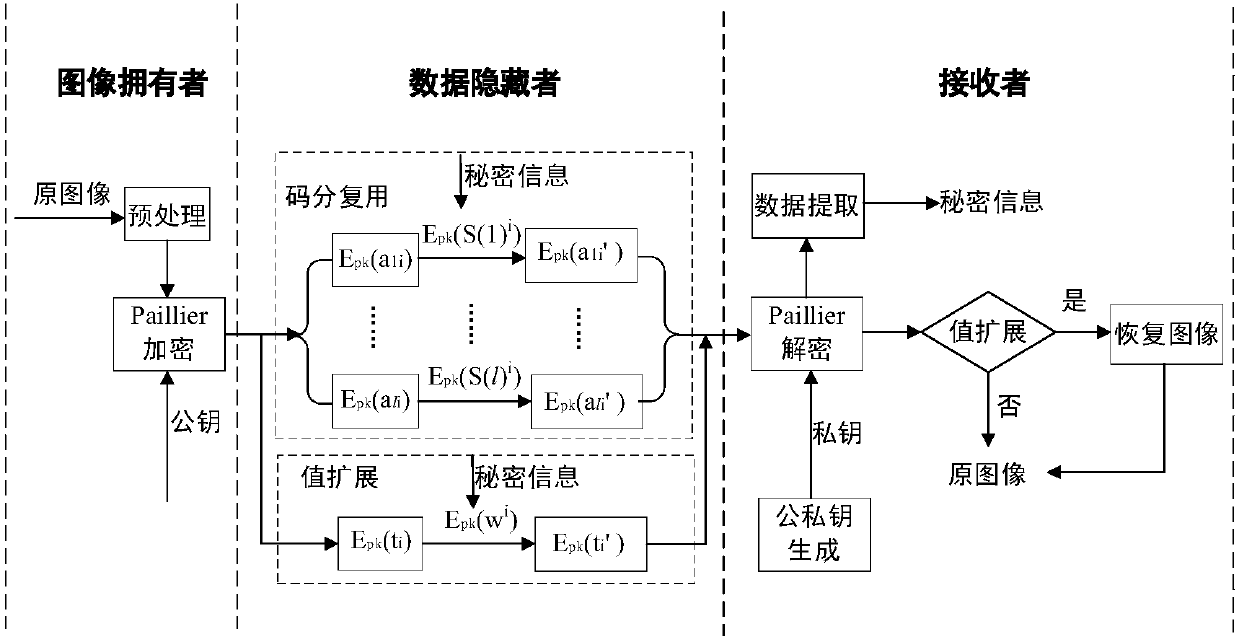
Reversible data hiding method in homomorphic encryption domain based on code division multiplexing and value expansion
A code division multiplexing and homomorphic encryption technology, applied in the field of information hiding, can solve the problems that adjacent pixels do not meet the preprocessing and embedded secret information conditions, and the image embedding capacity and quality have not been significantly improved, so as to improve the quality. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0084] attached Figure 2A-2E are five original images as carrier images in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, with Figures 3A-3E is the image obtained after direct decryption in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, with Figures 4A-4E It is the image restored by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Figure 2A-Figure 2E The five original images are all standard images with a pixel value of 512×512, and the Figure 2A-Figure 2E The five original images are used as carrier images, using the reversible information hiding method in the homomorphic encryption domain based on code division multiplexing and value expansion provided by the present invention, when the chip sequence length l=2, the experimental results of the value expansion parameter k=1 like Figures 3A-3E , 4A-4E shown. At this time, the embedding capacity of the image has reached 2bpp, and the image quality PSNR is 46.37dB, 46.36dB, 46.37dB, 46.72dB and 46.73dB respectively. It can be seen from the abo...
Embodiment 2
[0086] attached Figure 5 It is a relationship diagram between embedding capacity and image quality obtained by using an original image as a carrier image in Embodiment 2 of the present invention. In this embodiment, a standard image with a pixel size of 512×512 is used as a carrier image, and the homomorphic encryption domain reversible information hiding method based on code division multiplexing and value expansion provided by the present invention is adopted. When the chip sequence length l=2, Value expansion parameter k=1, 2, the relationship between the obtained embedded capacity payload and image quality PSNR is as follows Figure 5 shown. At the same time, with Wuet al.2016 (X.T.Wu, B.Chen J.Wei, Reversible data hiding for encrypted signals by homomorphic encryption and signal energy transfer, J.Vis.Commun.ImageRepresent.41(2016)58-64.), Shui et al.2015 (C.W.Shui, Y.C.Chen, W.Hong, Encrypted image-based reversible data hiding with public key cryptography from differe...
Embodiment 3
[0088] attached Image 6 is a histogram of the influence of chip sequence length and value extension parameters on the maximum embedding capacity of an image in Embodiment 3 of the present invention. like Image 6 As shown, in the process of hiding the secret information, if only the method of code division multiplexing is adopted, as shown in the figure, when l=2 and l=4, the maximum embedding capacity is respectively 1bpp and 3bpp; The reversible information hiding method of homomorphic encryption domain based on code division multiplexing and value expansion, that is, on the basis of code division multiplexing, also adopts the method of value expansion, as shown in the figure l=2, k=1, the maximum embedding capacity is 2bpp.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com