Wind turbine rotor blade
A technology of rotor blades and wind energy equipment, which is applied to the wake of rotor blades and the field of rotor blades of wind energy equipment, and can solve the problems of wind energy equipment output power loss, large wake, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
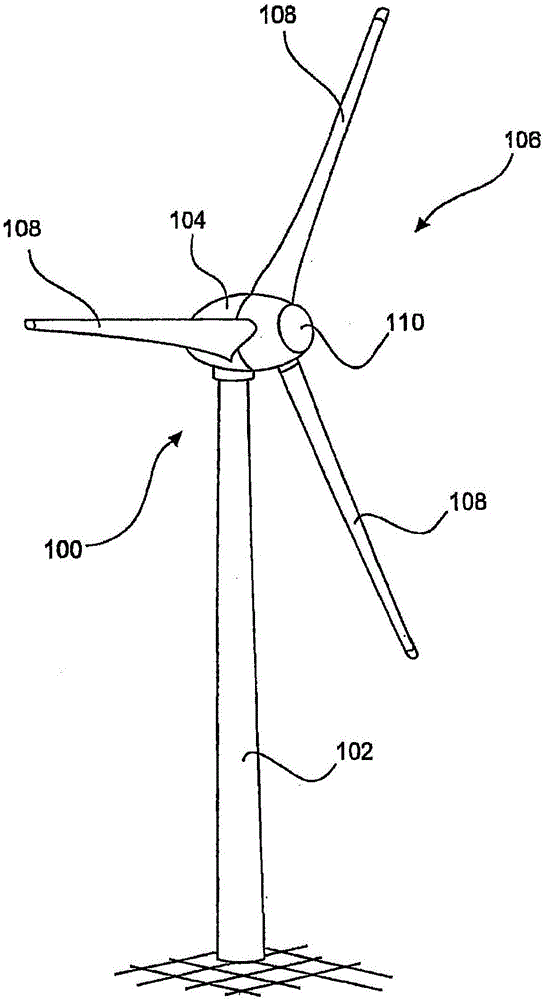
[0037] figure 1 A wind energy installation 100 is shown with a tower 102 and a nacelle 104 . A rotor 106 with three rotor blades 108 and a spinner 110 is arranged on the nacelle 104 . In operation, the rotor 106 is brought into rotational motion by the wind to drive a generator in the nacelle 104 .
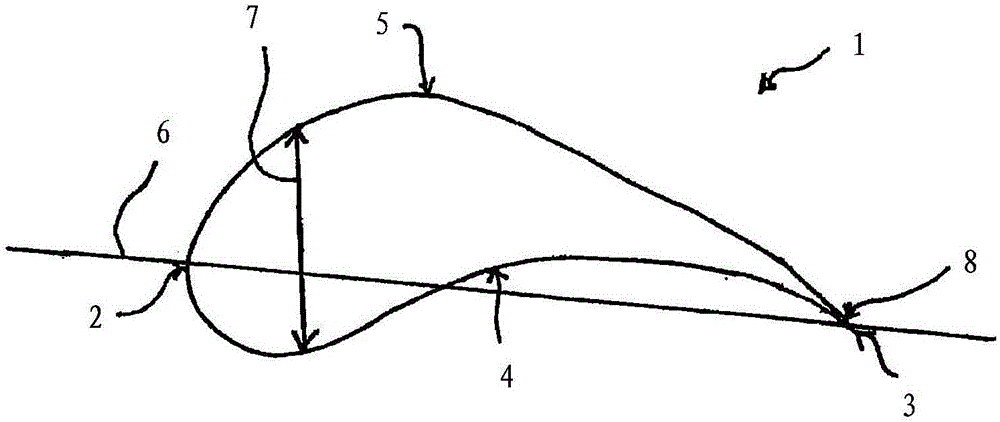
[0038] figure 2 A cross-section through an airfoil 1 of a rotor blade of a wind energy installation according to the prior art is shown. This cross section here has a leading edge 2 and a trailing edge 3 . The lower side 4 and the upper side 5 meet each other at the trailing edge 3 . The trailing edge 3 tapers and flattens here. The trailing edge thickness 8 , ie the thickness of the airfoil 1 at the trailing edge 3 , is here approximately zero. The greatest airfoil thickness 7 of the airfoil 1 is arranged here towards the leading edge 2 . In addition, in figure 2 A chord 6 is shown in , which runs from the leading edge 2 towards the trailing edge 3 .
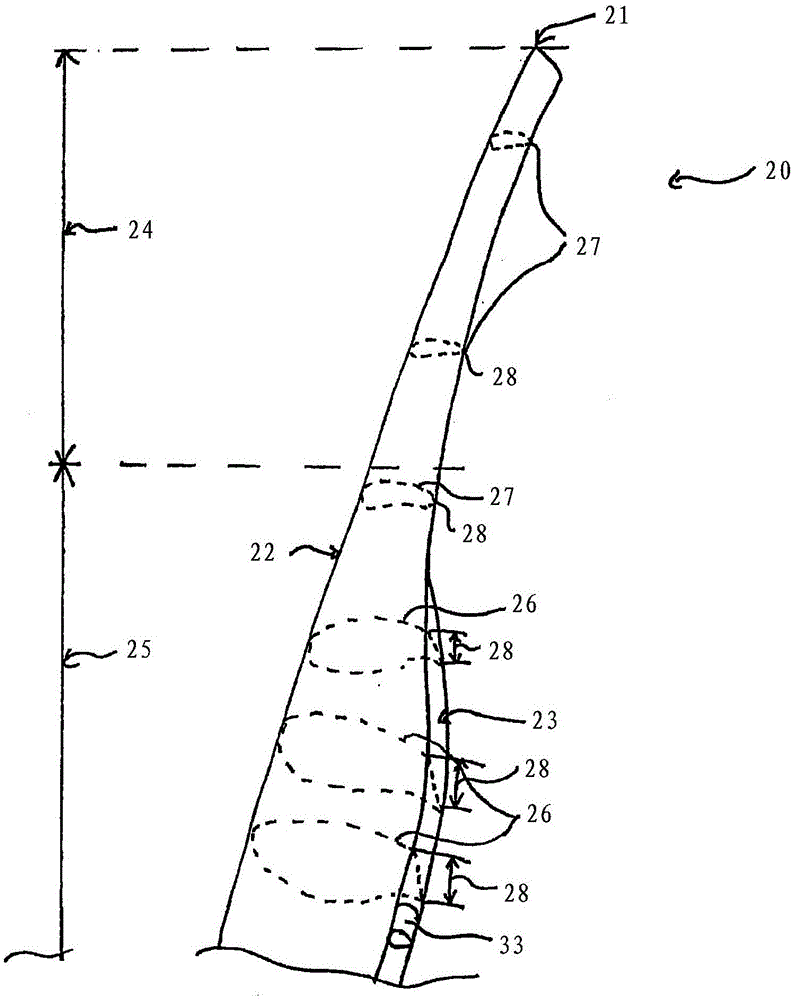
[0039] image 3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com