Method for analyzing CT scanning result based on box counting method
A technology of CT scanning and analysis method, which is applied in the field of industrial CT scanning, and can solve problems such as large error in results and loss of information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
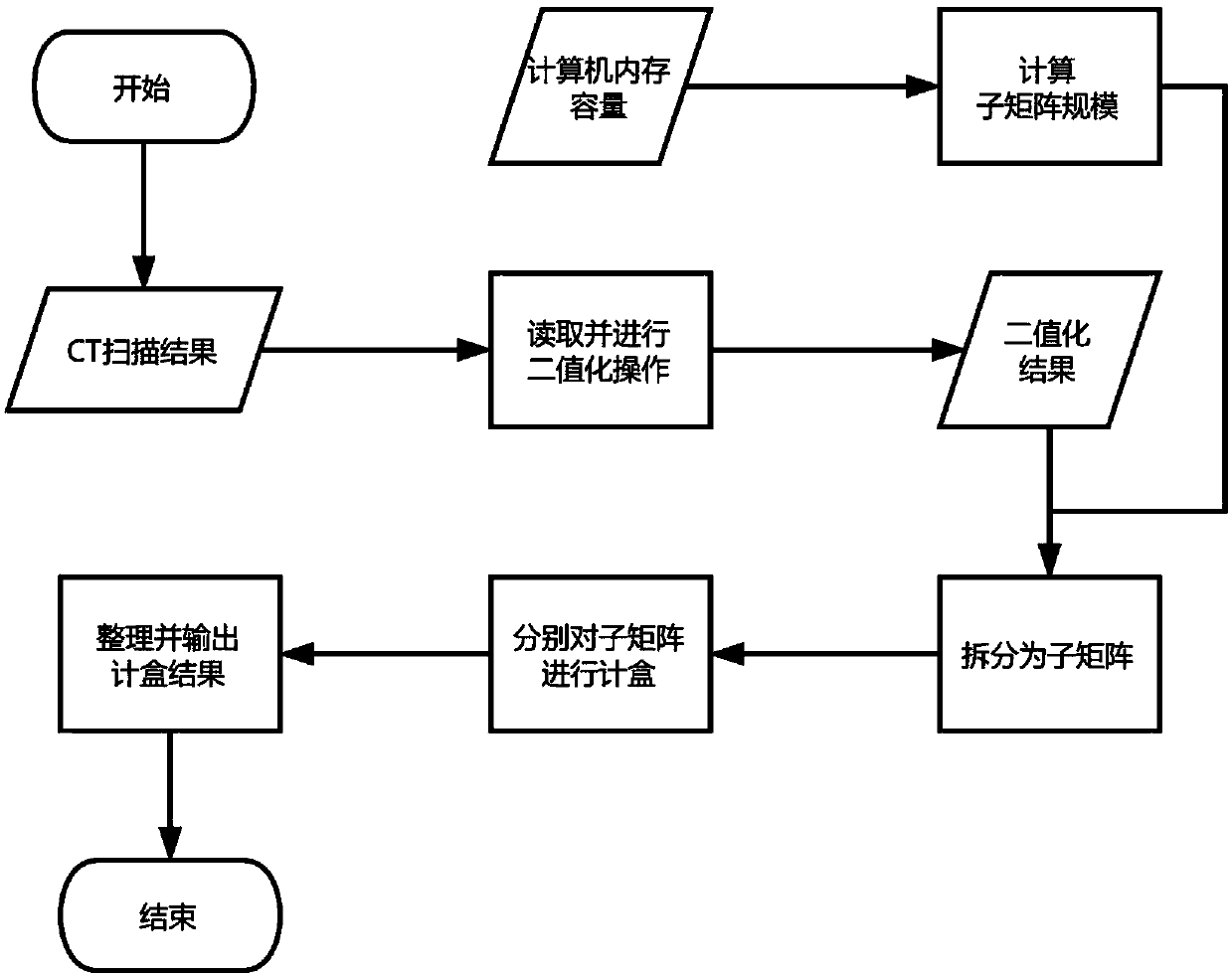
[0020] Specific implementation mode one: as figure 1 Shown, a kind of CT scan result analysis method based on counting box method comprises the following steps:
[0021] Step 1: The computer reads all CT scan pictures and performs binarization processing on all CT scan pictures, and obtains the binarization result of each picture as a two-dimensional matrix [A];
[0022] Step 2: Arrange the two-dimensional matrix [A] of all pictures obtained in step one according to the height order to obtain the three-dimensional matrix [C], and the number of layers of [C] is the number of CT scan pictures (the total number of tomograms);
[0023] Step 3: divide the three-dimensional matrix [C] that step two obtains into L three-dimensional sub-matrices according to the memory capacity of the computer itself;
[0024] Step 4: Carry out box counting to the L three-dimensional sub-matrices divided in step 3, and obtain a box counting result sequence;
[0025] Step 5: Integrate the box countin...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0027] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is: in the step 1, the computer reads the CT scan pictures and adopts the method of parallel computing to perform binarization processing on all CT scan pictures to obtain the value of each picture The specific process of binarizing the result into a two-dimensional matrix [A] is:
[0028] The element A in row i and column j in the two-dimensional matrix [A] is calculated from the pixels in the picture ij value; if the gray value of the i-th row and j-column pixel is greater than or equal to the threshold, then A ij The value of is counted as 1, otherwise it is counted as 0. The method of parallel computing is used to calculate as many pixels as possible at the same time.
[0029] If the CPU of the computer executing the invention has multiple threads at the same time, all the threads of the computer are called to process different pixels at the same time.
[0030] Other steps and...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0031] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the threshold is 50% of the default value of the computer or artificially set (according to the brightness of the picture).
[0032] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com