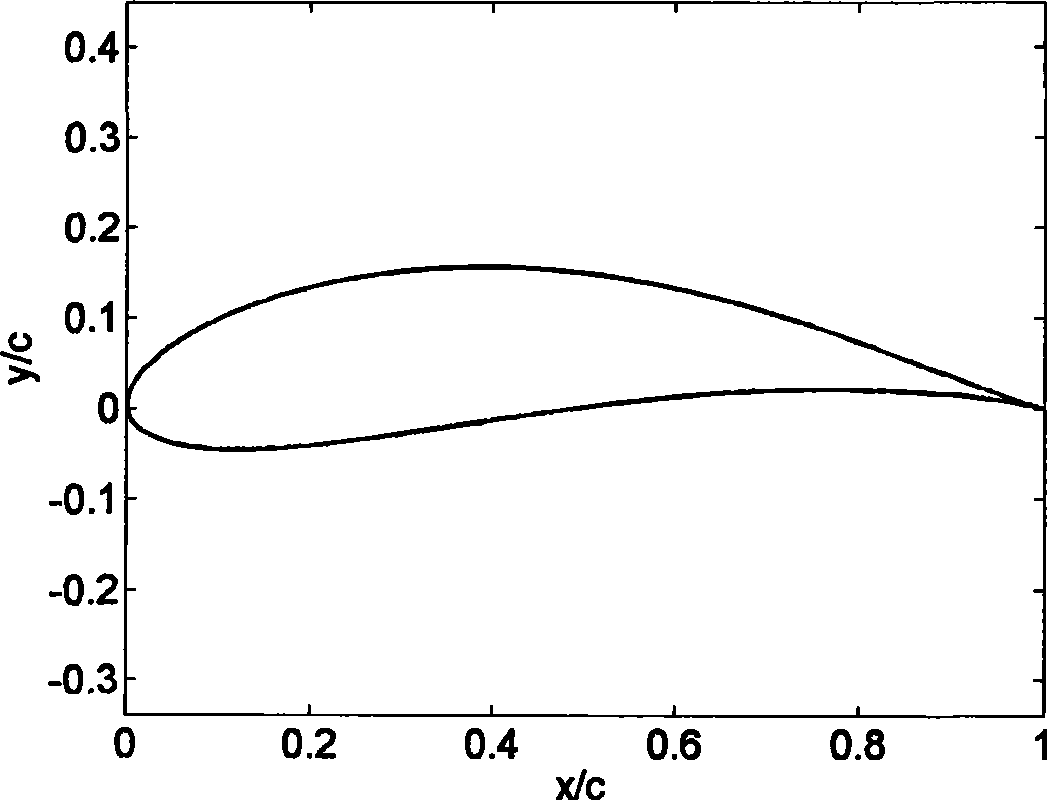
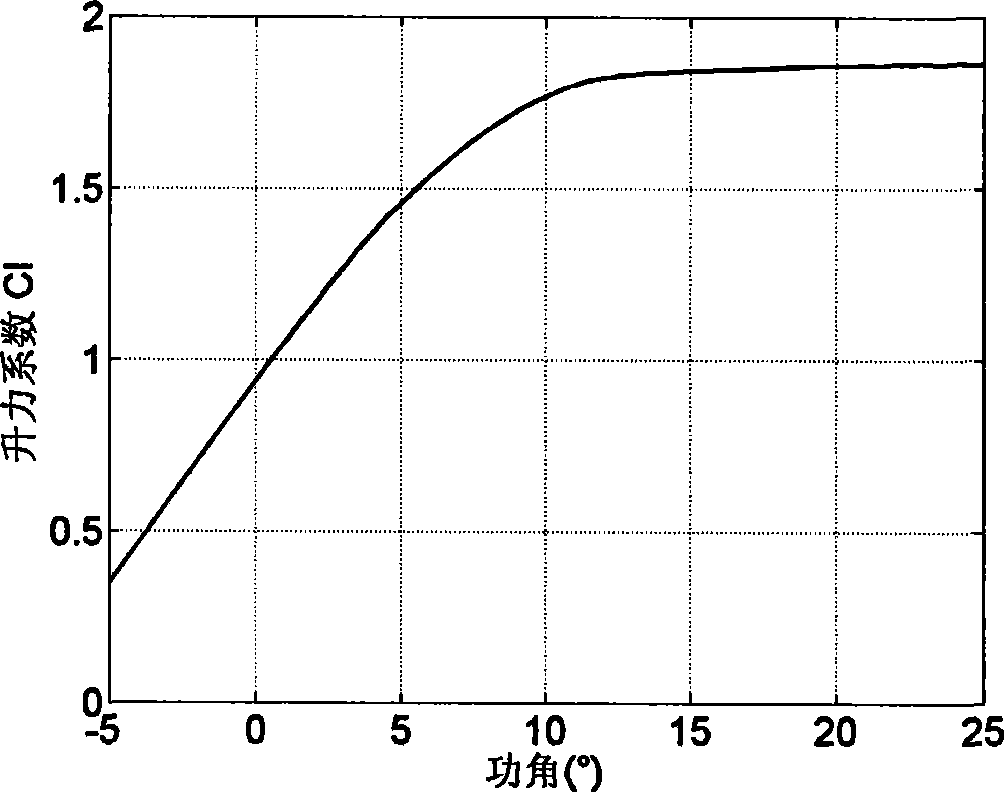
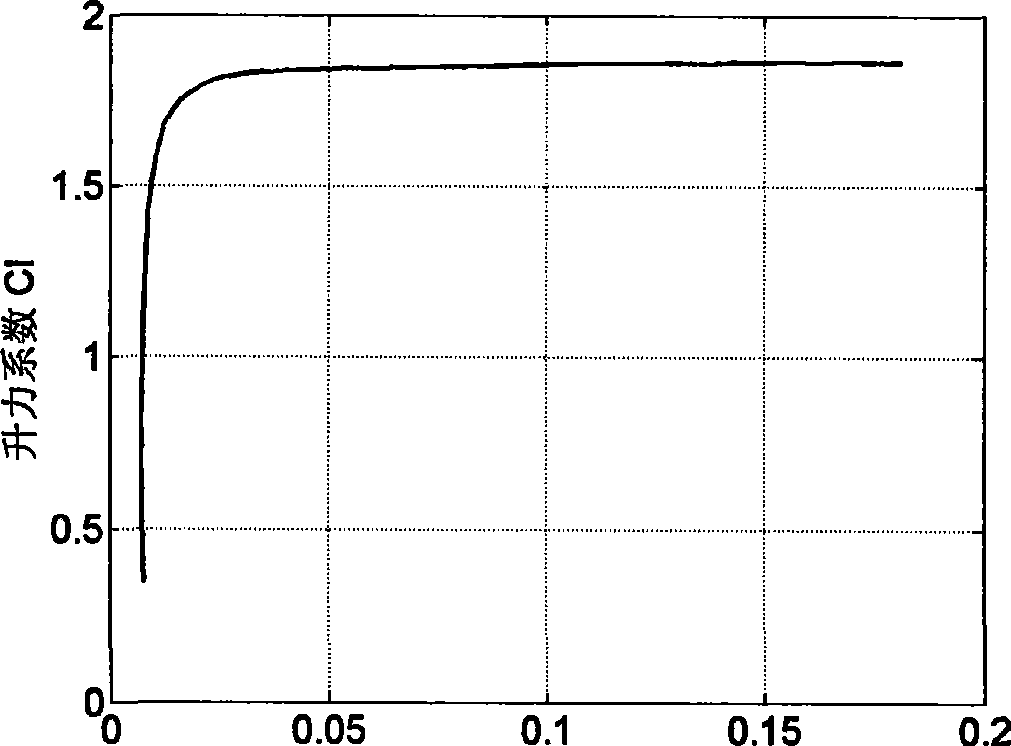
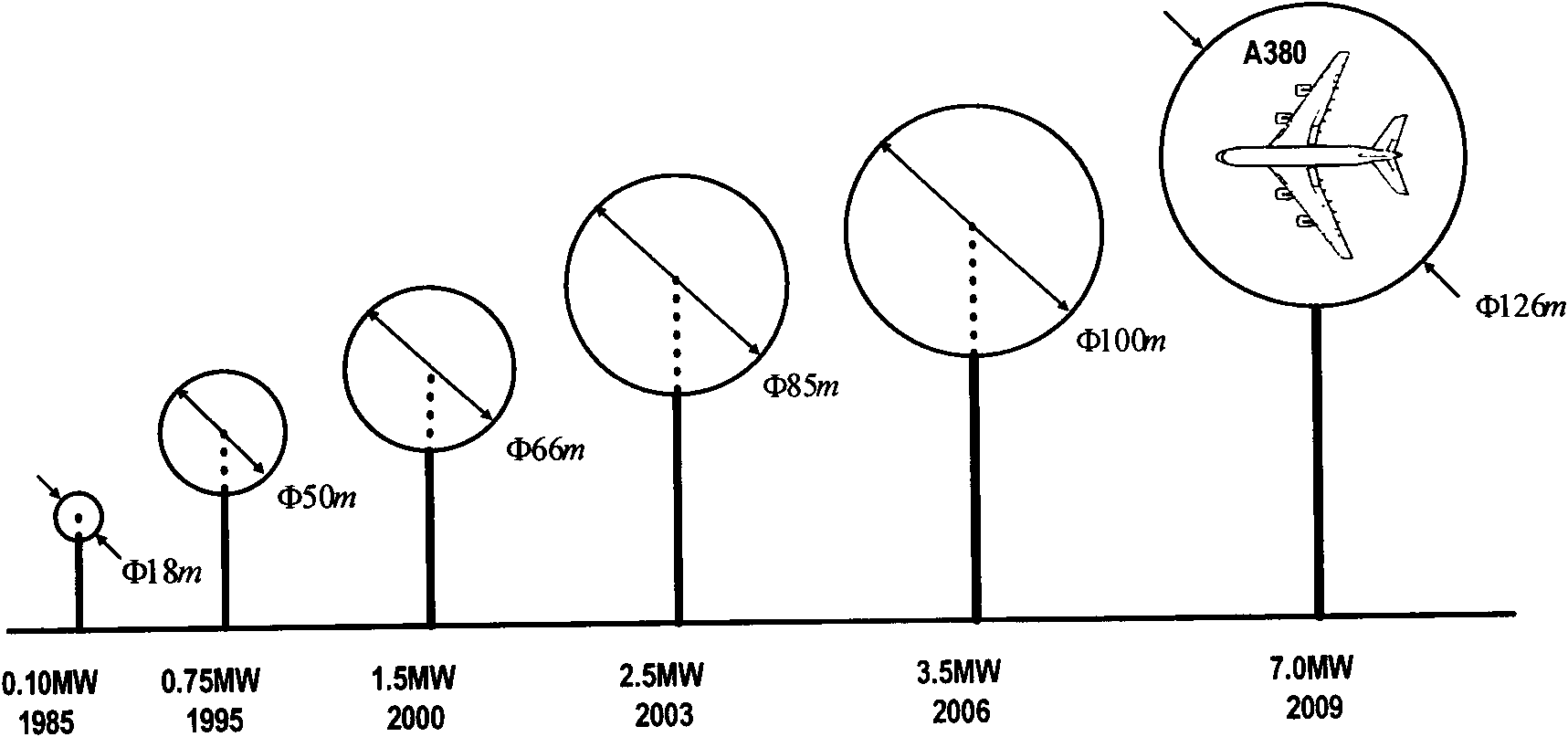
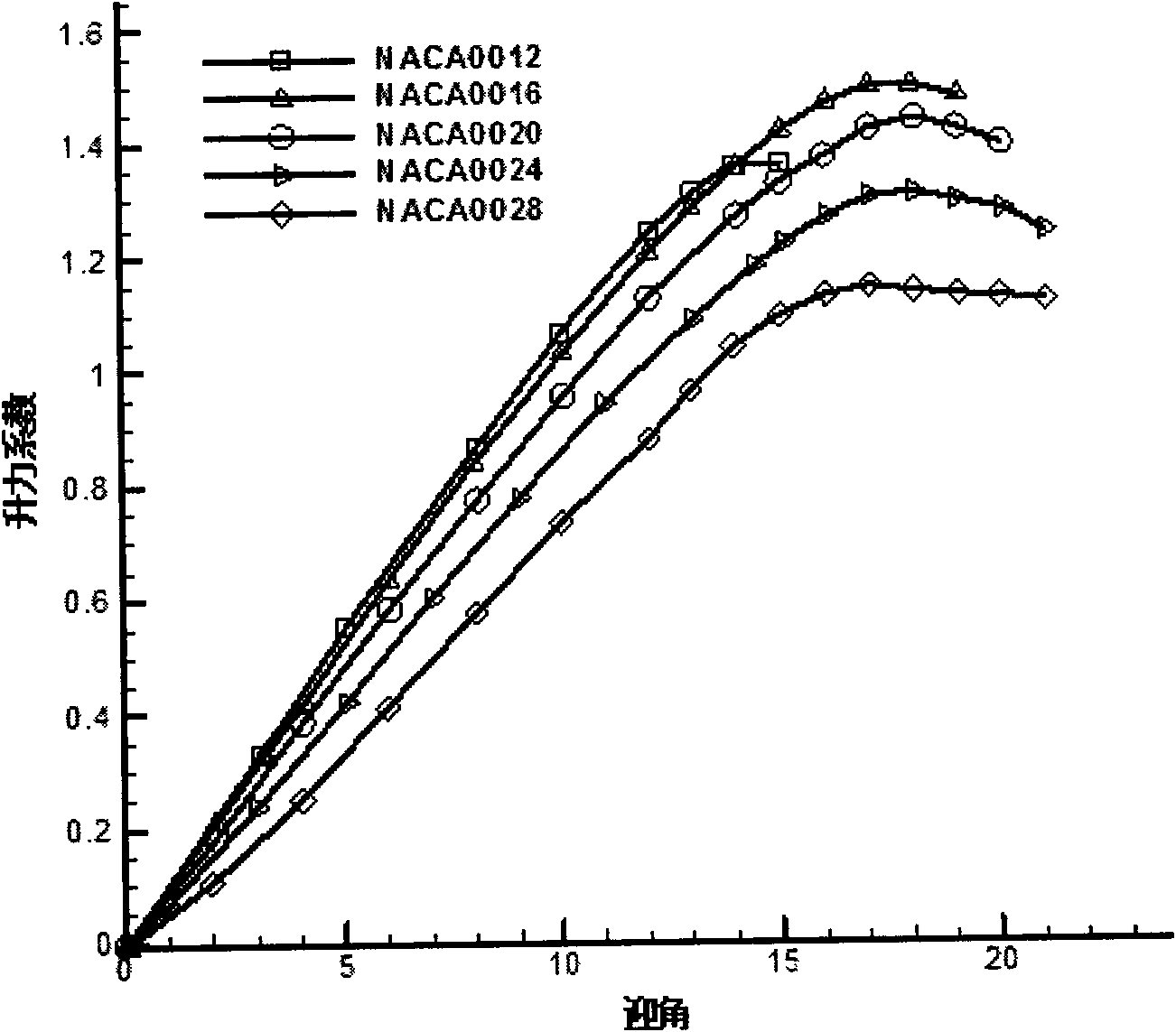
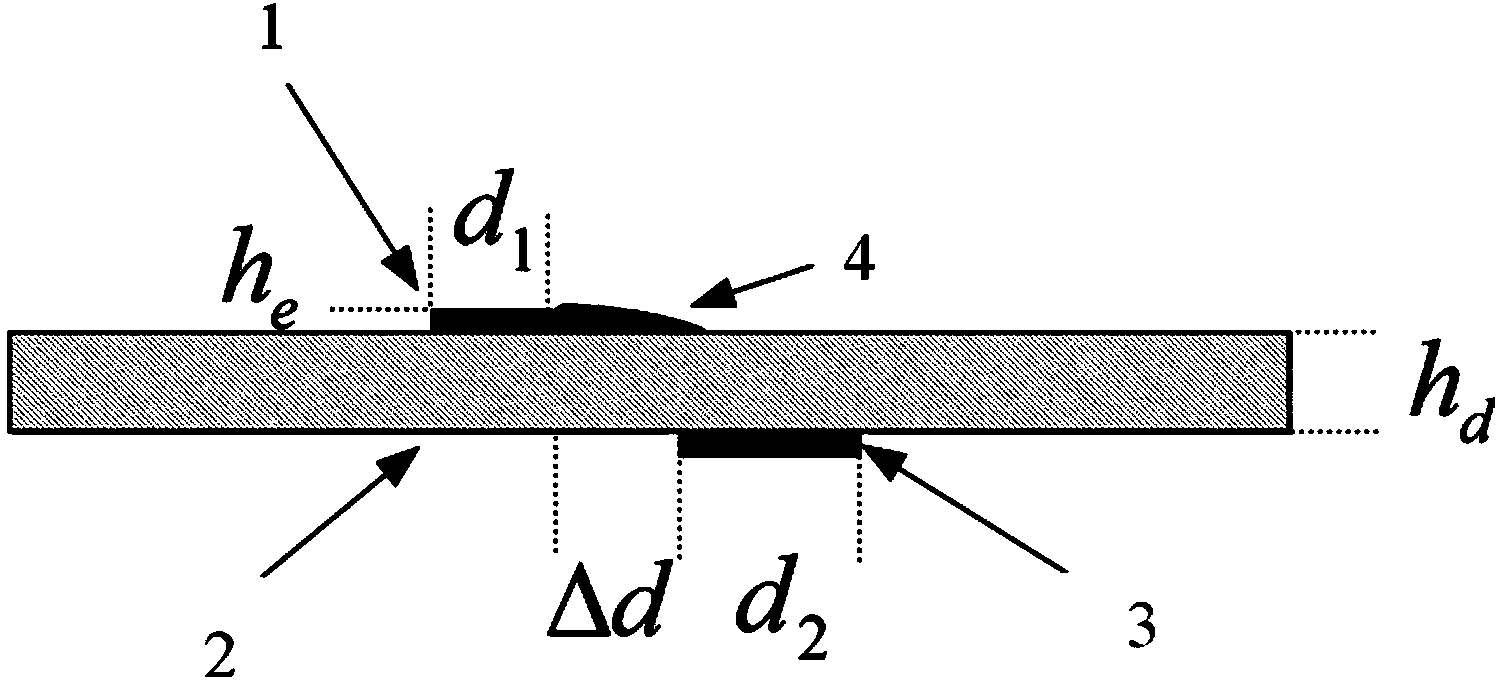
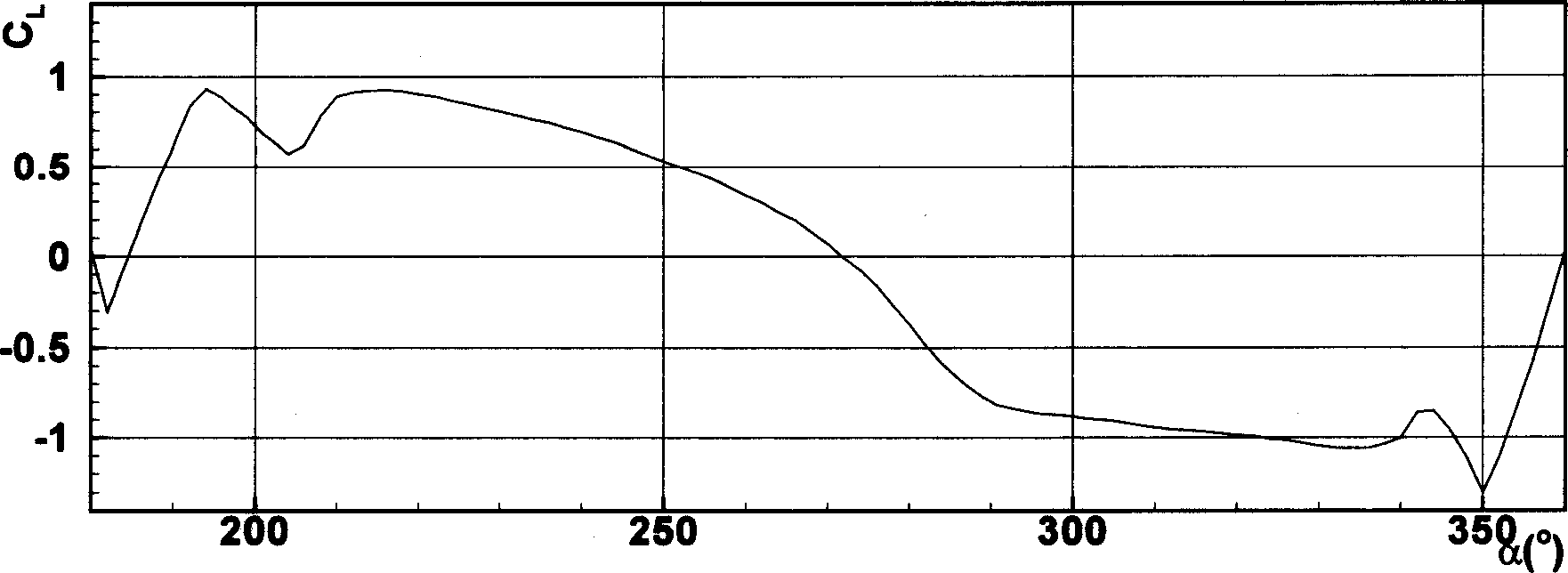
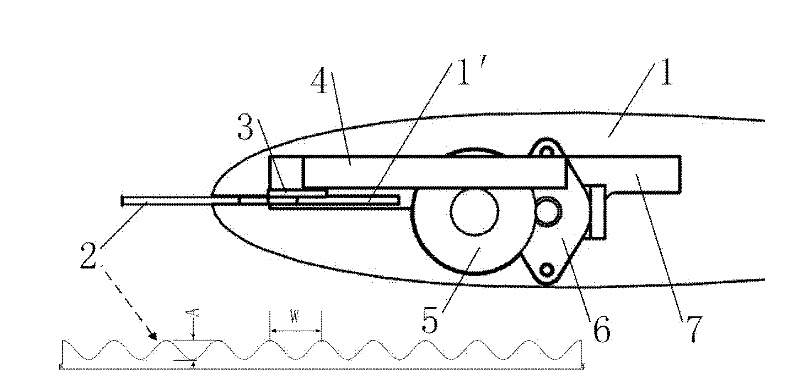
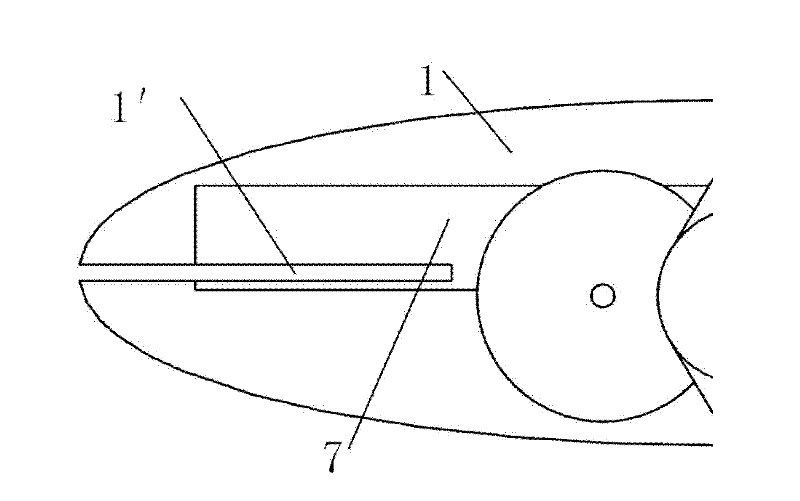
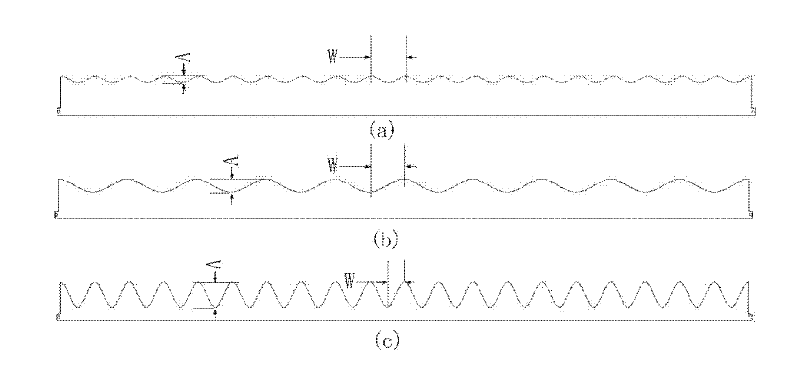
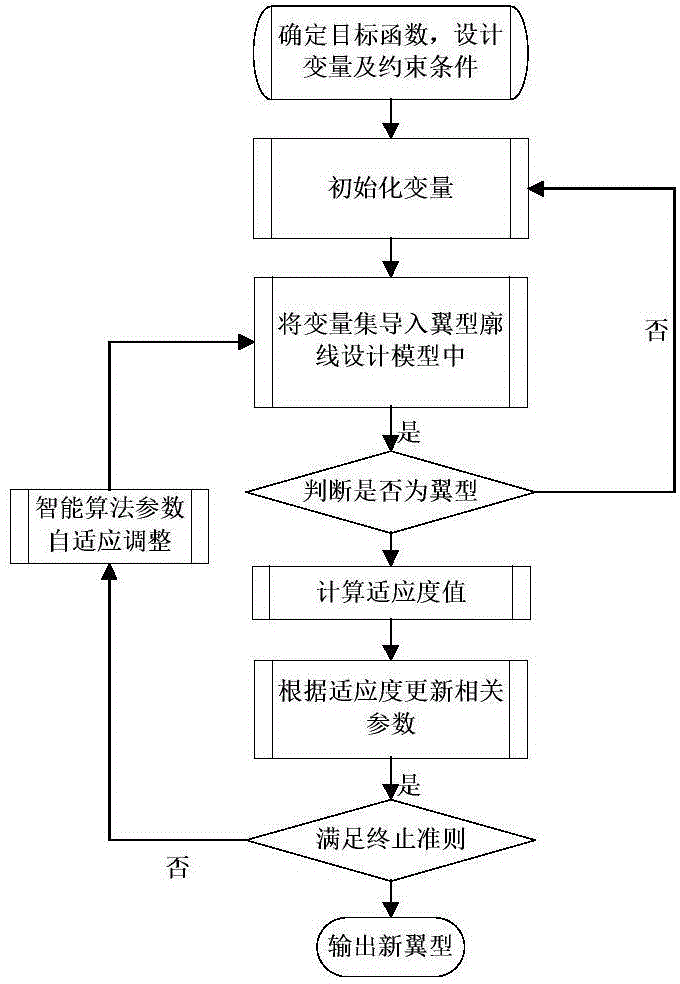
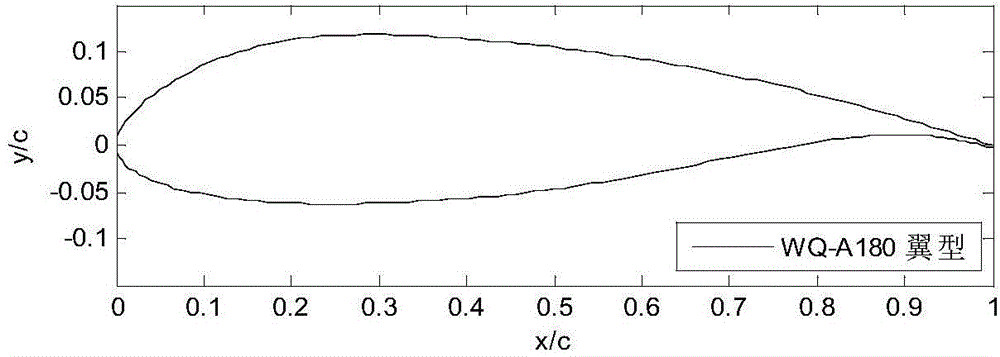
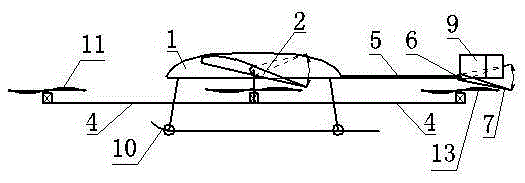
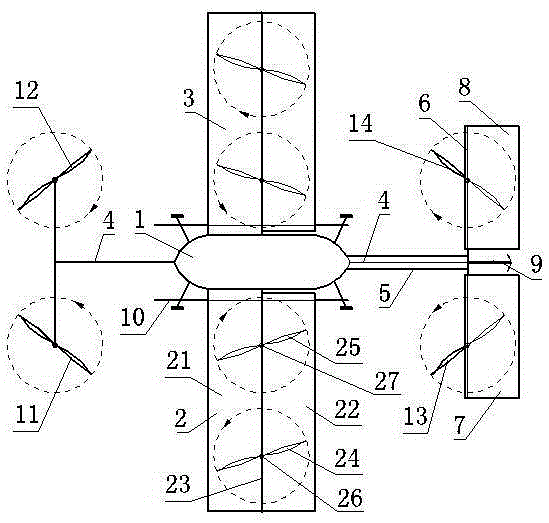
Patents
Literature
162results about How to "Increase lift coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
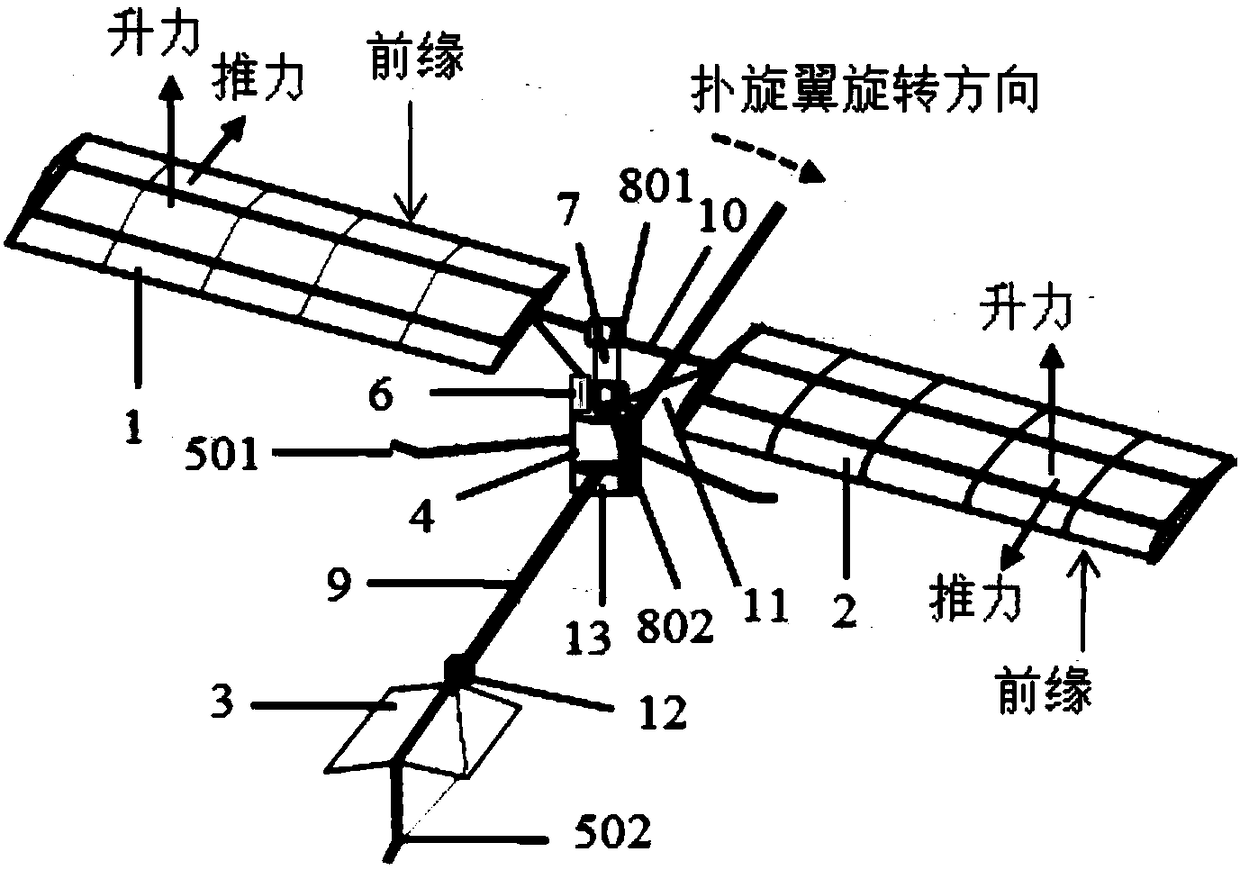
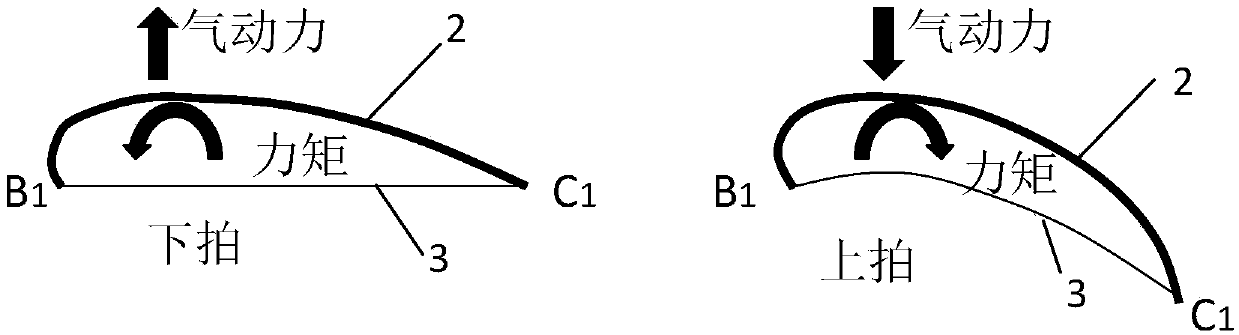
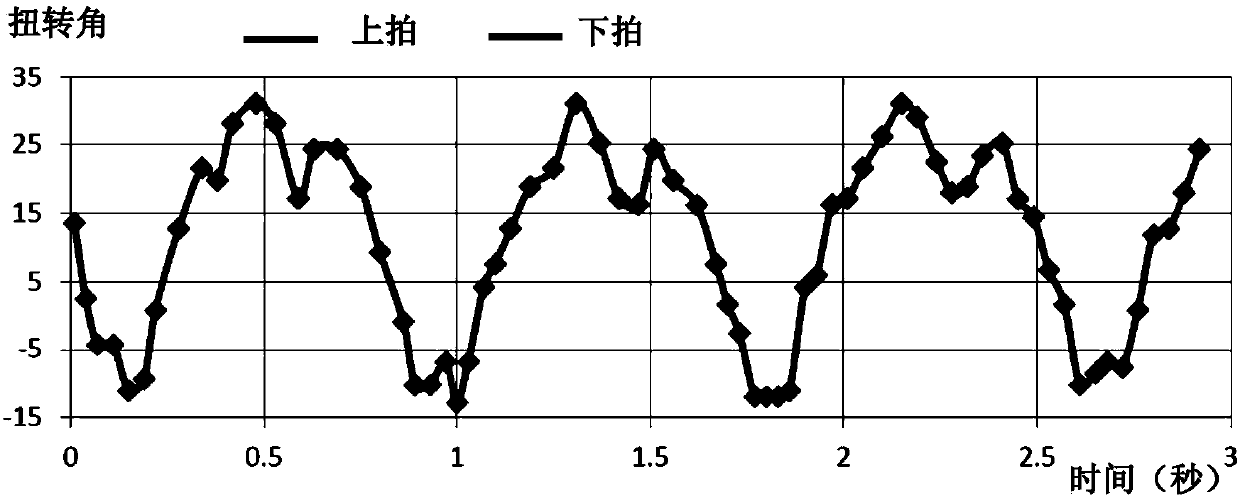
A bionic aircraft which realizes the conversion of a flapping rotor and a flapping wing flight mode based on a deformable wing
The invention discloses a bionic aircraft which realizes the conversion of a flapping rotor and a flapping wing flight mode based on a deformable wing, and belongs to the technical field of bionic aircraft design. When it is in vertical take-off, landing and hovering, it is a flapping rotor flight mode, and its structure is characterized by that the flapping wings on both sides are mounted in an axisymmetric manner, that is, the airfoils on both sides are antisymmetrical; When in forward flight or gliding, the flapping wing or fixed wing flight mode is characterized by symmetrical mounting ofthe flapping wing on both sides in a fixed wing symmetrical manner, i.e., symmetrical wing profiles on both sides. At that same time, an elastic bow beam is adopt, In the structural design of deformable wing rib composed of chord and multi-bar mechanism, when the shape of deformable wing is changed, by rotating the tie rod installed at the root of wing and the cable connecting each wing rib, the multi-bar mechanism is pulled to force the connected bow beam to produce the elastic deformation required, that is, the overall structure of the airfoil is kept unchanged, but the leading edge and thetrailing edge of the deformable wing are interchanged. The invention simplifies the driving mechanism and the integral configuration of the aircraft, and remarkably improves the aerodynamic efficiencyand the lift coefficient.
Owner:陕西斯凯迪物联科技有限公司
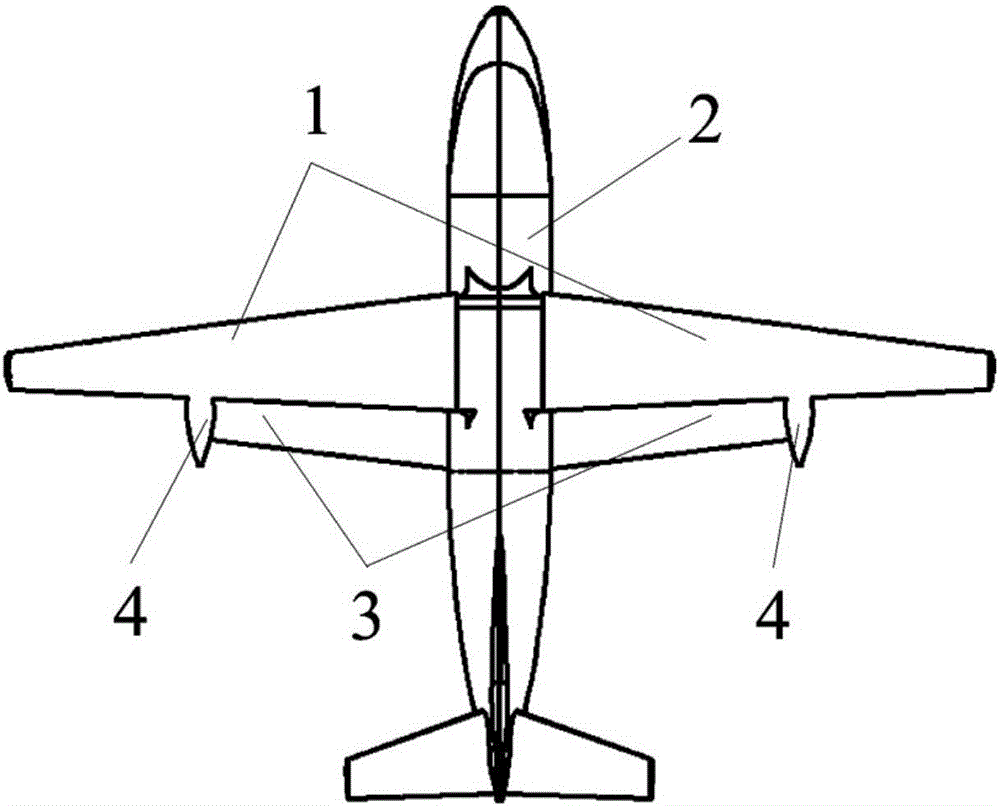
Vertical takeoff and landing unmanned aerial vehicle with foldable fixed wings based on dual-duct fan power system
ActiveCN107176286AImprove aerodynamic performanceBarrier formationPropellersRemote controlled aircraftLow speedTrailing edge
The invention discloses a vertical takeoff and landing unmanned aerial vehicle with foldable fixed wings based on a dual-duct fan power system. A dual-duct fan power system which is horizontally arranged at the tail of the body of the unmanned aerial vehicle in a tail-driving arrangement is adopted, so that lifting force for vertical takeoff and landing and thrust for horizontal flying are provided for an aircraft; a control surface which is arranged at the exit of each duct in a deflected manner is used for providing vector thrust, so that quick attitude change is realized; wings adopt a folding wing configuration, when the aircraft vertically takes off and lands / flies at a low speed, the wings are folded to decrease the frontal area of cross wind, and when the aircraft flies horizontally, the wings are unfolded to obtain large lifting force; and combined optimization of ducts and the wings is adopted, the wings are arranged in a specific duct air flow region, the duct suction generates a Coanda effect at a wing edge, so that the properties of the wings are improved. Multi-mold flight tasks such as vertical takeoff and landing, high-speed cruise, and the like of the aircraft are realized; the vertical takeoff and landing aircraft is high in aerodynamic efficiency during hanging in the air / flying at a low speed; and the vertical takeoff and landing unmanned aerial vehicle is high in anti-disturbance capacity during takeoff and landing / hanging in the air. The vertical takeoff and landing unmanned aerial vehicle is low in energy consumption, small in noise and high in safe reliability.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Shape memory spring driven hinder margin camber variable wing
InactiveCN101503113AImprove pressure distributionIncrease lift coefficientWing adjustmentsEngineeringMetal sheet
The invention provides a wing with changeable trailing edge camber driven by a shape memory spring, relating to a wing with a changeable trailing edge camber, and aiming at the problems of traditional airplanes that a mechanism is complex and heavy, airflow breakaway is quite early and aerodynamic efficiency is low. The front end face and the back end face of an upper metal plate are fixedly connected with the front end faces of a connecting plate and the trailing edge; the front end face and the back end face of the lower metal plate are fixedly connected with the front end face of the connecting plate and the trailing edge; the same side surface of the upper metal plate and the lower metal plate are fixed with an upper prop stay and a lower prop stay; the two ends of a first shape memory spring are fixedly connected with a fixed plate and the upper metal plate; the two ends of a second shape memory spring are fixedly connected with the front end faces of the upper prop stay and the trailing edge; the two ends of a third shape memory spring are fixedly connected with the fixed plate and the lower metal plate; and the two ends of a fourth shape memory spring are fixedly connected with the front end faces of the lower prop stay and the trailing edge. The invention has the advantages of light weight, simple structure and high aerodynamic efficiency.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Aerofoil with high lift-drag ratio
InactiveCN101458735AIncrease output powerReduce power generation costsSpecial data processing applicationsInformation technology support systemEngineeringHigh lift
The invention relates to an airfoil model for general airfoil profile line shape design based on functional theory, comprising: establishing a functional integrated equation for airfoil profile line, establishing an optimization design model for the integrated equation, according to required target function, selecting different equation term number and coefficients to complete target airfoil designing. Comparing the inventive airfoil model of high lift-drag ratio for general airfoil profile lines based on functional theory with traditional wind turbine airfoil, in normal working power and angle ranges, the airfoil model has high lift coefficient, high lift-drag ratio and later stalling, while the established profile line can express the advantages of general airfoil profile lines and realize the unachievable technical indexes of single profile line, thereby improving the output power and reducing the generation cost of wind turbines.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Wind machine blade airfoil profile capable of controlling flow stalling through standing vortex
InactiveCN102094769AReduce unsteady loadReduced risk of structural damageWind energy generationWind motor componentsTrailing edgeWinding machine
The invention relates to a wind machine blade airfoil profile capable of controlling flow stalling through standing vortex. An airfoil profile between a shaping starting point and an airfoil profile trailing edge point is modified, thus a concave pit is formed; the shaping starting point and the airfoil profile trailing edge point are connected through a straight line, a concave pit starting point and a concave ending point are connected by virtue of a 1 / 4 circular arc, and the concave ending point, a first transition point, a second transition point and the airfoil profile trailing edge point are connected through a B spline; and the airfoil profile trailing edge is provided with a Gurney wing flap. According to the invention, the amplitude of the thickness reduction of the upper surface is slowed down to delay the separation of the flow field of the upper airfoil, vortex with a fixed position is formed by the air flow at the concave pit of the upper surface, under the action of the vortex, the separation of the upper surface of the airfoil can be controlled effectively, the irregular falling of separated vortex is avoided, and vortex lifting force is formed at the upper surface of the airfoil, and the stalling of the airfoil is slowed down, so that the stalling incidence of the airfoil is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
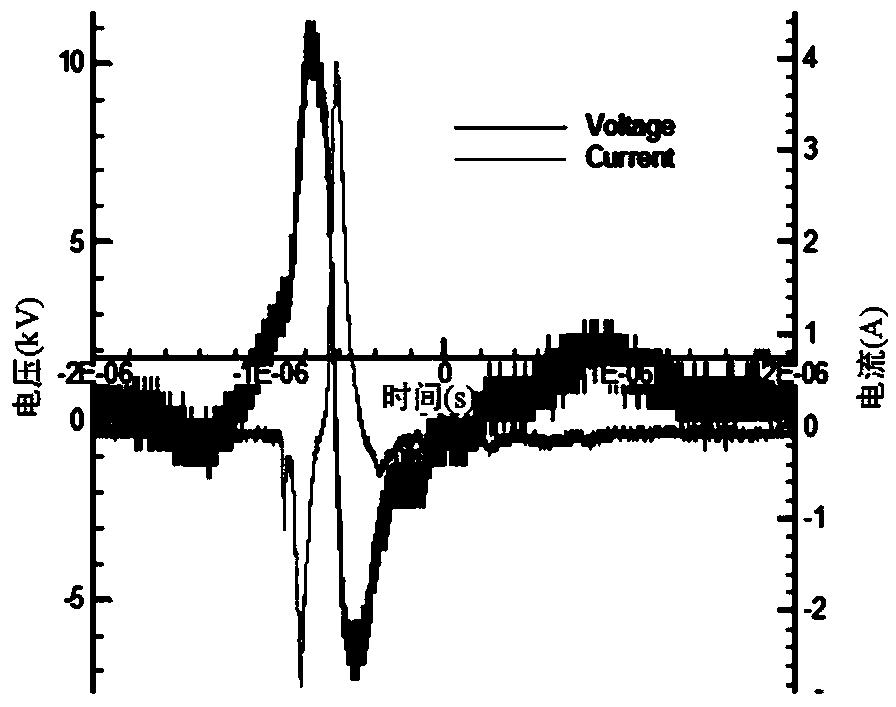
Method for controlling plasma flow of wing lift-rising apparatus
InactiveCN103523208AImprove the lift-to-drag ratioIncrease lift coefficientAir-flow influencersLeading edgeTrailing edge
The invention relates to a method for controlling plasma flow of wing lift-rising apparatus, and the technical scheme is characterized in that: plasma exciters are laid on the suction face of the leading edge slat, the suction face of the main wing trailing edge and the suction face of the trailing edge flap. The plasma exciter is composed of electrodes in asymmetric layout and separated by an insulating material, the electrode on the upper surface of the insulating material is connected with the high-voltage terminal of a pulse plasma power supply, and the electrode on lower surface is earthed. The laying positions of the plasma exciters are at the leading edge and the trailing edge of a separation point. When the leading edge slat and the trailing edge flat are deployed during the launching and the landing of an airplane, a signal of 'on' is emitted and the plasma exciters are turned on; and when the leading edge slat and the trailing edge flat are fold by the airplane, a signal of 'off' is emitted and the plasma exciters are turned off. The method helps to effectively control the flow separation of the suction faces of the leading edge slat, the main wing trailing edge and the trailing edge flap when the airplane is in a launching or landing state, substantially improving wing lift-drag ratio and maximum lift coefficient, and further improve the launching and landing weight of the airplane and shorten the running distance.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
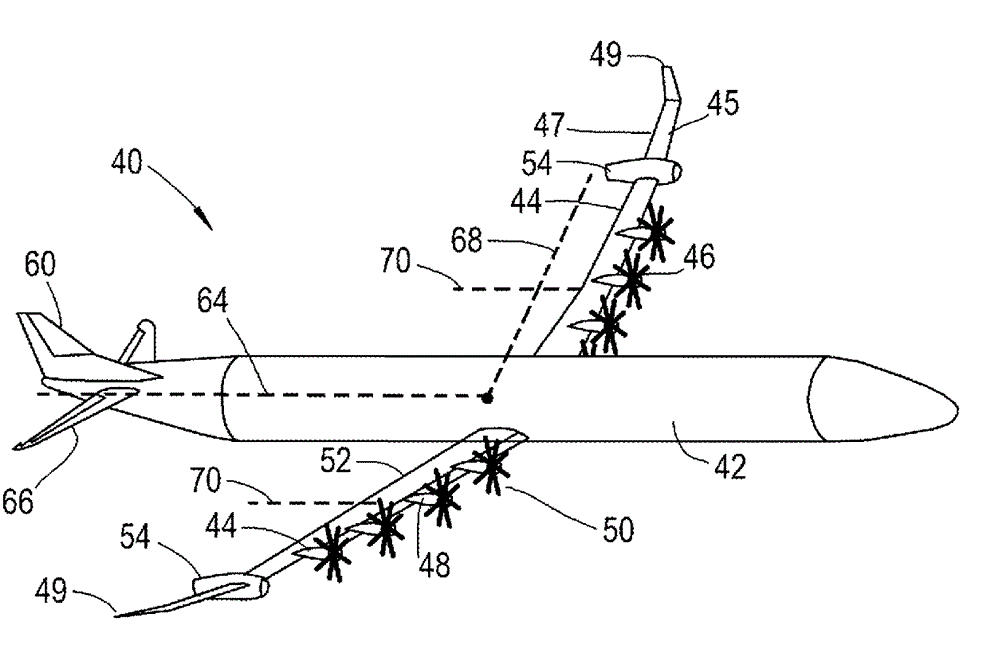
Aircraft
ActiveCN104670503AReduce loadImprove structural efficiencyPropellersGas turbine type power plantsLeading edgeCombustion
An aircraft (40). The aircraft (40) comprises a propulsion system comprising a pair of internal combustion engines (10) each driving an electrical power generator (56), each electrical power generator (56) being electrically coupled to a plurality of electrically driven propulsors (46). The propulsors (46) are located forward of a leading edge (45) of the wings (44) such that an airstream generated by the propulsors flows over the wings (44) in use. Each internal combustion engine (10) and electrical generator (56) is mounted on a respective wing (44) outboard of a centre of thrust (70) of the propulsors (46) on that wing (44).
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
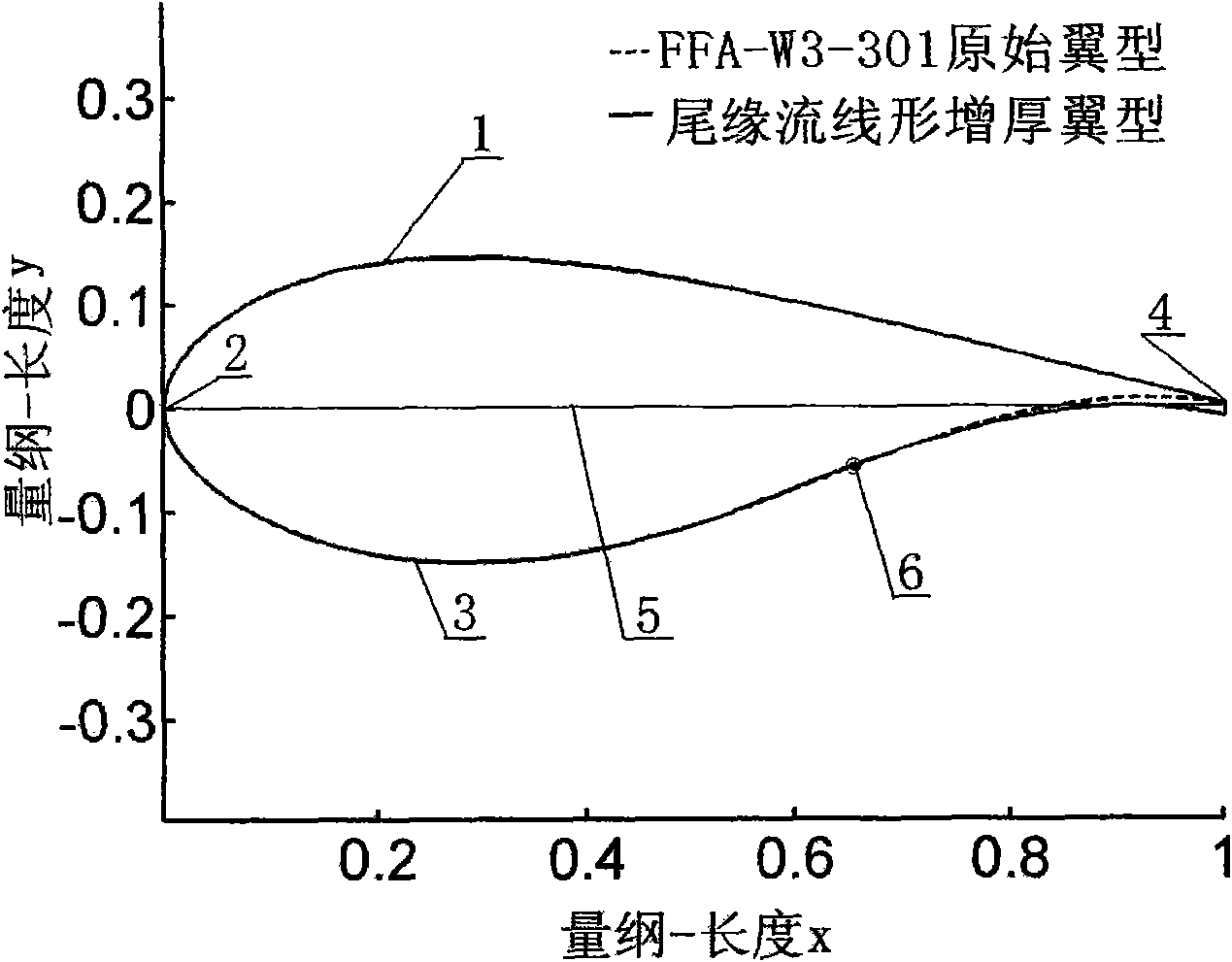
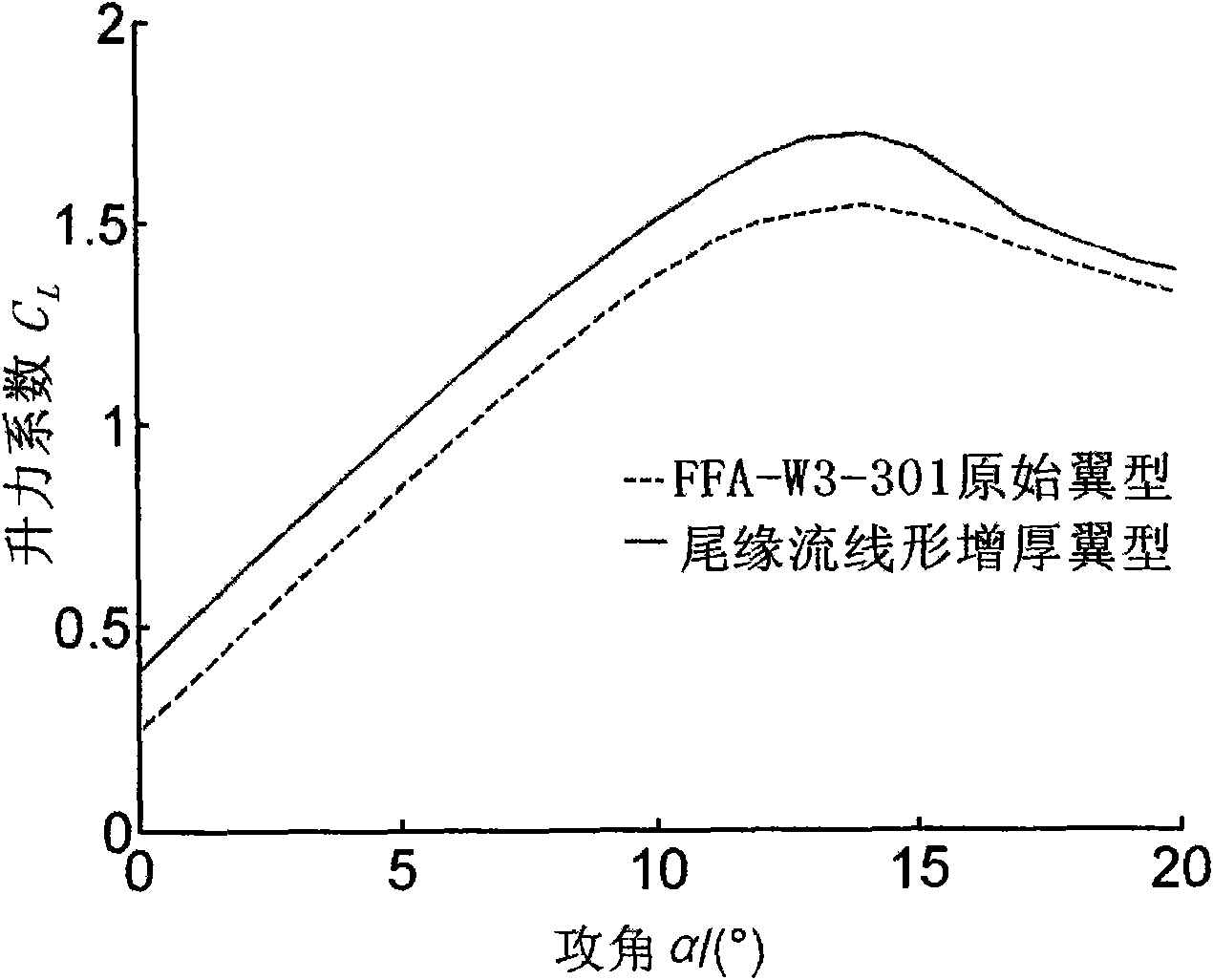
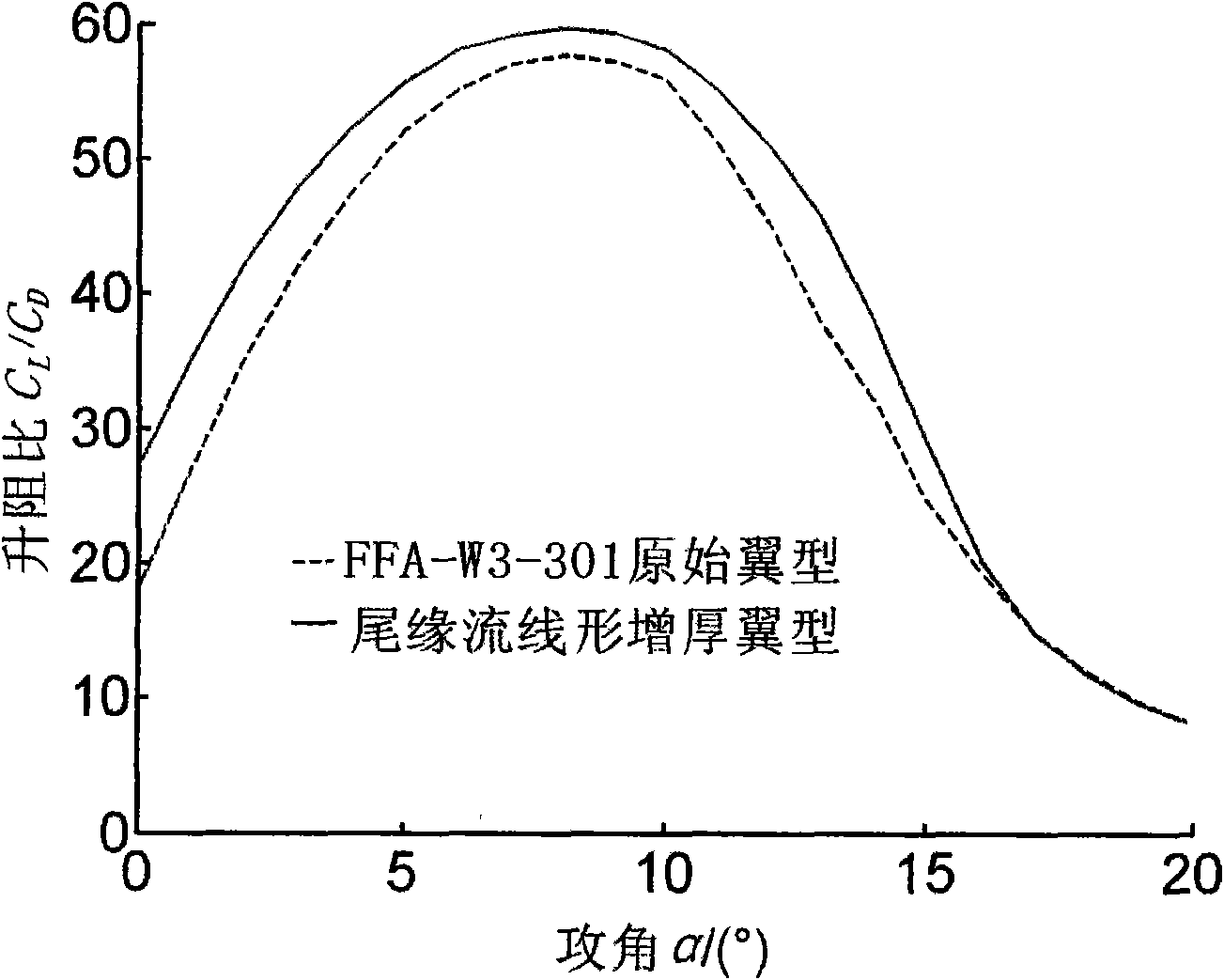
Method for carrying out streamline-form thickening on airfoil shape tailing edge
InactiveCN101615216AIncrease lift coefficientGuaranteed streamlined characteristicsMachines/enginesWind energy generationWinding machineEngineering
The invention discloses a method for carrying out streamline-form thickening on airfoil shape tailing edge, which is mainly applied to the improvement field of wind machine blades; the reformed airfoil shape designed by the method has better pneumatic performance than the original airfoil shape; in the proper functioning angle of attack range, not only the lift coefficient of the improved the airfoil shape is increased, but also the control method provided by the invention guarantees the streamline-form characteristics of the airfoil shape pressuring surface, thereby the resistance coefficient of the airfoil shape is very small, the airfoil shape has higher lift drag ratio, simultaneously, is later in stall, and has good social and economic values.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Variant stealth aircraft and variant method and application thereof
PendingCN110203372AIncrease lift coefficientImproved heading stabilityAircraft stabilisationMilitary adjustmentScattering cross-sectionHigh lift
The invention provides a variant stealth aircraft and a variant method and application thereof. According to stealth requirements, the aircraft is designed by adopting a force-lifting body edge-wing variable-configuration pneumatic layout scheme, and comprises two retractable full-motion canards and two deflectable full-motion empennages. The retractable full-motion canards can be retracted into amachine body during cruising of an aircraft or flying at a high speed, so that the scattering cross section of a radar is reduced, thus improving the invisibility. The deflectable full-motion empennages can be deflected to different angles in different flight states so as to serve as V-shaped tails, flat tails or ventral fins. Thus, transformation of the pneumatic layout of the aircraft is achieved, and the layout comprises a canard-type layout, a tail-free layout and a three-wing-surface layout. Through the switching of the three pneumatic layouts, the advantages of the three pneumatic layouts can be combined, thus better satisfying the requirements for the maneuverability and invisibility of the aircraft under different flight profiles and flight states. As a new-generation manned and unmanned aerial combat platform with high lift-drag ratio, high maneuverability and good invisibility, the variant stealth aircraft can be used for executing air dominant combat tasks.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method and device for enforcing canard spanwise pulse blowing indirect vortex control technology
The invention which aims at close-coupled canard type configuration aircrafts provides an efficient indirect vortex control method and a device thereof. Places over a canard leading edge and at a certain height from the canard surface are respectively symmetrically provided with a jet tube, nozzle directions of the jet tubes parallel to the canard leading edge, high-speed pulse jets are jetted through the nozzles to generate a fluid vortex ring so as to increase the intensity of canard leading edge vortex and increase the angle of attack of canard configuration during canard leading edge vortex breakdown, and beneficial interference of the canard leading edge vortex and wing leading edge vortex is utilized to generate an indirect vortex control effect so as to enhance the intensity of the wing leading edge vortex and delay wing leading edge vortex breakdown when the angle of attach is large, so the configuration lift of the canard configuration aircraft is improved, the stall angle of attack is increased; and simultaneously the pulse frequency and the pulse width of pulse blowing are controlled through a solenoid valve, so the air entrainment amount is reduced to realize high efficiency and energy saving.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Quiet urban air delivery system
ActiveUS11198519B1Manageable wing weightManageable ride qualityPropellersArresting gearElectric carsEmbedded system
A public transportation system combines a unique combination of components that includes interoperable electric-powered vehicles, facilities, hardware and software having specifications, standards, processes, capabilities, nomenclature, and concepts of operations that together include a concerted, comprehensive, multi-modal, future system for moving people and goods that is herein named Quiet Urban Air Delivery (QUAD) and in which uniquely-capable, ultra-quiet, one to six-seat, electrically-powered, autonomous aircraft (SkyQarts) fly sub-193 kilometer trips on precise trajectories with negligible control latency and perform extremely short take-offs and landings (ESTOL) with curved traffic patterns at a highly-distributed network of very small, airports (“SkyNests”) that themselves have standardized compatible facilities that interoperate with SkyQarts as well as with versatile, autonomous electric-powered payload carts (EPCs) and robotic delivery carts (RDCs) to provide safe, fast, on-demand, community-acceptable, environmentally friendly, high-capacity, affordable door-to-door delivery of both passengers and cargo across urban, suburban and rural settings across the globe.
Owner:SEELEY BRIEN AVEN
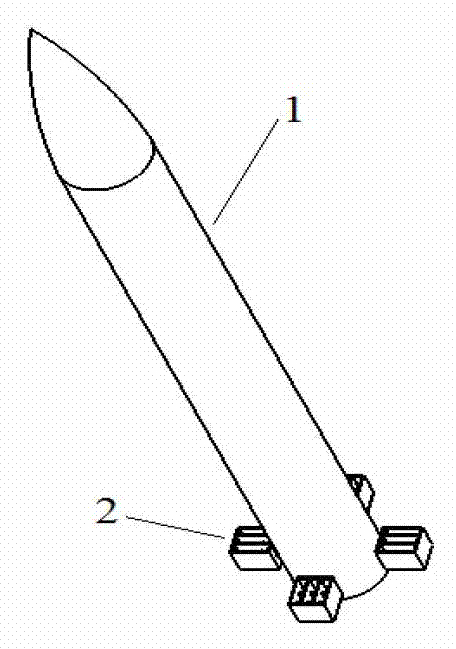
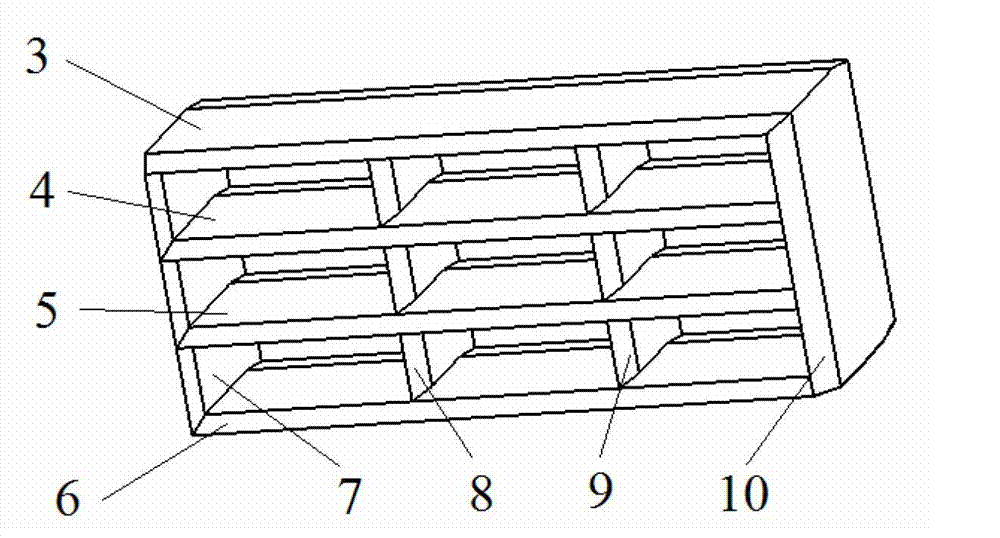
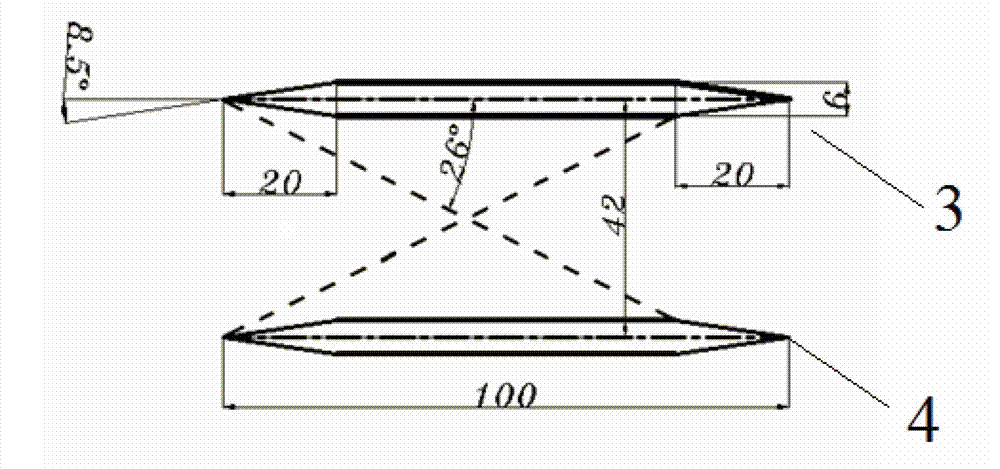
Grid fin of supersonic velocity guided missile
InactiveCN103162580AReduce the effect of shock-absorbing ideal interferenceReduce shock wave resistanceProjectilesShock waveEngineering
A grid fin of a supersonic velocity guided missile comprises spanwise clapboards and chordwise clapboards. An upper supper surface and a lower surface of two sides, in the length direction, of each spanwise clapboard are symmetrical wedge surfaces. A surface, located at a long edge of the front edge of the grid fin, of a fifth clapboard and an eighth clapboard is processed into a wedge surface, and the wedge surface is located on an outer surface of the grid fin. Two surfaces, located at the front edge of the grid fin, of long edges of a sixth clapboard and a seventh clapboard are both processed into wedge surfaces. Wedge surfaces of all the spanwise clapboards and the chordwise clapboards can effectively reduce interference effect from shock waves produced by the chordwise clapboards to reducing shock waves of the spanwise clapboards.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Air vehicle aerodynamic configuration with trailing edge supporting wing
ActiveCN105905277AImprove effectivenessHigh structural efficiencyAircraft stabilisationHeat reducing structuresVertical planeFlight vehicle
The invention discloses an air vehicle aerodynamic configuration with two trailing edge supporting wings. The supporting wings are installed below trailing edges of main wings at the two sides of a fuselage of an air vehicle. Wingtips of the supporting wings are connected to the middle parts of the trailing edges of the wings through connection sections. Wing roots of the supporting wings are connected to the fuselage through connection sections. The relative positions of the supporting wings and the main wings are reasonably designed. In a main wing cross section and a supporting wing cross section which are truncated by air flowing to a vertical plane in wingspans of the support wings upwardly during the flying process, the vertical distance between the centroids is a% of the chord length of the cross section of the main wing, wherein a is a constant value from 10 to 40; and meanwhile, the overlapping length of projections of the chord lines of the main wing cross section and the supporting wing cross section on a horizontal plane is b% of the chord length of the cross section of the main wing, wherein b is a constant value from 0 to 15. The aerodynamic configuration increases the total lift-drag ratio and achieves better aerodynamic performances, and also improves the rigidity of large-span-chord ratio wings and improves the total structural efficiency of the air vehicle.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Energy-saving fishtail flap type rudder
ActiveCN106184688AIncrease lift coefficientImprove maneuverabilitySteering ruddersAbsorbed energyPropeller
The invention relates to an energy-saving fishtail flap type rudder. The flap type rudder comprises a lifting bolt, an upper rudder bearing, an upper rudder bearing holder, a middle sleeve, a rudder stock, a lower rudder bearing, a bushing, a lower seal assembly and a main rudder blade. The flap type rudder is characterized in that the main rudder blade is divided into an upper part and a lower part from the central line of a corresponding propeller, the front end of the main rudder blade at the upper half part deviates towards one side relative to the horizontal central line of the main rudder blade, the front end of the main rudder blade at the lower half part deviates symmetrically towards the other side of the horizontal central line of the main rudder blade, a rectification cap is fixedly integrated at the front end of the main rudder blade and corresponds to the horizontal central line of the propeller in position; a tail wing is arranged at the rear part of the main rudder blade and connected with the main rudder blade through a hinging shaft, and the upper end of the tail wing is connected with the lower rudder bearing through a transmission mechanism for driving a flap to rotate. Compared with a conventional flap type rudder, the energy-saving fishtail flap type rudder has higher manipulation performance, has a cavitation bubble reduction function, can absorb energy of wake flow of the propeller and realizes an energy-saving effect.
Owner:WUXI DONGZHOU MARINE EQUIP CO LTD
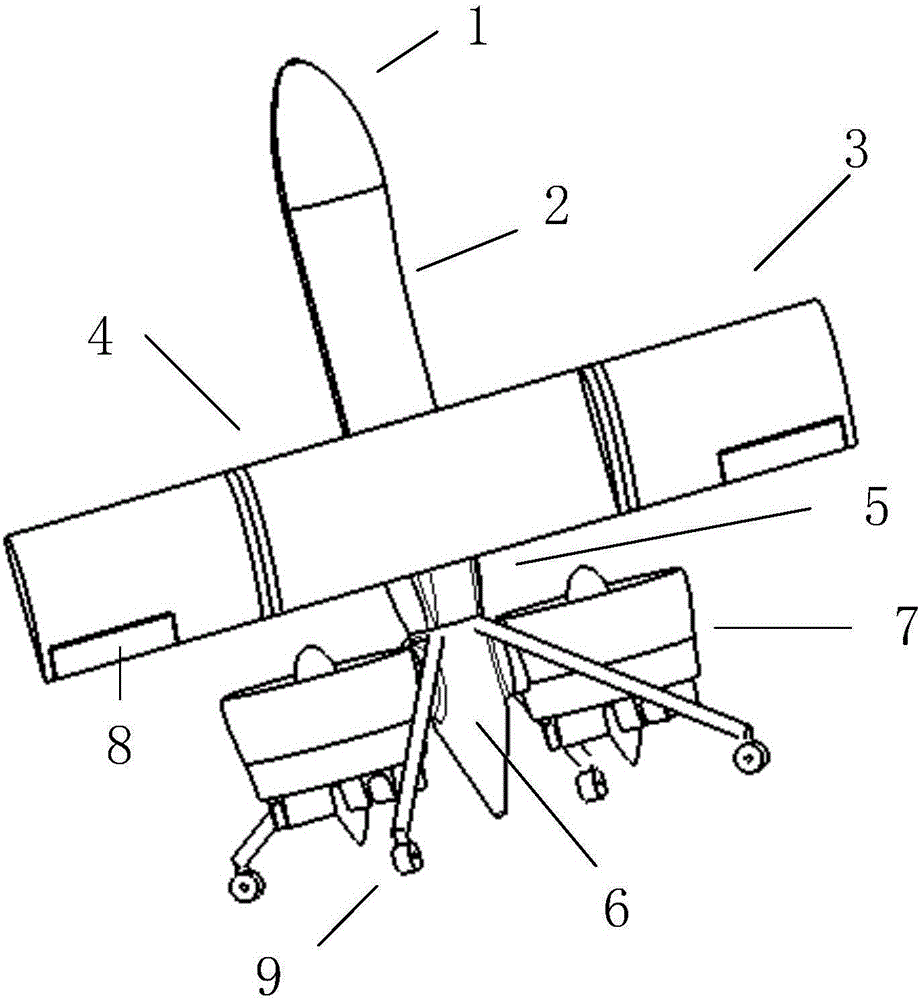
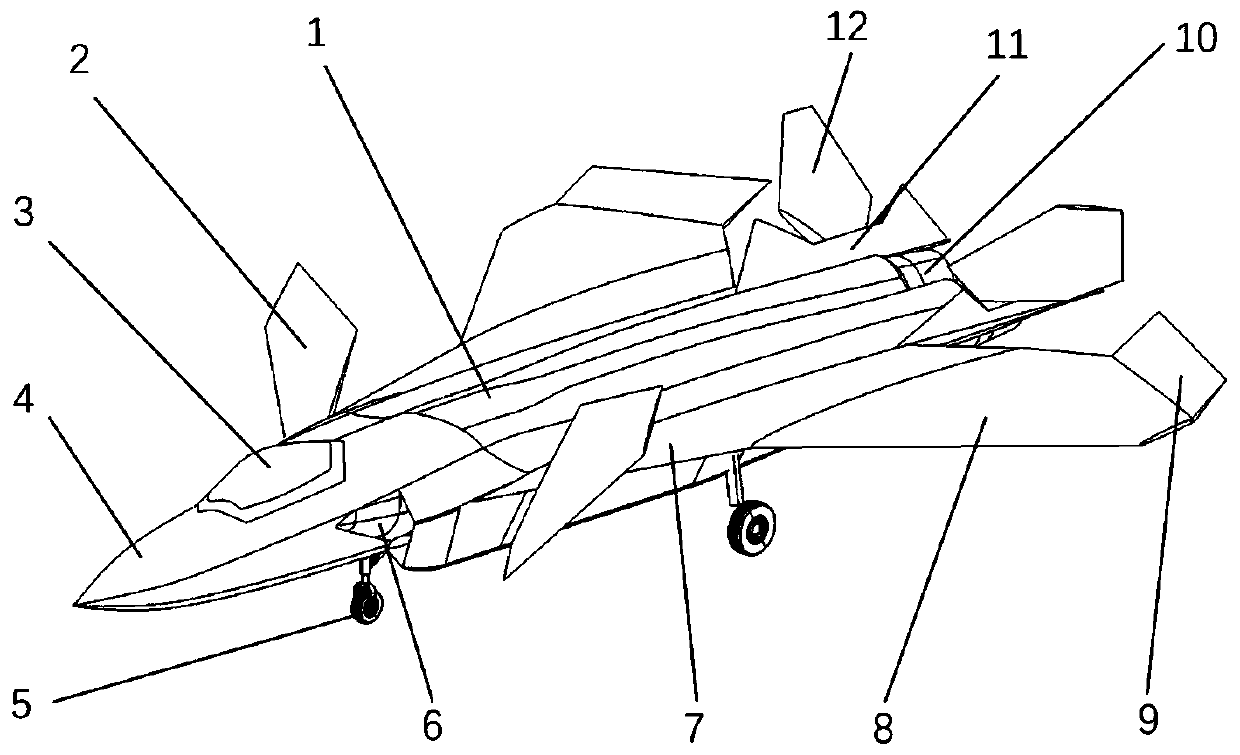
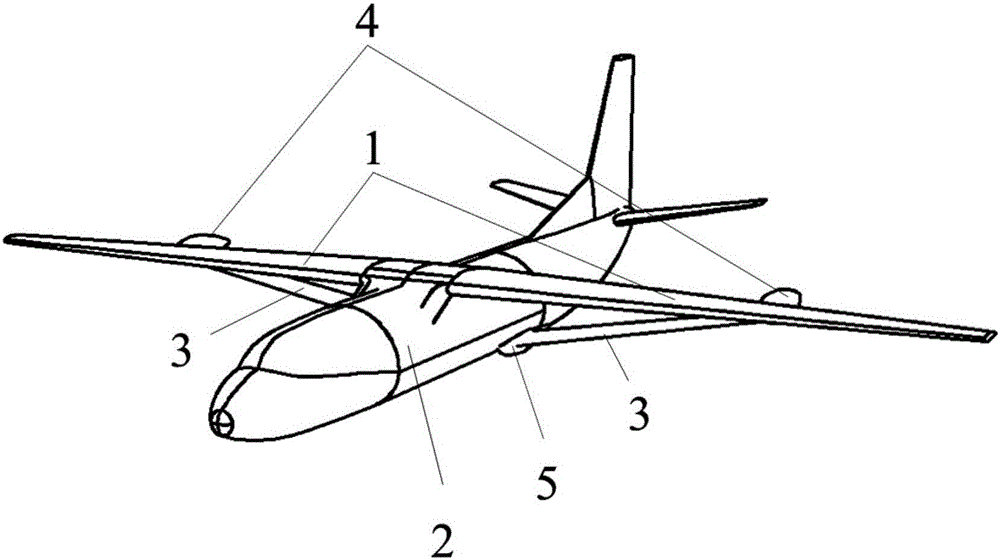
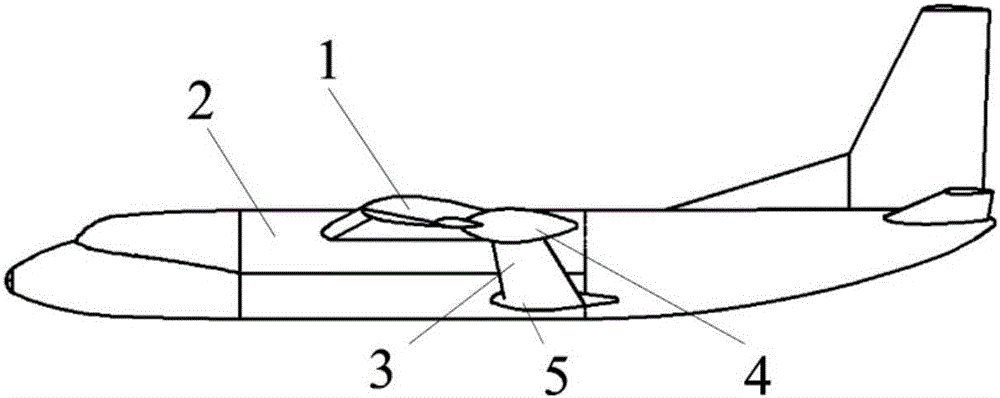
Vertical take-off and landing aircraft with wing body blended with single duct
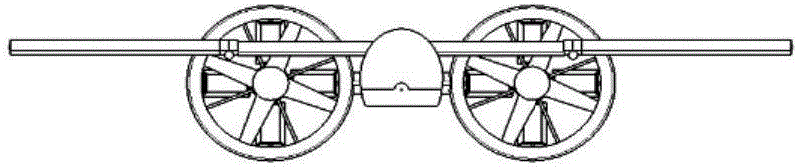
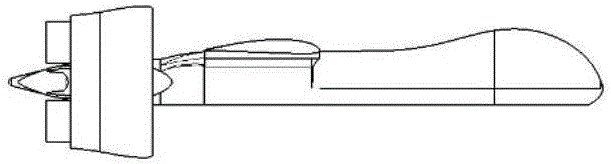
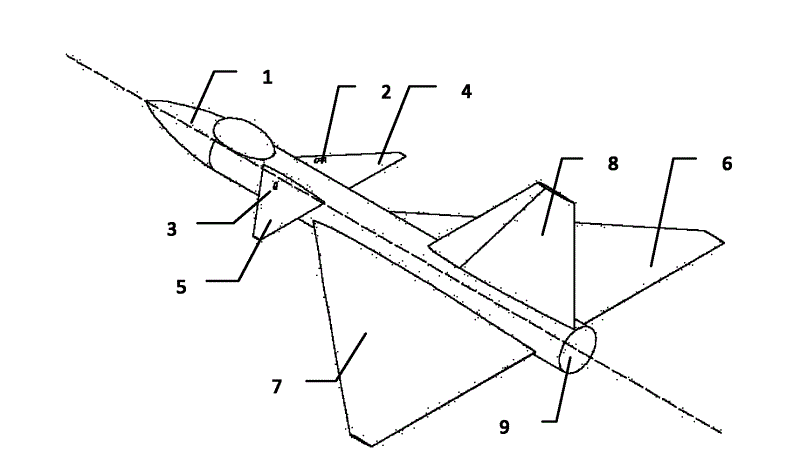
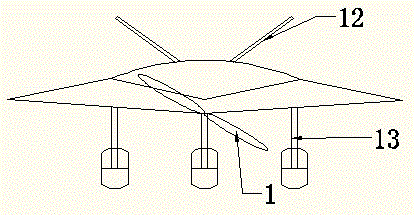
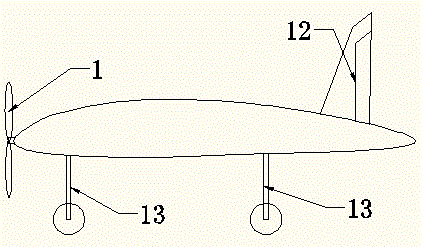
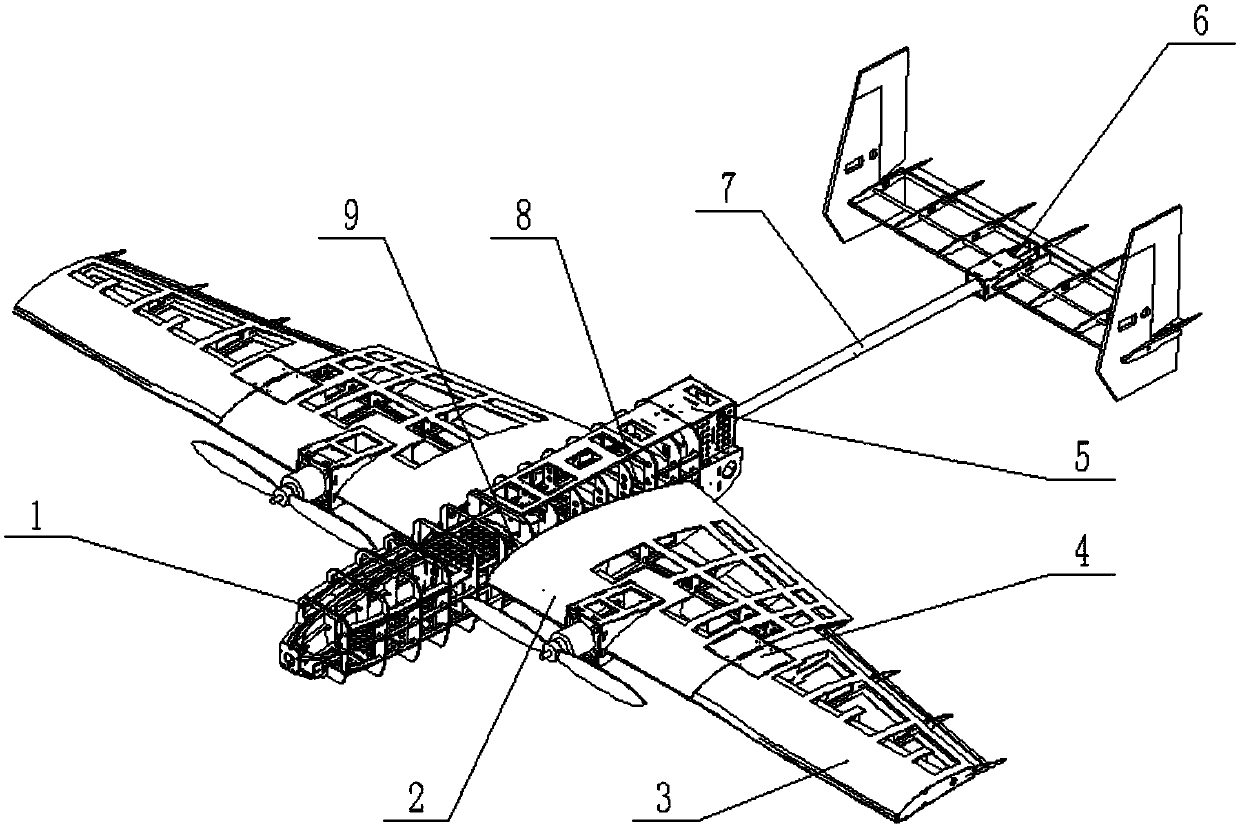
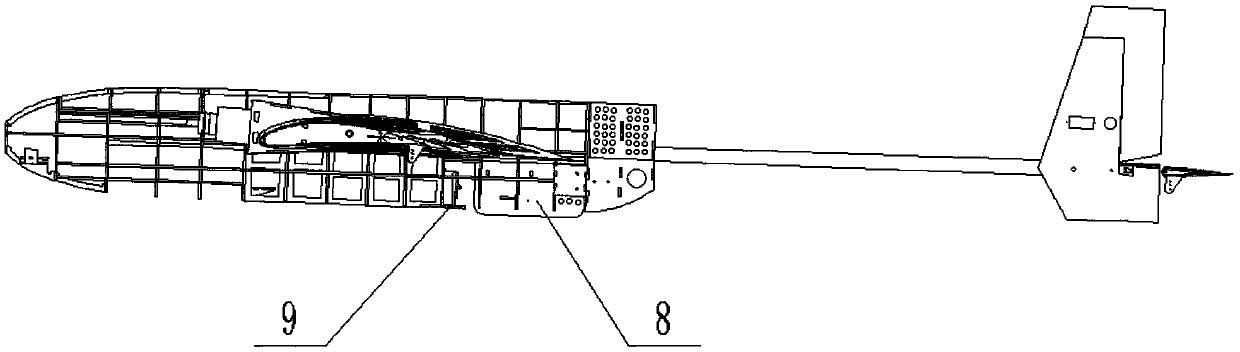
The invention discloses a vertical take-off and landing aircraft with a wing body blended with a single duct. The aircraft mainly consists of an aircraft fuselage 3, a front engine 2 and a duct engine 8. The aircraft fuselage 3 is in a blended wing body layout. The front engine 2 is installed on the front part of the fuselage of the aircraft, and the duct 7 is positioned in the middle part of the fuselage 3 of the aircraft. Parts 4 are folding wings positioned on two sides of the fuselage 3. The duct engine 8 is positioned in the middle of the duct 7, and fixedly arranged on the fuselage of the aircraft by a fixing rod 11. Parts 5 and 6 are flaps of the aircraft, and are positioned on the back part of the aircraft and the back parts of the wings. Parts 9 are folding positions of the wings of the aircraft. A front propeller 1 of the aircraft is positioned at the front end of the aircraft. Empennages 12 of the aircraft are positioned at the tail of the aircraft, and are in V-shaped symmetrical distribution. Three undercarriages 13 of the aircraft are distributed on the lower part of the aircraft in a manner that one undercarriage is at the front and two undercarriages are at the back, and the undercarriages 13 can also be supporting rods 14. The vertical take-off and landing aircraft disclosed by the invention is mainly applicable to the field of aviation, and can be applied as small and medium-sized airplanes, unmanned aerial vehicles, model airplanes and aerial photography airplanes.
Owner:张飞
Self-adaptive wide-band fluid energy harvesting device
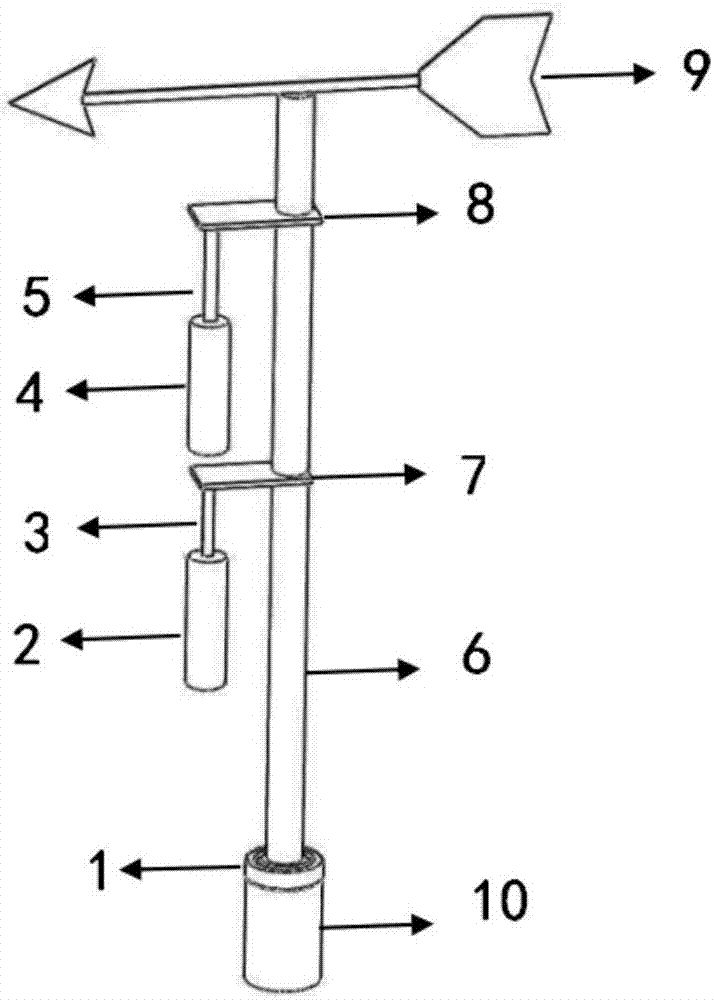
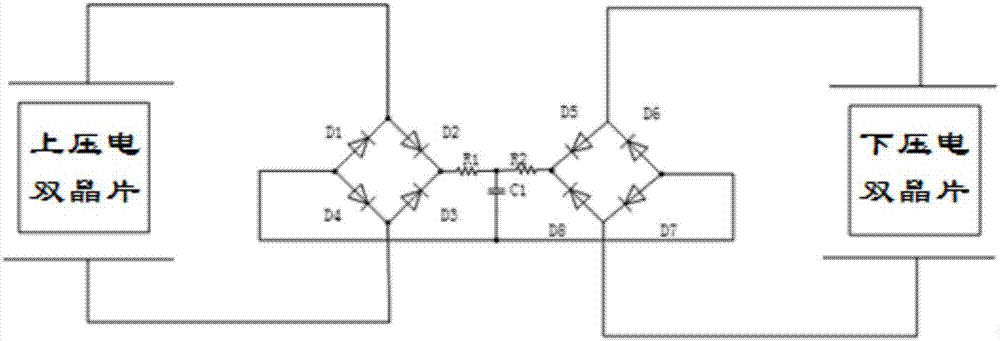
ActiveCN107134948AIncreased velocity rangeImprove collection effectBatteries circuit arrangementsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEffective powerVibration amplitude
The invention discloses a self-adaptive wide-band fluid energy harvesting device. The device is characterized in that the device comprises a base, a supporting rod, an energy harvesting mechanism and a rectification storage circuit, wherein the lower end of the supporting rod is movably connected to the base to make the supporting rod rotate along with the wind; one or more energy harvesting mechanisms are arranged, each energy harvesting mechanism comprise a cantilever beam, a piezoelectric bimorph and a light cylinder, one end of each cantilever beam is fixed to the supporting rod, the top of each piezoelectric bimorph is fixed to the other end of the corresponding cantilever beam, and the bottom of each piezoelectric bimorph is fixed to the center of the top of the corresponding light cylinder. The energy harvesting device is simple in structure; since the energy harvesting device interferes with the influence of the cylinders on a flow field, the energy harvesting device can obviously improve the vibration amplitude and frequency locking range of each light cylinder, and accordingly more effective power can be outputted.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Wing structure
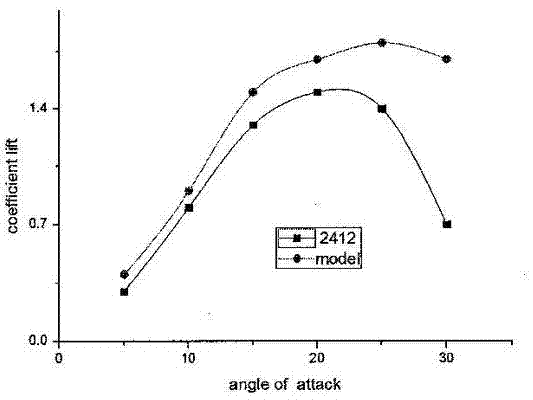
InactiveCN103693187AHigh lift coefficient at low speedLarge stall angleWing shapesLeading edgeClassical mechanics
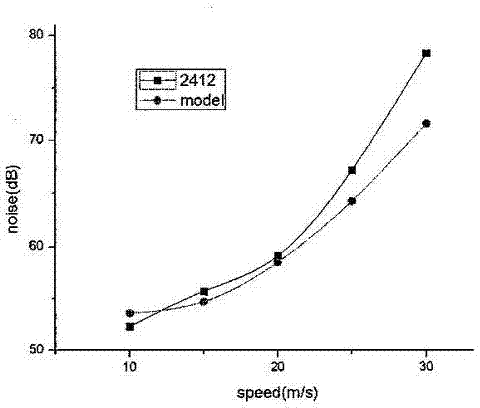
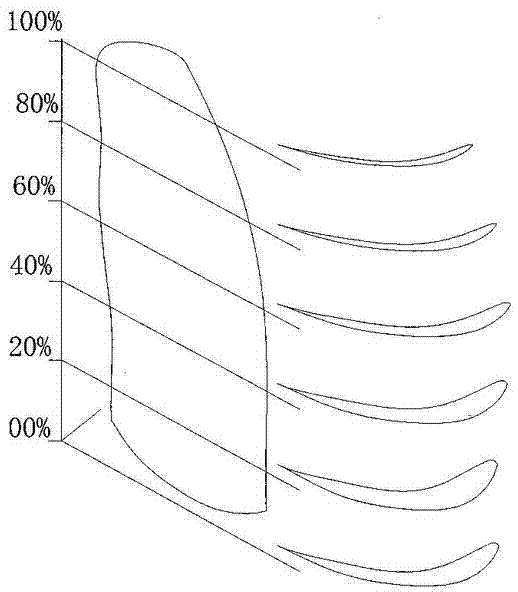
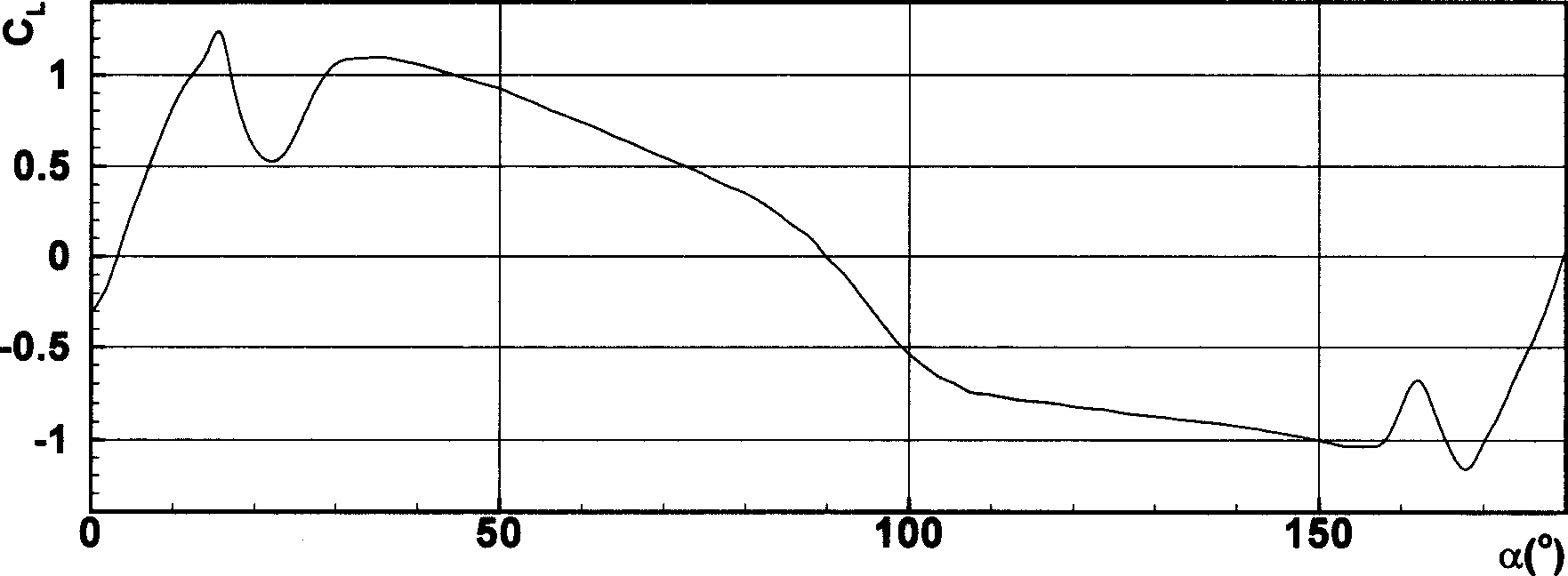
The invention discloses a wing structure. The wing structure consists of continuous wing profiles, wherein the spans of the wing profiles away from the root of a wing are 0 percent, 20 percent, 40 percent, 60 percent, 80 percent and 100 percent respectively; the ratio of wingspan to chord length is 5.50-7.24; the leading edge of the wing is a high-order curved line of an approximately parabolic shape; the maximum relative curvature of each wing profile is 7.5 percent and is positioned at a position at 17-33 percent of the chord length; the maximum relative thickness of each wing profile is 13.1 percent and is positioned at a position at 11-24 percent of the chord length; the curvature and the thickness of each wing profile tend to be increased and then decreased along the corresponding span. Compared with a parametrically-similar NACA (national advisory committee for aeronautics) 4-digit wing profile, the wing structure has the advantages that a low-speed lift coefficient is large, a resistance coefficient is small, and a large angle of stall is formed; under the condition of same flight parameters, according to the wing structure, the flight noise is low, and the lift coefficient is relatively large when an angle of attack is 25 degrees, and slowly declines when the angle of attack is greater than 25 degrees.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Water turbine wingsection for ocean current generation
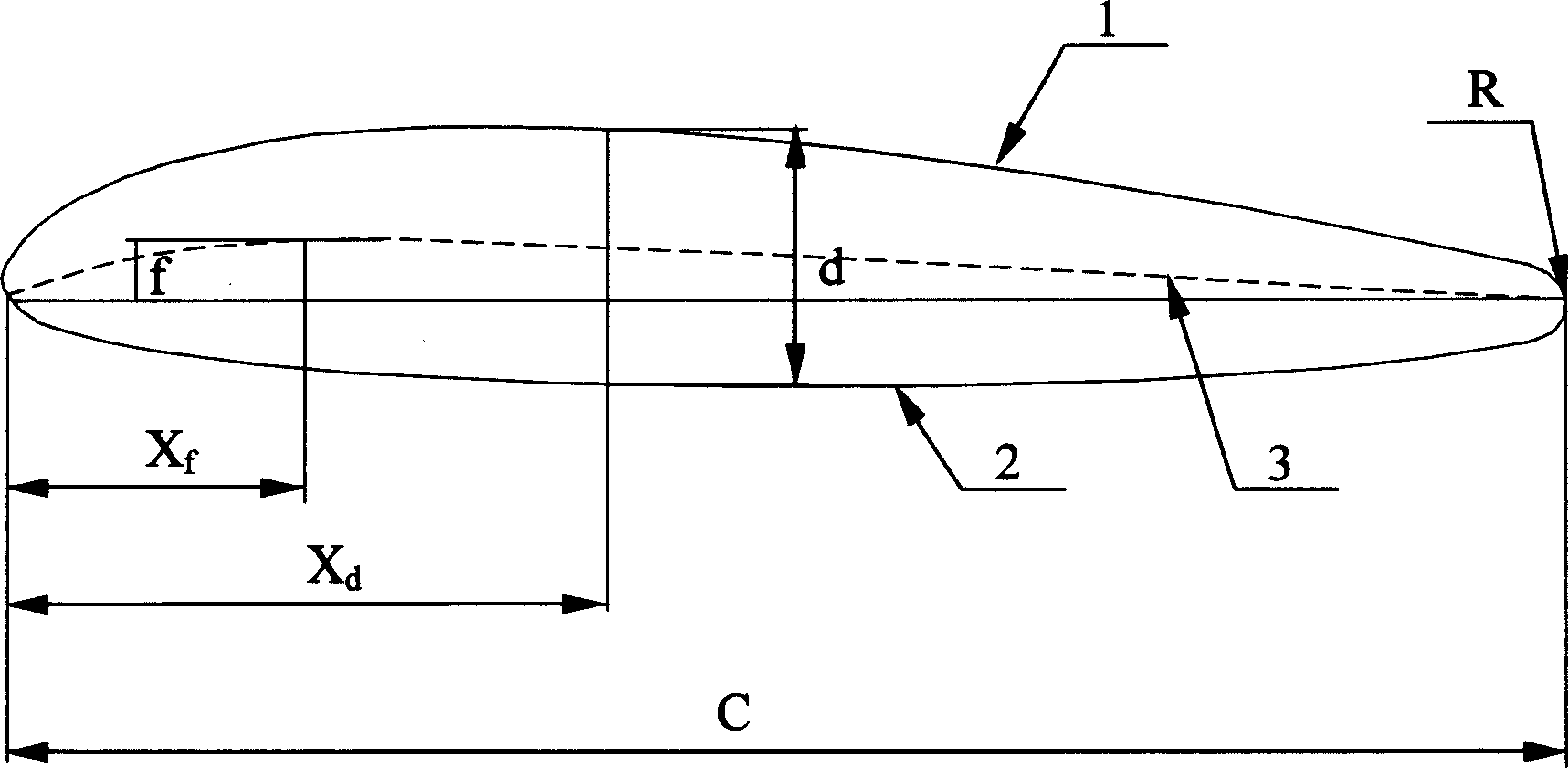
InactiveCN1587674AImprove performanceAvoid damageHydro energy generationEngine componentsElectricityWater turbine
The invention relates to a kind of wing section used rof the ocean current electricity-generating water turbine. According to the fairly wide range of working condition of the ocean current electricity-generating water turbine, select the fairly small curvature and the fairly small greatest thickness. The ratio of the greatest thickness and length of chord is d / c=0.1570, the ratio of the greatest curvature and the length of chord is f / c=0.0229. The wing section has sacrificed part of functions under the routine angle, but meanwhile, it obtains the superior function of condition changing. Moving the position of the greatest thickness backward, can improve the reserve working capacity and also improve the left coefficient of wing section. At the point X r / c=0.95 of back edge, the wing section takes are as transition. The ratio of arc radius and chord length of wing section is R / c=0.0208. Enlarging the radius of back edge 1f wing section can weaken the influence when the slight wing stalls under a big angle, and reduce the damages objects uotside have done with the wing section.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Variable flat plate type bionic leading edge flap device
ActiveCN102407939AChange aerodynamic performanceIncrease lift coefficientAircraft controlJet aeroplaneLeading edge
The invention discloses a variable flat plate type bionic leading edge flap device, which comprises a bionic leading edge flap, a leading edge flap receiving cavity and a telescopic drive mechanism; the bionic leading edge flap is placed in the leading edge flap receiving cavity on the leading edge of a wing and is connected with the telescopic drive mechanism; the telescopic drive mechanism is driven by a rack mechanism driven by a micro step motor; the bionic leading edge flap has a similar sine curve shape, and the bionic leading edge flaps with different performances can be obtained by changing wavelength and amplitude; the leading edge flap receiving cavity is used for receiving the bionic leading edge flap; the telescopic drive mechanism is composed of a step motor, a first speed reduction gear, a rack and a connecting piece; the step motor is mounted in the wing and is engaged with the high speed end of the first speed reduction gear; the rack is placed in a sliding groove on the wing and is engaged with the low speed end of the first speed reduction gear; and the rack is connected with the bionic leading edge flap through the connecting piece. The lift coefficient of the airplane after stalling angle of attack is increased and maneuvering performance of the airplane is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Wind turbine blade aerofoil of horizontal axis wind turbine
ActiveCN102444540AImprove aerodynamic performanceIncrease lift coefficientMachines/enginesWind energy generationTurbine bladeHorizontal axis
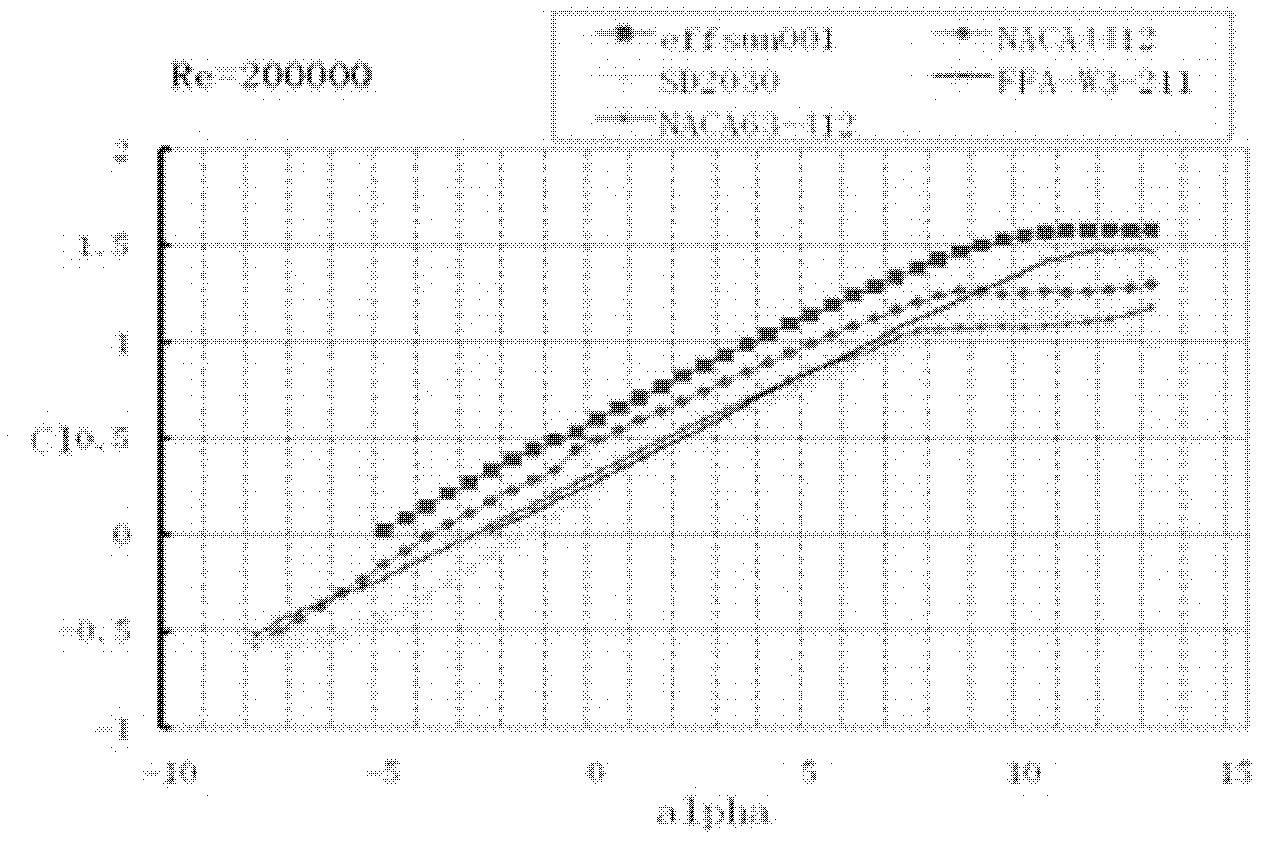
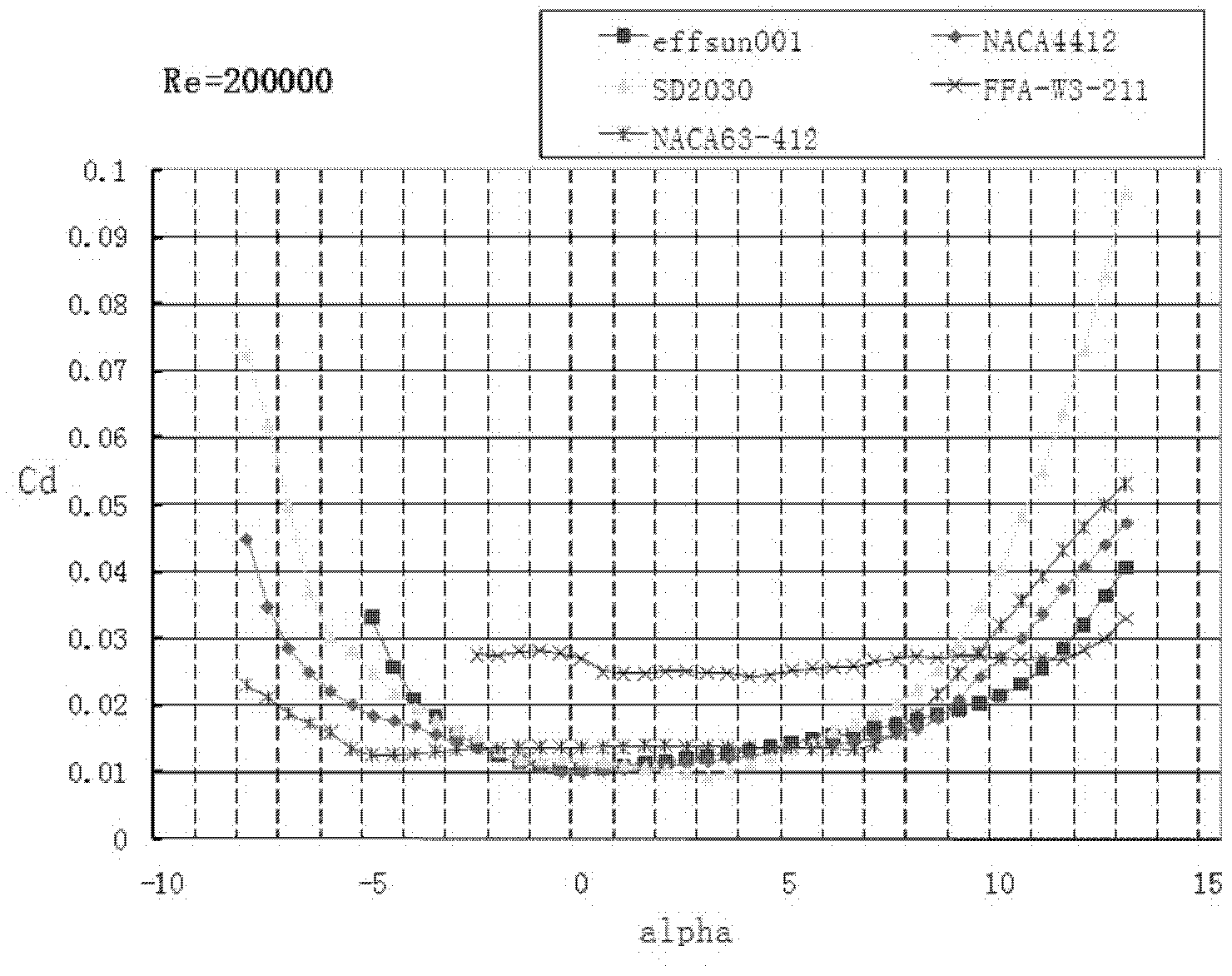
The invention discloses a wind turbine blade aerofoil of a horizontal axis wind turbine. The wind turbine blade aerofoil comprises a front edge, a tail edge, a suction surface and a pressure surface, and is characterized in that the suction surface and the pressure surface are divided into upper and lower parts along a wing chord; the upper and lower parts are formed by connecting circular curves of different radiuses in a tangential manner; the maximum relative thickness of the wind turbine blade aerofoil is 12.38% of the chord length, and is at 29.6% of the chord length; and the maximum relative bending is 5.24%, and is at 40.4% of the chord length. The wind turbine blade aerofoil has the advantages that the corresponding shape and structure of the wind turbine blade aerofoil are designed, particularly the relative thickness and the relative bending positions are designed, so that the wind turbine blade aerofoil acquires a high lift coefficient under the same Reynolds number and at different angles of attack; moreover, under the same resistance coefficient, the bigger the lift coefficient, the better the aerodynamic performance effect of the aerofoil, thus the high output efficiency effect is achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN EFFSUN WIND POWER
Method for designing wind turbine airfoil by using Bessel function curve
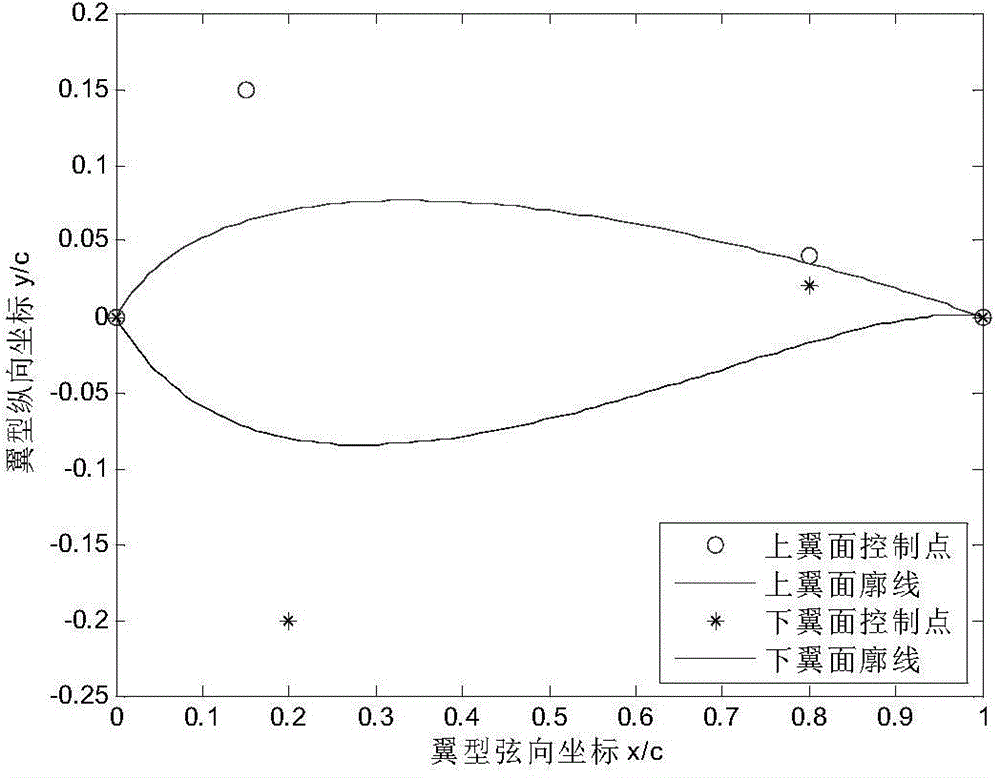
InactiveCN104863799AControl profileImprove design efficiencyWind motor componentsTurbine bladeEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a method for designing a wind turbine airfoil by using a Bessel function curve. According to the method, the third-order Bessel function is adopted and can represent a section of curve through four control points only, and in addition, the starting point and the end point are fixed, so that only two control points are required to be changed for a section of the curve; each of an upper wing surface and a lower wing surface of the airfoil is represented by a section of curve, the starting points and the end points of the upper wing surface and the lower wing surface respectively coincide, and then the staring points and the end points are in smooth connection. According to the invention, the airfoil profile can be controlled more conveniently and effectively by using several points in space, so that optimization design time of the airfoil is shortened, and airfoil design efficiency is improved; the designed airfoil has an extremely high lift coefficient, so that chord length of a blade is reduced, and the material required by the blade is reduced; a higher lift-drag ratio is realized, so that the wind-power utilization coefficient is increased; the method can be popularized to design of wind turbine airfoils of different thicknesses, plane airfoils, turbine blade profiles and other complex curves and has a high social value and a good economic benefit.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Symmetric eight-axle aircraft
ActiveCN105270614ARoll outImprove up and downAircraft stabilisationRotocraftHelicopter rotorTailplane
The invention relates to a symmetric eight-axle aircraft, which belongs to the technical field of aircrafts. The symmetric eight-axle aircraft comprises an aircraft body, a left composite wing, a right composite wing, a bracket, a tail rod, a tail wing axle, a left transverse tail wing, a right transverse tail wing, a vertical tail wing, a landing gear, a front left rotor wing, a front right rotor wing, a rear left rotor wing and a rear right rotor wing. The front left rotor wing, the front right rotor wing, the rear left rotor wing and the rear right rotor wing have same structures and are mounted on the left and right sides in front of the aircraft and on the left and right sides behind the aircraft. The left transverse tail wing and the right transverse tail wing are symmetrically mounted on the left section and the right section of the tail wing axle, respectively; and the left transverse tail wing and the right transverse tail wing can deflect up and down around the tail wing axle. The left composite wing and the right composite wing have same structures and are symmetrically mounted on the left side and the right side of the aircraft body; and two rotor wings are mounted in both the left composite wing and the right composite wing. Wing sheets of the left composite wing comprise a fixed front wing sheet and a rear wing sheet which is capable of deflecting around a wing axle. The symmetric eight-axle aircraft provided by the invention is advantaged in that a takeoff and landing site for the aircraft is not big, the aircraft can vertically take off and land, the lifting force generated by the aircraft is large and the aircraft is safe, stable and flexible.
Owner:CHINA AIRCRAFT MAINTENANCE & ENG
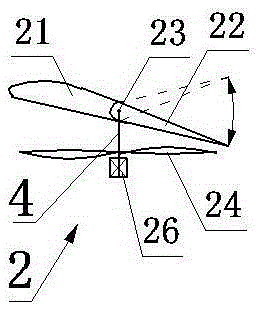
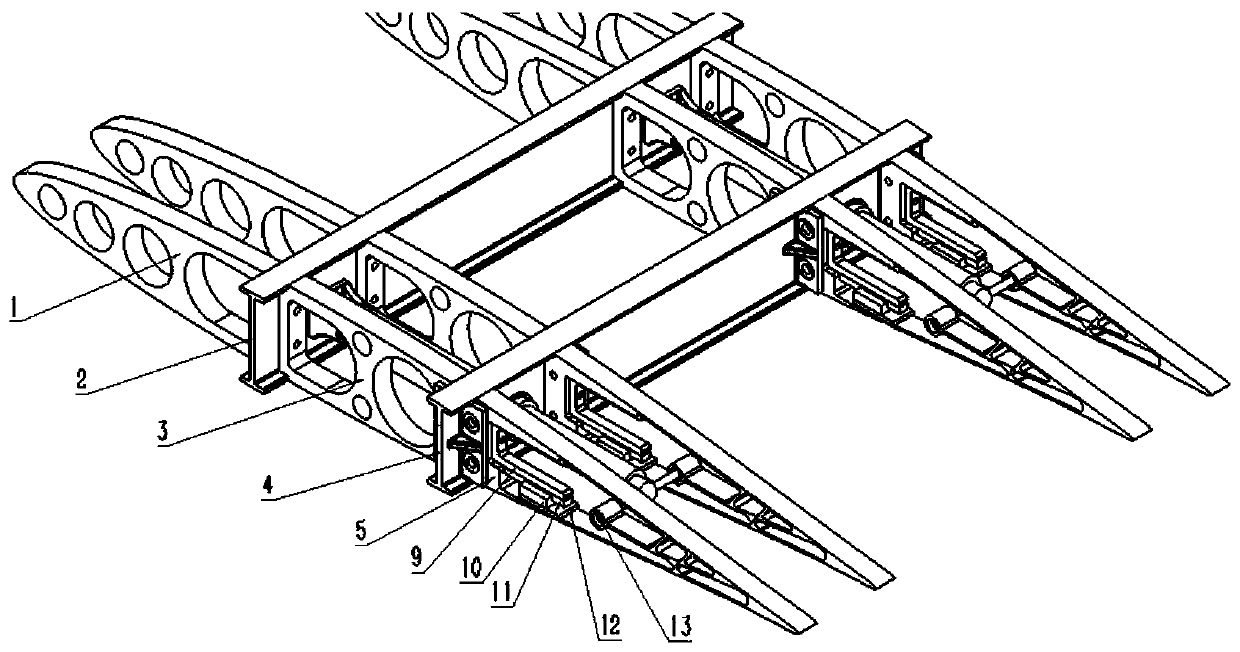
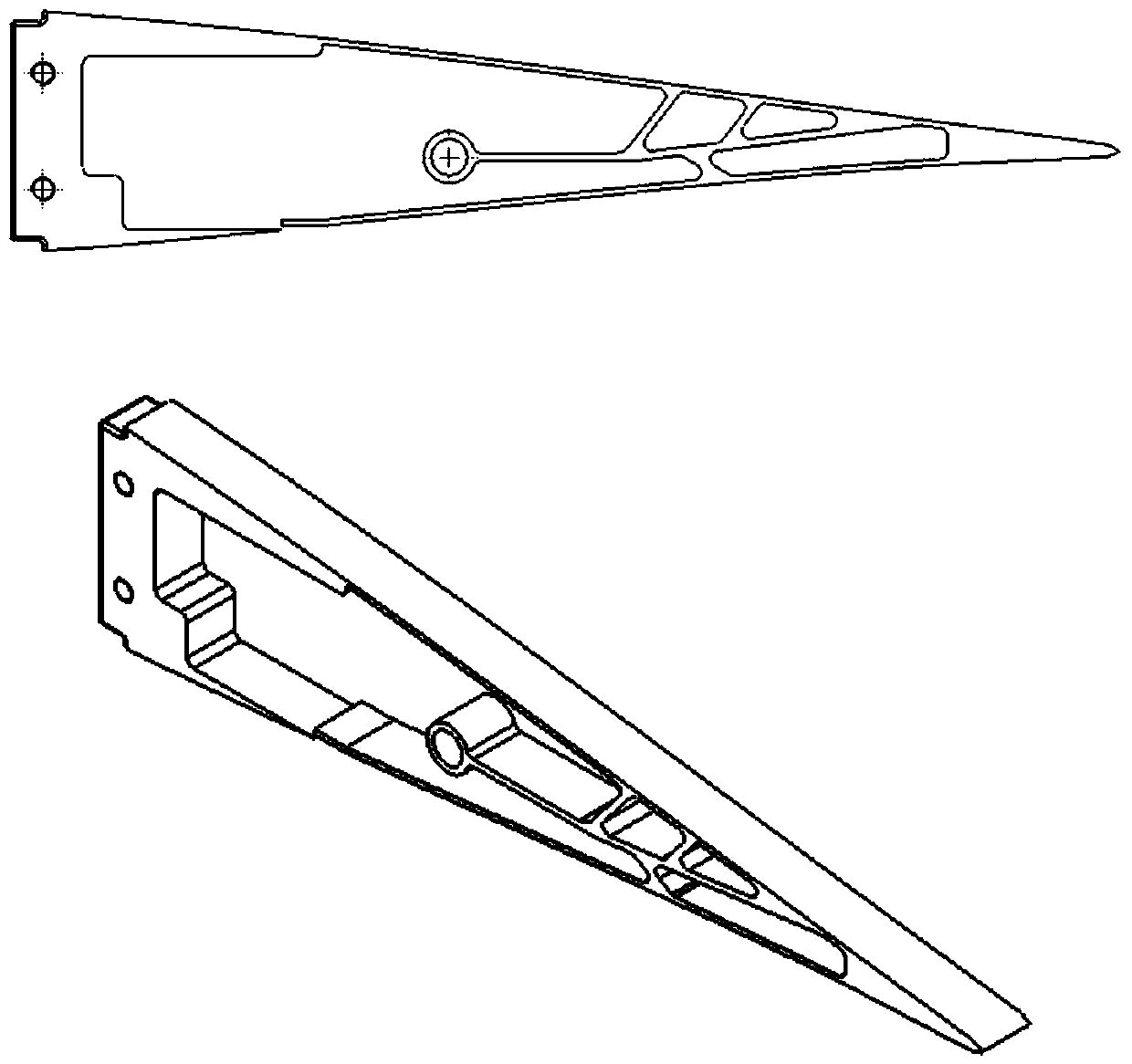
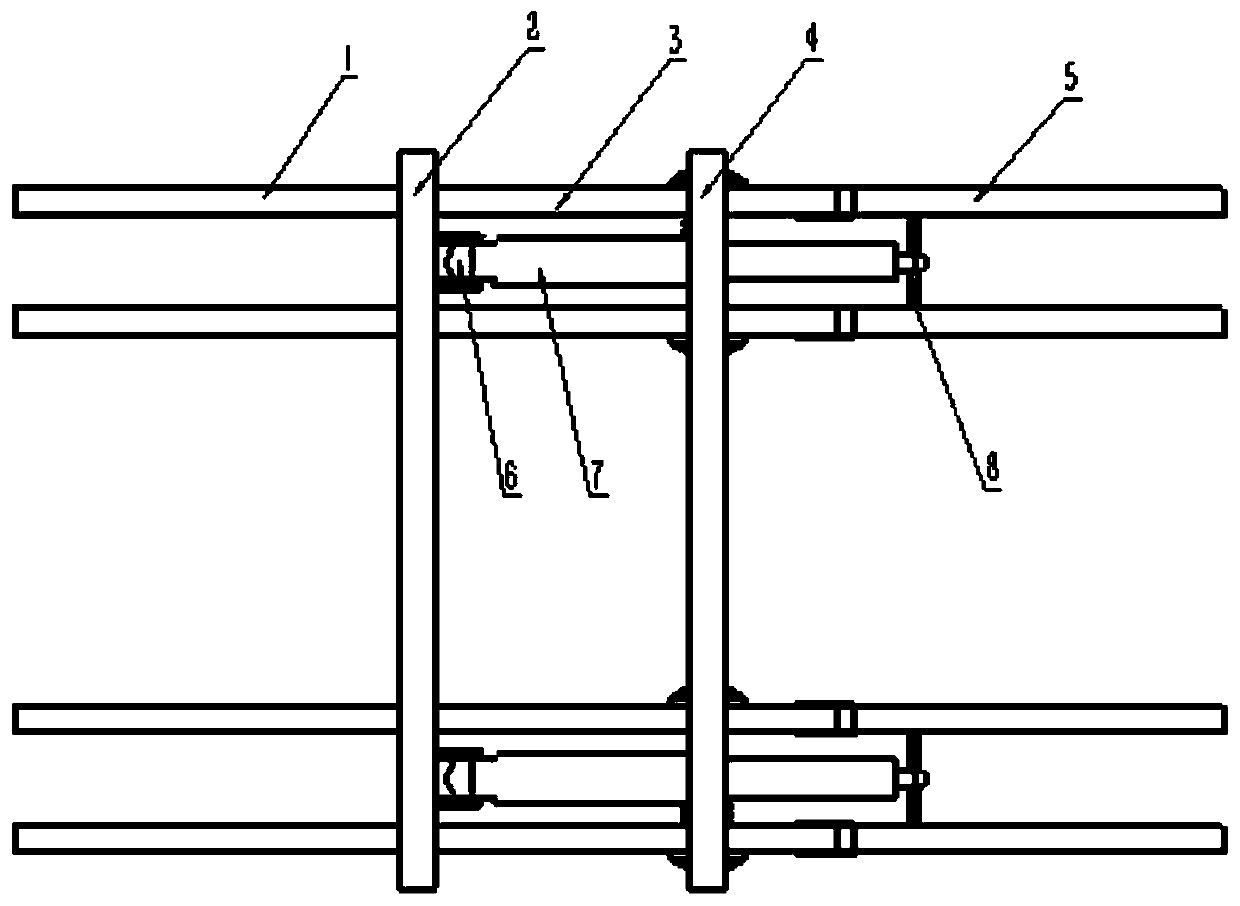
Light flexible wing with variable-camber trailing edge
PendingCN110834714AReduce structural weightStrong achievabilityWing adjustmentsTrailing edgePull force
The invention provides a light flexible wing with a variable-camber trailing edge. The light flexible wing comprises a leading edge ribbed plate (1), a front spar (2), a middle ribbed plate (3), a rear spar (4), the flexible trailing edge (5), a motor support base (6), a linear motor (7), a motor and flexible trailing edge connecting rod (8), a flexible trailing edge and guide rail connecting plate (9), a slider (10), a guide rail (11), a slider and flexible trailing end connecting plate (12), a pull ring (13) and a skin. The linear motor (7) is electrified, the pull ring (13) on the flexibletrailing edge (5) is pulled or pushed, under the action of the push-pull force, and the pull ring (13) does linear motion and drags the upper and lower sides of the flexible trailing edge (5) to be bent and deformed. Aiming at the limitations of a traditional wing flap and an existing adaptive wing flap, the whole structure can have high stability when a large deformation is generated, and the light flexible wing has the advantages that the mass is low, and the light flexible wing does not occupy extra wing space.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Light-weight foldable reconnaissance/attack integrated unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN107776892AIncrease lift coefficientReduce structural weightFuselage framesWing adjustmentsUncrewed vehicleAtmospheric sounding
The invention relates to the field of unmanned aerial vehicles and especially relates to a light-weight foldable reconnaissance / attack integrated unmanned aerial vehicle, which includes a fuselage, wings, a folding mechanism, flat vertical tails, reconnaissance cloud deck, and a dispensing mechanism. The fuselage includes a front section, a rear section, a central wing box, wing main beams, wing connection boxes, and a tail connection box. Each wing includes an inner section and an outer section. The two wings are arranged respectively at the left and the right of the fuselage symmetrically. The folding mechanism includes two set of wing folding mechanisms and a fuselage folding mechanism. The reconnaissance / attack integrated unmanned aerial vehicle can be quickly folded and expanded, is low in cost, has simple and easy-to-repair structure, and has excellent maneuverability and certain dispensing load. The unmanned aerial vehicle is used for military reconnaissance and quick and accurate strike tasks, and also can be applied to civil and scientific researching fields, such as atmospheric sounding and topographic mapping, etc.
Owner:哈尔滨模豆科技有限责任公司
Flapping-wing energy-acquiring device of self-moving flaps
InactiveCN107021222AImprove energy harvesting efficiencyIncrease the curvatureOrnithoptersFlapping wingTrailing edge
The invention relates to a flapping-wing energy-acquiring device of self-moving flaps comprising an energy-acquiring part, flapping wings and a main shaft, wherein the two flapping wings are connected to each other by the main shaft to form a whole; the main shaft of the two flapping wings is positioned through the middle of the energy-acquiring part; the two flapping wings can rotate around the main shaft and the whole can make a heaving motion in a vertical direction; and the energy-acquiring part acquires the energy transmitted by the flapping wings by the movement of the main shaft. The Gurney flaps are applied in the flapping-wing energy-acquiring device of the self-moving flaps. According to Archimedes' principle, the Gurney flaps are designed to be arranged at the trailing edge of airfoils to automatically change the direction based on different directions of the heaving motion, which is equivalent to increasing the camber of the airfoils, thereby increasing the lift coefficient of the airfoils and the energy-acquiring efficiency of the flapping wings. The flapping-wing energy-acquiring device of the self-moving flaps is simple in structure, and automatically realizes the direction changing of the self-moving flaps on the surface of the airfoils based on the different directions of the heaving motion by using Archimedes' principle.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
High-efficiency and environmentally-friendly shilling rudder body
InactiveCN102390516AReduce manufacturing costIncrease lift coefficientSteering ruddersEngineeringRudder
The invention relates to a high-efficiency and environmentally-friendly shilling rudder body, which comprises a rudder stock, wherein one end of the rudder stock is provided with rudder blade bodies; each rudder blade body comprises a rudder blade side plate; the front end of the rudder blade side plate is provided with a bow transom plate; the other side of the rudder blade side plate corresponding to the bow transom plate is provided with a stern transom plate; the end parts of the two ends of the rudder blade side plate are respectively provided with a swash plate; the upper end of the rudder blade side plate is provided with an upper swash plate, and the lower end of the rudder blade side plate is provided with a lower swash plate; and the rudder blade side plate is provided with a plate body reinforcing mechanism. The shilling rudder body has a simple structure manufacturing process and low manufacturing cost and is easy to generalize; due to the stern transom plate, the tail part of the rudder blade body forms circular flow, the lift coefficient of the rudder blade body is increased, and the moment of turning a ship is increased; since the upper swash plate and the lower swash plate are designed, transverse circular flow on the end part of the rudder blade body is suppressed, the longitudinal circular flow speed is increased, the revolving performance and the sideslip capacity of the ship are improved; the shilling rudder body has a simple and compact structure, low manufacturing cost and large lift coefficient; the rudder efficiency is increased; the course avoidance and the course keeping quality of the conventional rudder at a small rudder angle are improved; and a wide application range is guaranteed.
Owner:WUXI DONGZHOU MARINE FITTINGS
Special airfoil for blade tip of wind driven generator
InactiveCN101886619AWork lessIncrease lift coefficientWind energy generationWind motor componentsWind drivenHigh lift
The invention discloses a special airfoil for a blade tip of a wind driven generator. In the invention, on the basis of the optimized airfoil molded line model, an airfoil molded line which is suitable for the blade tip is designed by using nine control parameters of the parsec airfoil expression method as variants. In the range of the normal working attack angle, the special airfoil has very high lift coefficient and lift-to-drag ratio and very slow stall performance; the front edge of the special airfoil has good roughness and non-sensitivity so that the wind turbine can still work normally even if the front edge is frozen or polluted. Thereby, the special airfoil meets the requirements of the pneumatic performance of the blade tip of the wind turbine.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Solar-powered airplane airfoil profile design method and solar-powered airplane airfoil profile
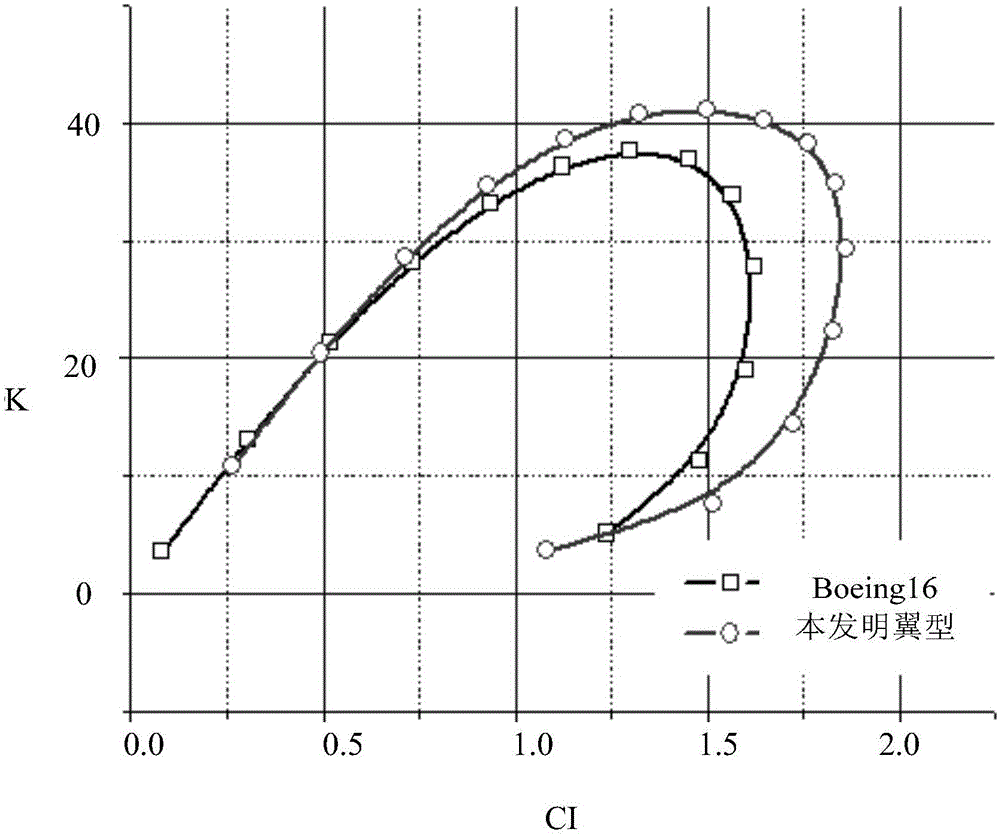
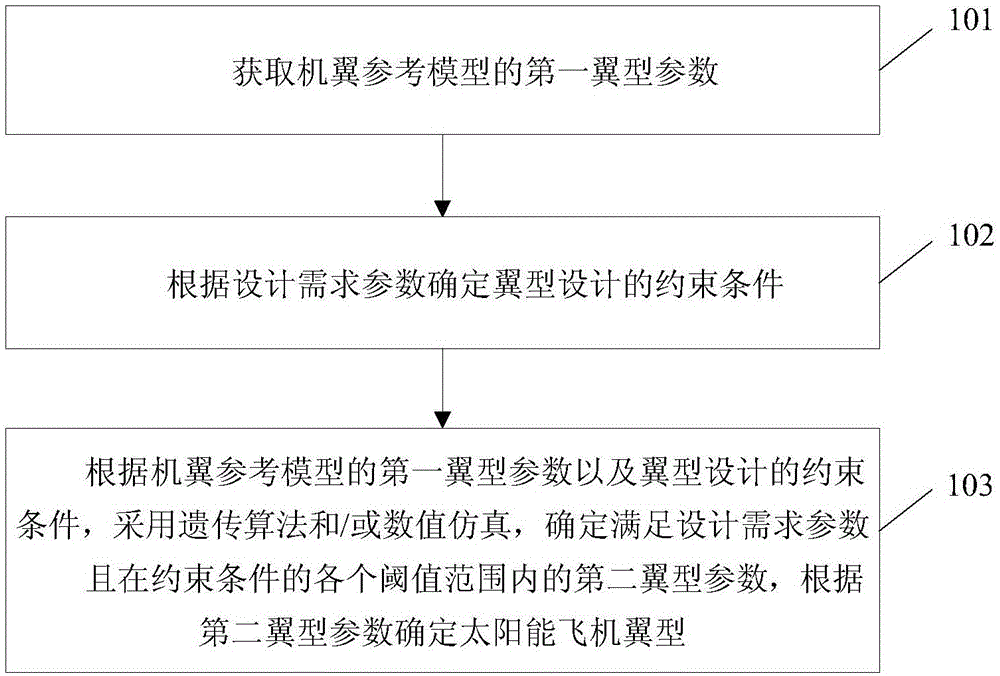
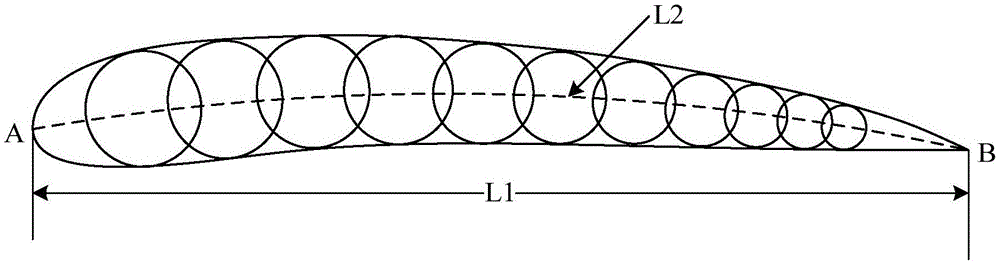
ActiveCN105129071AIncrease lift coefficientImprove aerodynamic efficiencyWing shapesJet aeroplaneReference model
The invention provides a solar-powered airplane airfoil profile design method and a solar-powered airplane airfoil profile, wherein the method includes the steps: first airfoil profile parameters of an airfoil reference model are acquired, wherein the first airfoil profile parameters include a first airfoil profile maximum relative thickness, a relative position of the first airfoil profile maximum relative thickness, a first airfoil profile maximum relative camber, a relative position of the first airfoil profile maximum relative camber, and a first airfoil profile head radius; constraint conditions of an airfoil profile design are determined according to design demand parameters, wherein the design demand parameters include the flight speed, the elevating force coefficient and the Reynolds number, and the constraint conditions include a maximum relative thickness threshold, and an airfoil profile thickness threshold having the distance in the range of 20%-60% of the chord length away from an airfoil profile front edge; according to the first airfoil profile parameters of the airfoil reference model and the constraint conditions of the airfoil profile design and with use of a genetic algorithm and / or numerical simulation, second airfoil profile parameters meeting the design demand parameters and in the range of all the thresholds of the constraint conditions are determined, and the solar-powered airplane airfoil profile is determined according to the second airfoil profile parameters.
Owner:BEIJING CHANGYUAN TECH
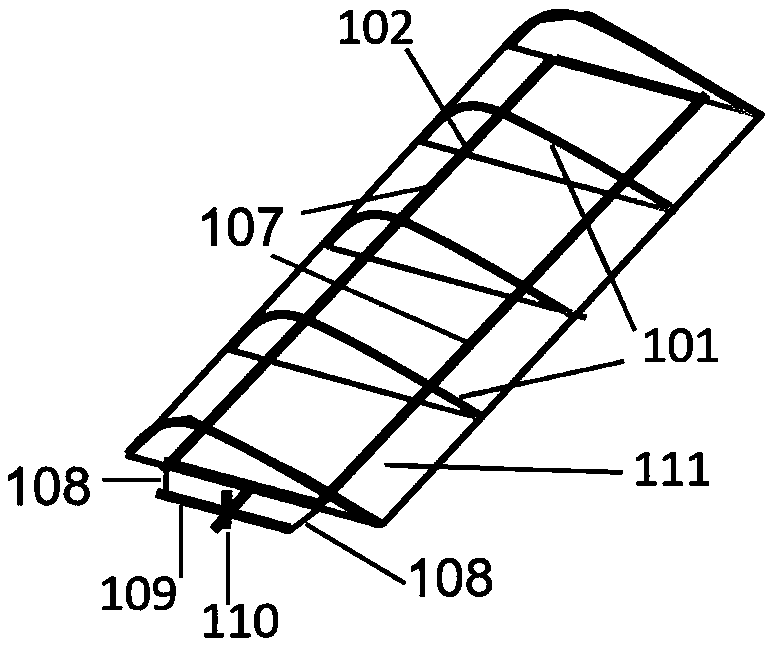
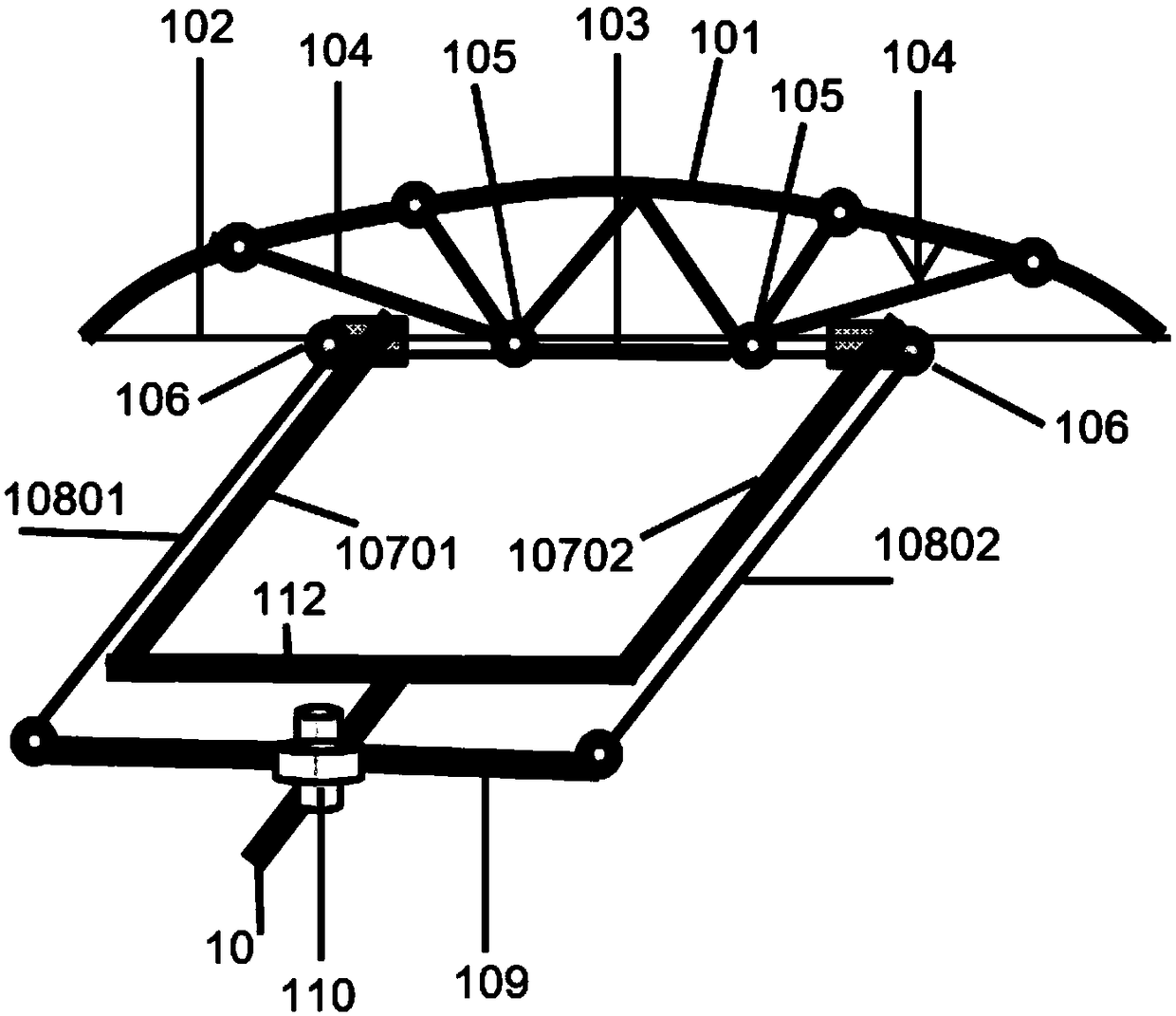
Self-adaption variable-rigidity bow wing for micro flapping-wing and flapping rotor crafts
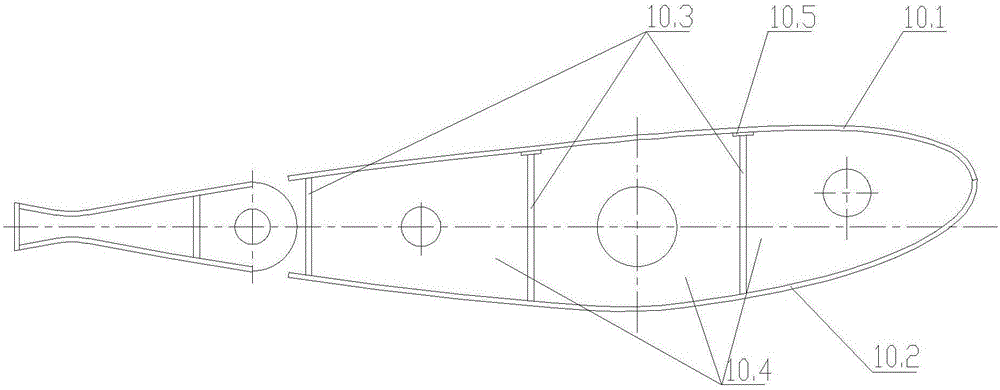
The invention belongs to the field of aircraft design and relates to a bow wing for micro flapping-wing and flapping rotor crafts. The bow wing comprises a main beam, bow beams, bowstrings and a wingmembrane. The main beam is a beam in a spanwise direction of the wing, one side of the wing membrane is fixedly connected with the main beam, the bow beams are fixedly connected with the wing membranes, two ends of each bowstring are fixedly connected with two ends of the corresponding bow beam, and a required pneumatic appearance is formed through the wing membrane. The wing surface of the bow wing is cambered to some extent intrinsically, and high lift coefficient in a steady flow field is realized. The negative lift of bow wing in an upbeat stage is reduced while instantaneous lift is increased in a downbeat stage, and high energy utilization rate is realized. In material selection of the bow wing, a material low in Young modulus is selected for the bow wing, and high chordwise flexibility is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Vertically-lifted fixed wing aircraft with balancing mechanism
InactiveCN109319112ASmall sizeWith vertical take-off and landing functionPower plant fuel tanksAircraft stabilisation by gravity apparatusJet aeroplaneNacelle
The invention discloses a vertically-lifted fixed wing aircraft with a balancing mechanism. The vertically-lifted fixed wing aircraft includes a fuselage, tail wings, power devices with tilting mechanisms and a balancing mechanism, and the power devices with the tilting mechanisms include fixed pitch propellers, engine nacelles, slipstream rudders, wings, tilting wings and steering engines; the engine nacelles are internally provided with engines which are connected with the fixed pitch propellers and the balancing mechanism; one ends of the tilting wings are fixedly connected to the engine nacelles, and the other ends of the tilting wings are rotatably connected to the wings; the slipstream rudders are movably connected to the tilting wings, and the steering engines drive the slipstream rudders; the power devices with the tilting mechanisms are symmetrically arranged on both sides of the fuselage and horizontally arranged with the wings; the head of the fuselage is provided with a through hole, the through hole is internally provided with a ducted fan; and the balancing mechanism is arranged inside the fuselage to maintain balance of the fixed wing aircraft. According to the vertically-lifted fixed wing aircraft with the balancing mechanism, the lifting inertia is small, running stability is good, and fuel consumption is low.
Owner:FOSHAN SHENFENG AVIATION SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com