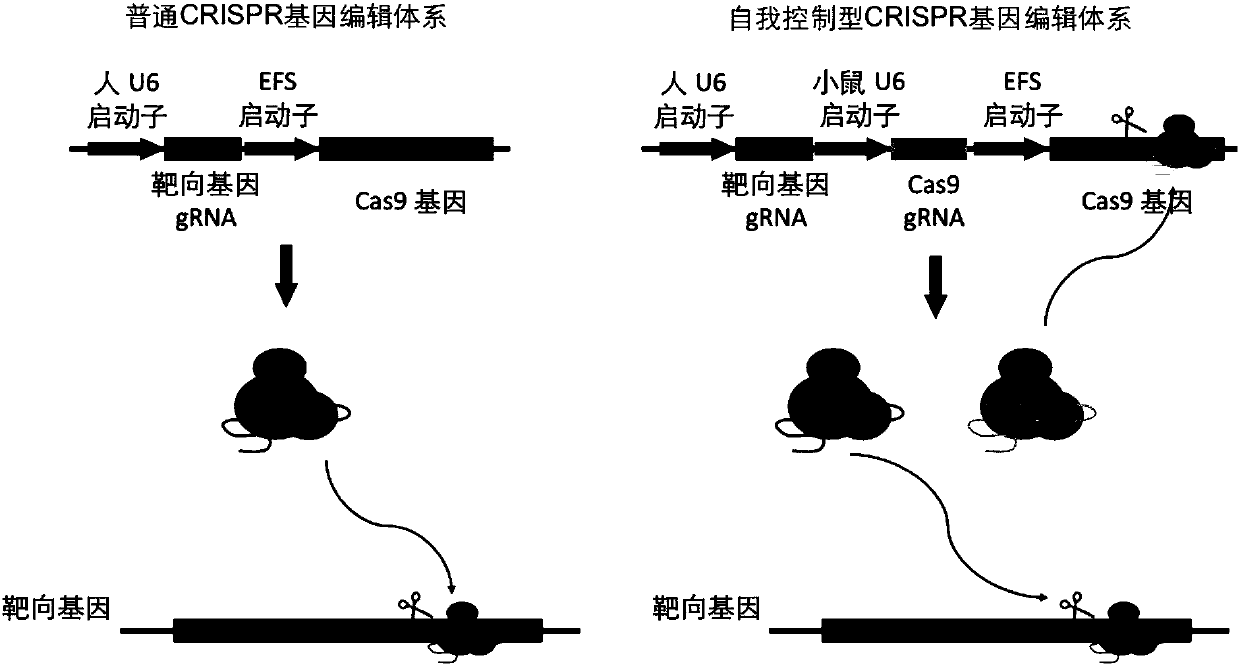
Highly specific CRISPR genome editing system
A genome editing, high-specificity technology, applied in the field of high-specificity CRISPR genome editing system, can solve problems hindering the application of genome editing technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Example 1 Design and screening of highly active gRNA targeting Cas9
[0084] Experimental steps:
[0085] 1) Through sequence alignment, design five highly active gRNAs targeting the Cas9 sequence, and the gRNA sequences are shown in Table 1.
[0086] 2) Clone five gRNAs into the lentiCRISPR v2 vector (addgene#52961)
[0087] 3) Infect 293T cells after packaging lentivirus respectively
[0088] 4) The cells were harvested at 48h and 96h after infection, and the Cas9 gene cleavage of the cells was analyzed by the T7E1 detection kit; and the Cas9 protein expression was analyzed by Western blotting reaction
[0089] Table 1 Targeting gRNA sequence designed for Cas9 and primer sequence information for T7E1 detection
[0090]
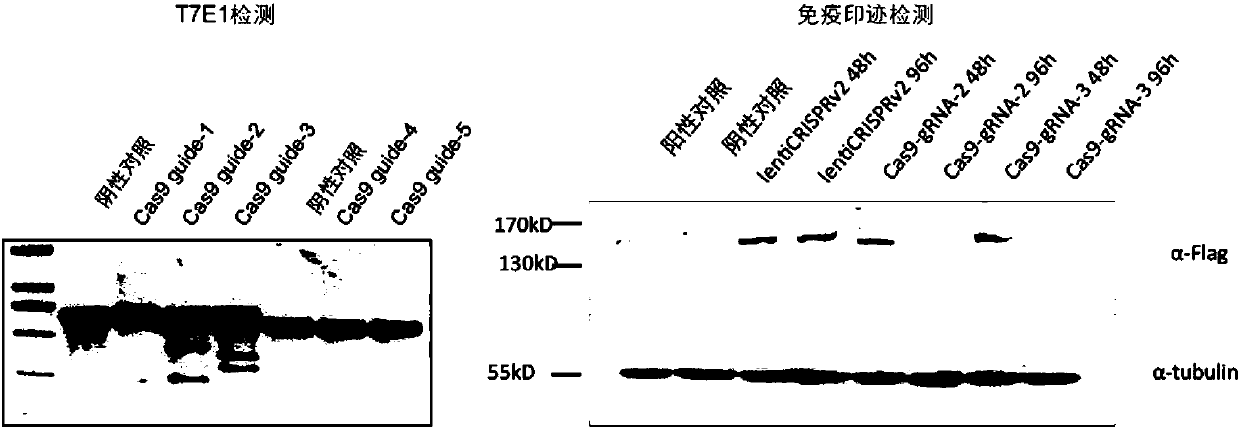
[0091] Experimental results such as figure 2 As shown, the left figure shows the T7E1 detection results. In the negative control group, the band did not cut, but in the Cas9guide-2 and Cas9guide-3 groups, the band clearly cut, showing guide-2 ...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Example 2 Construction of SeT CRISPR lentiviral vector
[0093] Experimental steps:
[0094] 1) In the synthetic plasmid pmU6-gRNA (synthesized by Jinweizhi Company, its sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.11), which contains the backbone sequence of the guide RNA targeting the genome of the target cell and the mouse U6 promoter, and in the mouse The 5' of the U6 promoter and the 3' of the gRNA backbone sequence have an EcoRI restriction enzyme cleavage site;
[0095] The sequence of the synthetic plasmid pmU6-gRNA is as follows (SEQ ID NO.11):
[0096] GAATTCAGATAGATCCGACGCCGCCATCTCTAGGCCCGCGCCGGCCCCCTCGCACAGACTTGTGGGAGAAGCTCGGCTACTCCCCTGCCCCGGTTAATTTGCATATAATATTTCCTAGTAACTATAGAGGCTTAATGTGCGATAAAAGACAGATAATCTGTTCTTTTTAATACTAGCTACATTTTACATGATAGGCTTGGATTTCTATAAGAGATACAAATACTAAATTATTATTTTAAAAAACAGCACAAAAGGAAACTCACCCTAACTGTAAAGTAATTGTGTGTTTTGAGACTATAAATATCCCTTGGAGAAAAGCCCACCTTGTCTTCGAGAAGACCTGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTAAAATAAGGCTAGTCCGTTATCAACTTGAAAAAGTGGCACCGAGTCGGTGCTTTTTTTGTA...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Example 3 Verify whether there is a difference in the gene targeting efficiency between the SeT CRISPR lentiviral system and the common CRISPR lentiviral system
[0100] Experimental steps:
[0101] 1) Taking the human P53 gene as an example, construct a common CRISPR lentivirus system (marked as "P53gRNA") and a SeT CRISPR lentivirus system (marked as "P53gRNA+Cas9gRNA")
[0102] 2) Infect human liver cancer cell line Huh7 after packaging lentivirus respectively
[0103] 3) Cells were harvested on day 4 and day 8 after infection, and the cleavage of P53 and Cas9 target sites were detected by T7E1 kits
[0104] Table 2. Targeting gRNA sequences designed for P53, and primer sequence information for T7E1 detection
[0105]
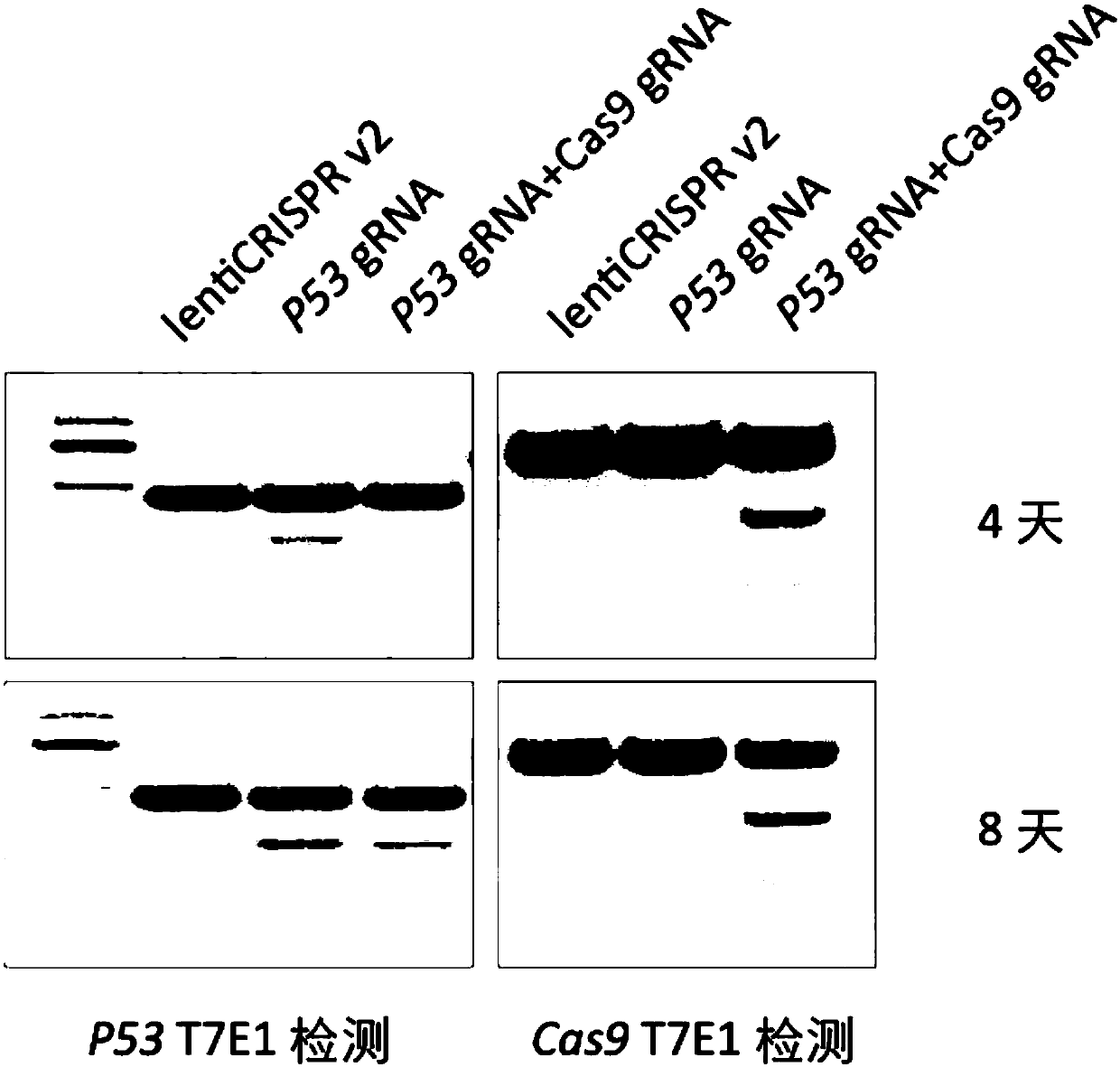
[0106] Experimental results such as image 3 As shown, in the P53T7E1 detection results, the negative control lentiCRISPR v2 group bands did not cut, while the P53gRNA and P53gRNA+Cas9gRNA group bands were clearly cut (the target band was 245bp+...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com