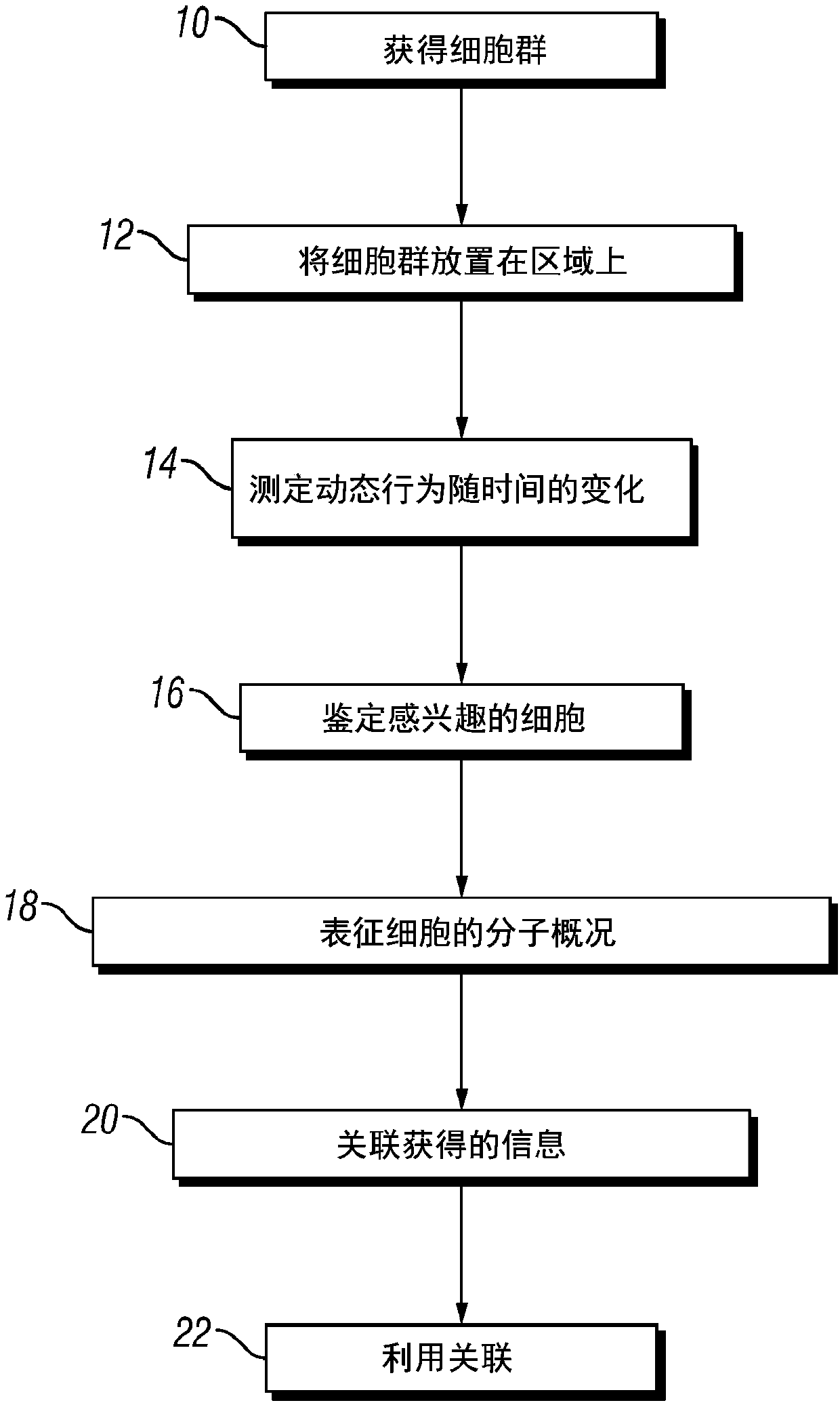
Integrated functional and molecular profiling of cells
A technology of cells and cell groups, applied in the direction of receptors/cell surface antigens/cell surface determinants, analysis materials, cancer antigen components, etc., can solve problems such as lack of integration capabilities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
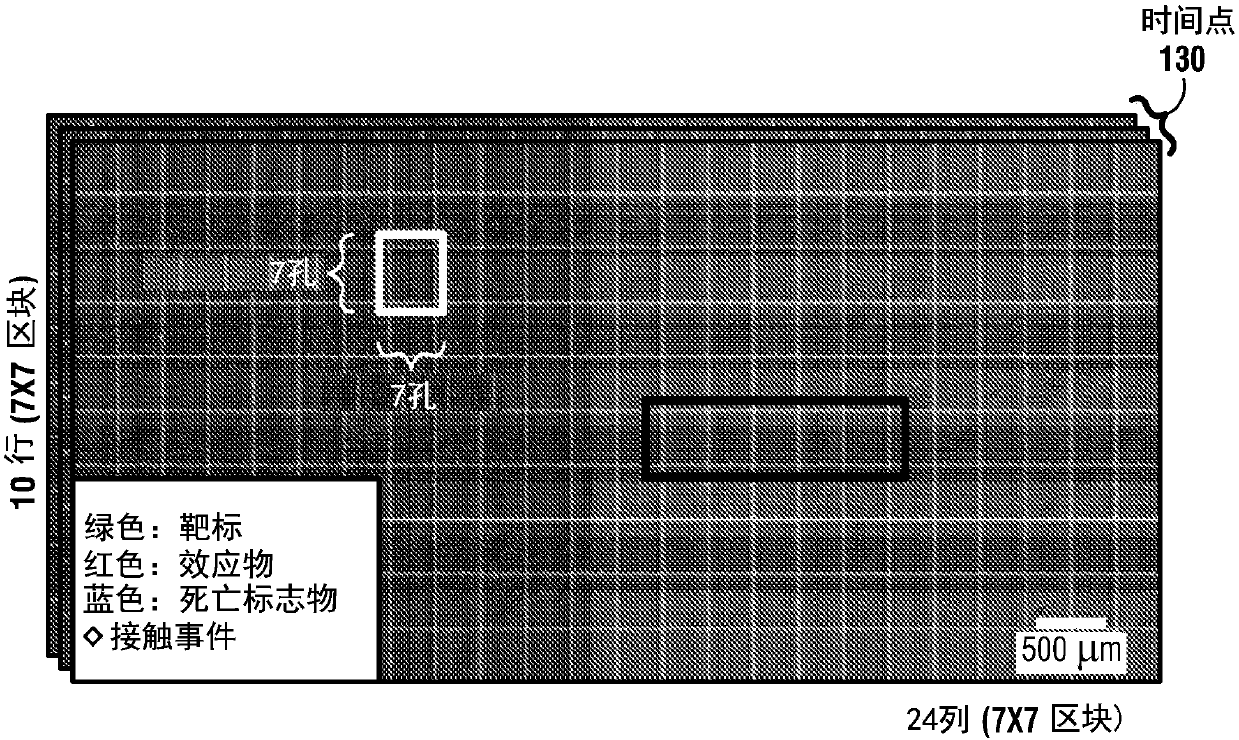
[0162] Example 1. Individual Cell-Cell Detection by High-Throughput Nanowell In-Grid Time-Lapse Imaging Microscopy (TIMING) Automatic overview of the interactions
[0163] In this example, fluorescently labeled human T cells, natural killer cells (NK), and various target cells (NALM6, K562, EL4) were placed in PDMS arrays with sub-nanoliter pores (nanopores) co-incubated and detected by multi-channel time-lapse microscopy. A novel cell segmentation and tracking algorithm that takes into account cell variability and nanopore limitations increases the yield of correctly analyzed nanopores from 45% (current algorithm) to 98% for nanopores containing effectors and single targets. This enables reliable automated quantification of cell location, morphology, movement, interaction, and death. Automated analysis of recordings from 12 different experiments demonstrated that, with default parameters, automated nanowell delineation was more than 99% accurate despite differences in il...
Embodiment 11
[0176] Example 1.1. Sample preparation and imaging
[0177] The TIMING dataset was derived from an ongoing study in which human T cells (genetically engineered to express a chimeric antigen receptor CAR) and natural killer (NK) cells were used as effectors. Human leukemia cell lines NALM6, K562 or mouse EL4 cells expressing appropriate ligands were used as targets (T).
[0178] Both cell types were washed once in serum-free medium, suspended to approximately 2 million / mL and labeled with PKH67 green and PKH26 red dyes, respectively, according to the manufacturer's (Sigma-Aldrich) instructions. Approximately 100,000 effector (E) cells were loaded onto the nanowell array, followed by approximately 200,000 target cells. Cells were allowed to settle within the nanotubes for 5 minutes, then excess cells were washed away.
[0179] Next, 50 μL of annexin V-Alexa Fluor 647 (AnnV-AF647, Life Technologies (Life Technologies)) in 3 mL of complete medium (PMI-1640+10% FBS, excluding p...
Embodiment 12
[0181] Example 1.2. Automatic positioning of nanopores
[0182] Automated positioning of nanowells is preferably used to delineate cell-confined regions, correct for stage repositioning errors, and decompose the entire TIMING dataset into a large number of motion-corrected video sequences, one for each nanowell. Preferably, this manipulation is reliable, since a single well-detection error can render a nanowell unusable for analysis, reducing experimental yield. Preferably, the manipulation must be process robust against focus drift (taking into account shrinkage / expansion / irregularities of the polymer matrix), holes with compromised geometry, variations in illumination, ringing artifacts, and debris or air bubbles possible will be displaced, appearing / disappearing abruptly in time from the camera's field of view ( Figure 4A ).
[0183] Content-independent image registration methods like SIFT are neither sufficiently reliable nor practical for TIMING data. They require t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com