An intelligent optical fiber fusion splicer based on the Internet of Things
A technology of intelligent optical fiber and fusion splicer, which is applied in the field of optical fiber equipment, can solve problems such as dust, lower quality of optical fiber communication, and inability to adjust the strength of the clamping mechanism to clamp the optical fiber, so as to achieve the effect of improving quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The present invention will now be described in further detail with reference to the drawings. These drawings are all simplified schematic diagrams, which merely illustrate the basic structure of the present invention in a schematic manner, so they only show the structures related to the present invention.
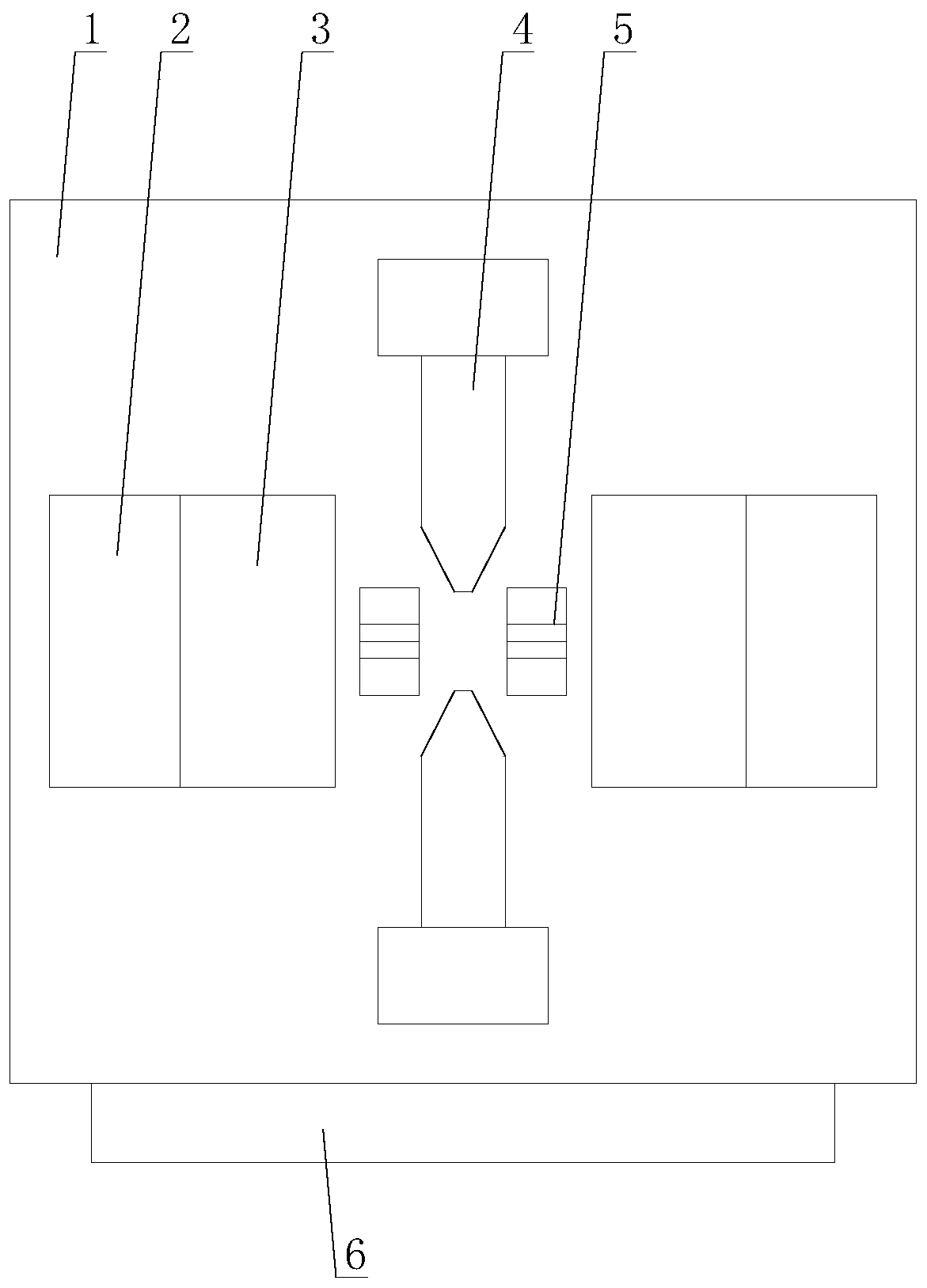
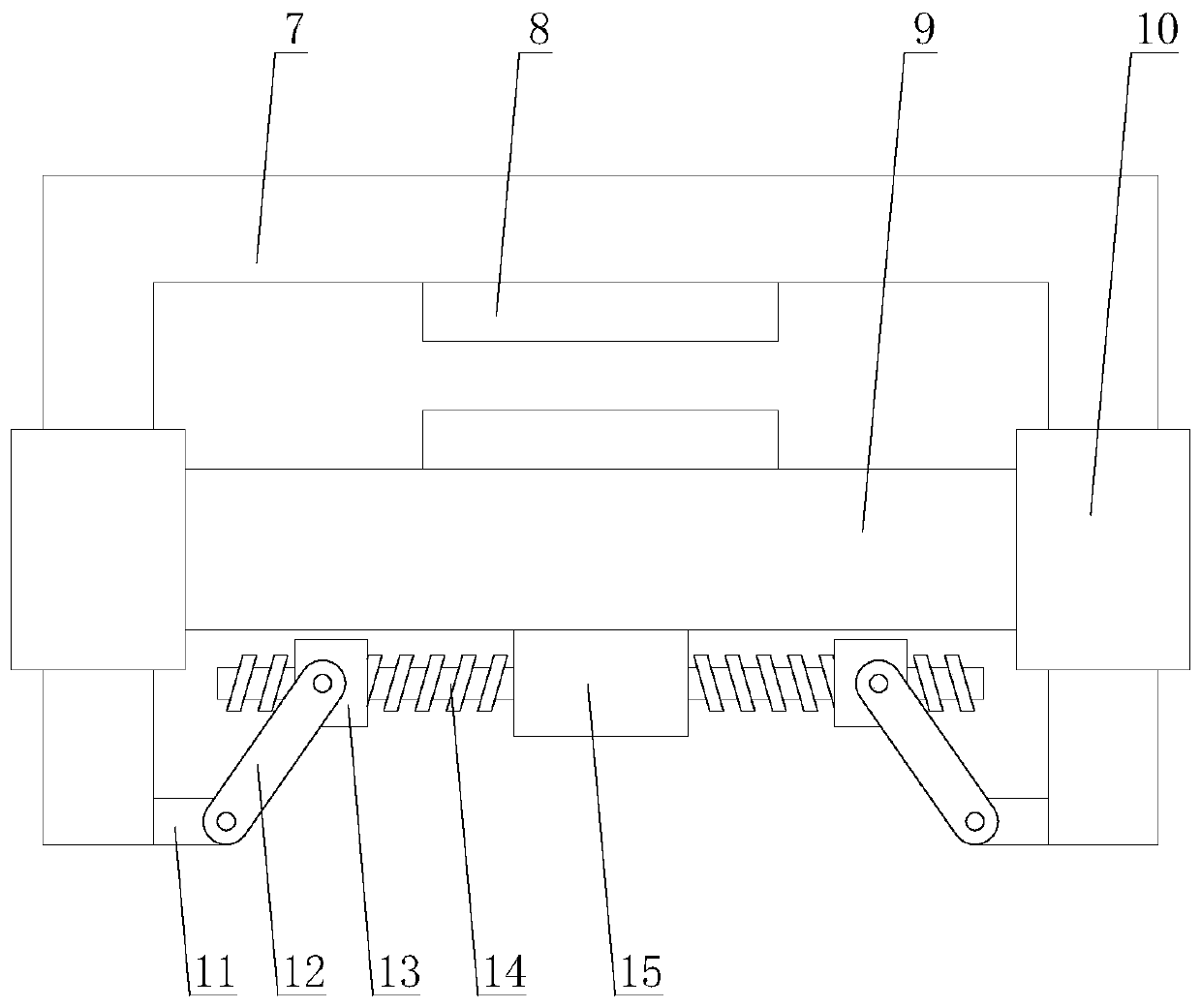
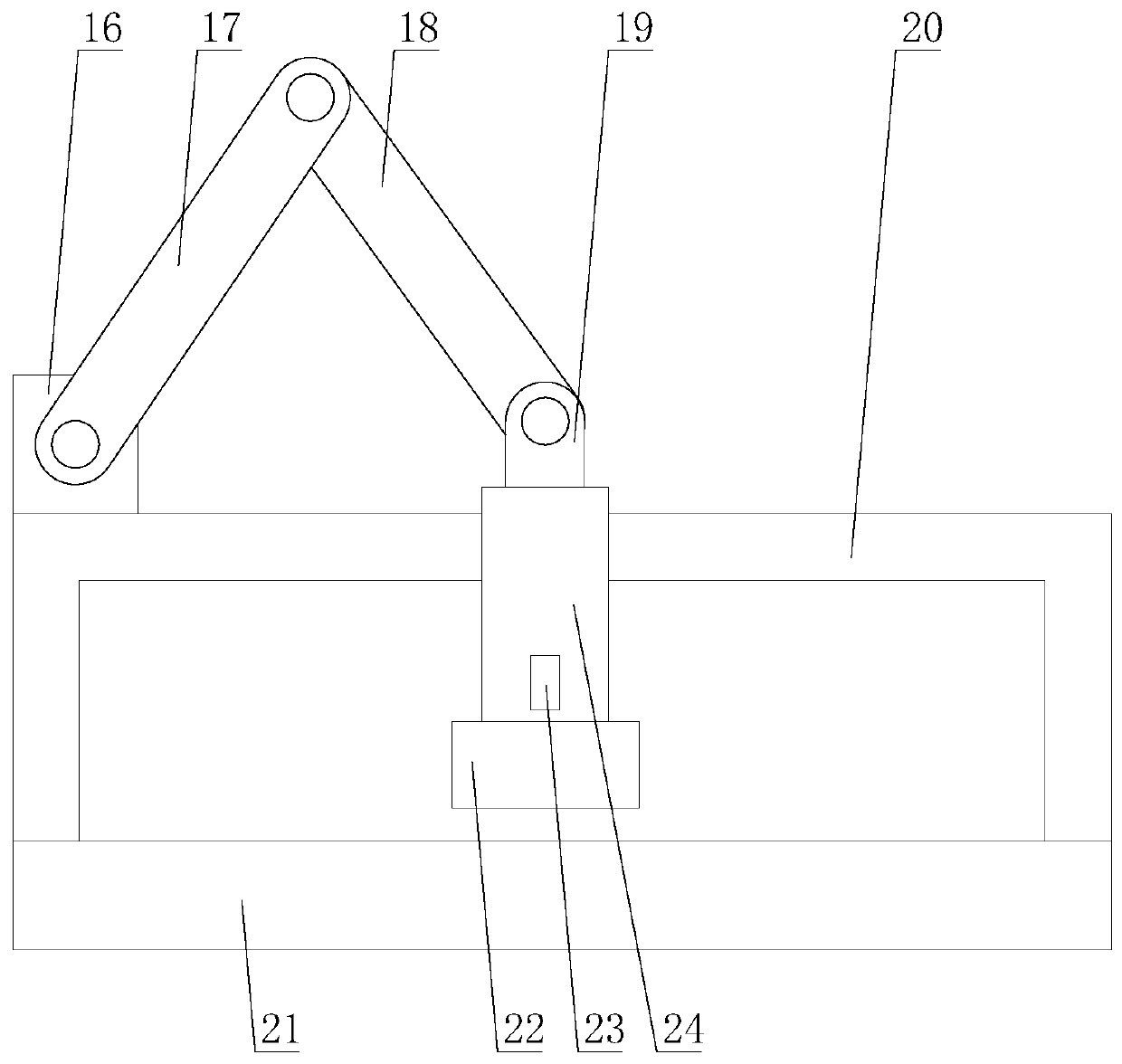
[0030] Such as Figure 1-Figure 5 As shown, an intelligent optical fiber fusion splicer based on the Internet of Things includes a body 1, a control panel 6, a central control mechanism, two wiping mechanisms 2, two clamping mechanisms 3, two electrodes 4 and two V-shaped grooves 5. The control panel 6 is arranged under the body 1, the two electrodes 4 are both arranged on the body 1, the two V-shaped grooves 5 are arranged in the middle of the two electrodes 4, and the two The clamping mechanism 3 is respectively arranged on one side of the two electrodes 4, the two wiping mechanisms 2 are respectively arranged on one side of the two clamping mechanisms 3, and the wip...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com