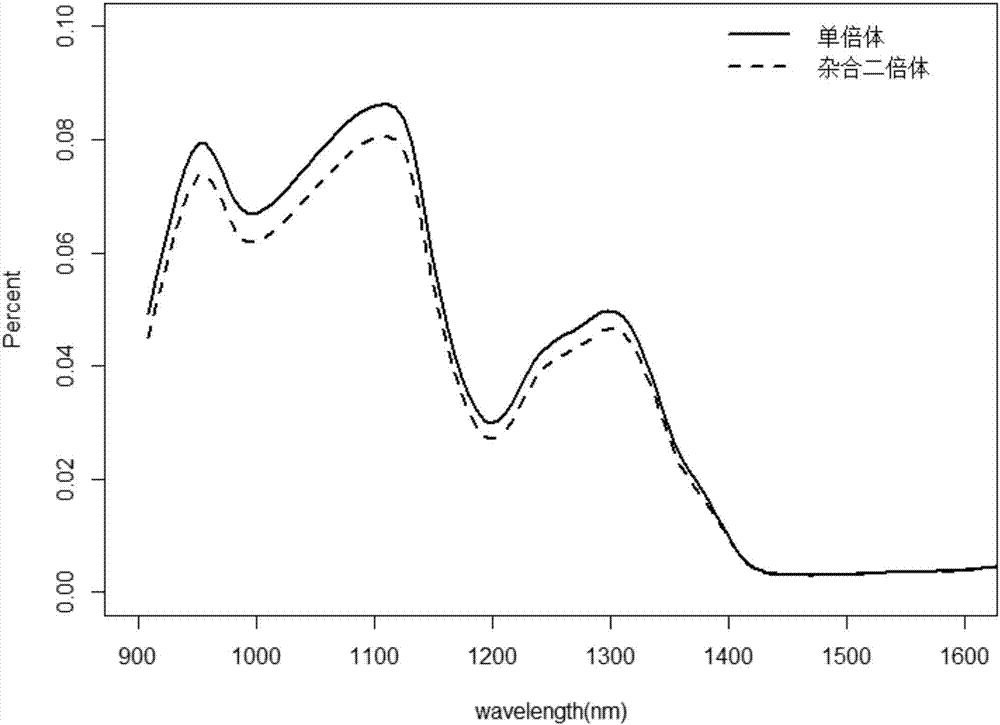
[0064] 1. Grain near-infrared transmission spectrum acquisition
[0065] Each grain in the hybrid population A prepared in Example 1, the hybrid population B prepared in Example 1, and the hybrid population C prepared in Example 1 was respectively subjected to near-infrared transmission spectrum scanning (the embryo surface of the grain faces the light source, and the light source is 3 cm away from the spectrometer ). The spectrometer is a micro spectrometer MicroNIR1700 produced by JDSU Company, the spectral range is 950-1600nm, and the single measurement time is 1s. Micro spectrometer MicroNIR1700 collects near-infrared transmission spectrum absorption values at 125 specific wavelengths in the spectral range 950-1600nm.
[0066] 2. Identification of pseudo-haploid and pseudo-diploid authenticity
[0067] After step 1 is completed, each seed in the hybrid population A prepared...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com