Antimicrobial materials exhibiting synergistic efficacy
A technology for biocides and coatings, applied in the direction of biocides, chemicals for biological control, biocides, etc., which can solve problems such as insufficient antibacterial activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] Examples 1A-1F were prepared to evaluate fungal growth control according to ASTM 5590. Examples 1A-1F include the formulations shown in Table 1. The copper-containing glass particles used in Examples 1B-1F included the following composition: 45 mole % SiO 2 , 35 mol% CuO, 7.5 mol% K 2 O, 7.5 mol% of B 2 o 3 and 5 mol% P 2 o 5 .
[0097] Table 1: Examples 1A-1F
[0098]
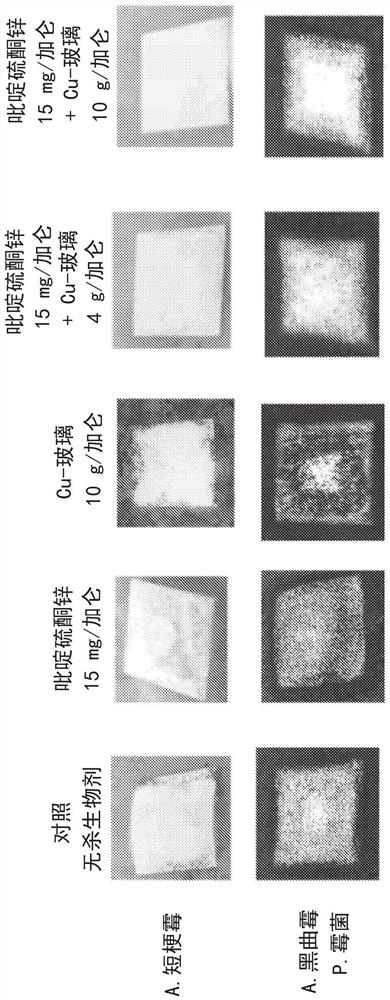
[0099] The coatings of Examples 1A-1F were applied to the same paper substrate and exposed to A. pullulans (mold) or A. niger by direct contact with a suspension of the corresponding fungus (A. niger) / P. fungi (P. funiculosum) (mold). Inoculated samples were placed in a sealed and humid environment at 30°C / saturated humidity and incubated for 28 days. Antifungal performance was determined by visual assessment of the percent fungal growth on the coating. Each substance was scored numerically based on the percent growth observed: 0 = no growth, 1 = trace growth (less than 10%), 2 = slight gro...
Embodiment 2
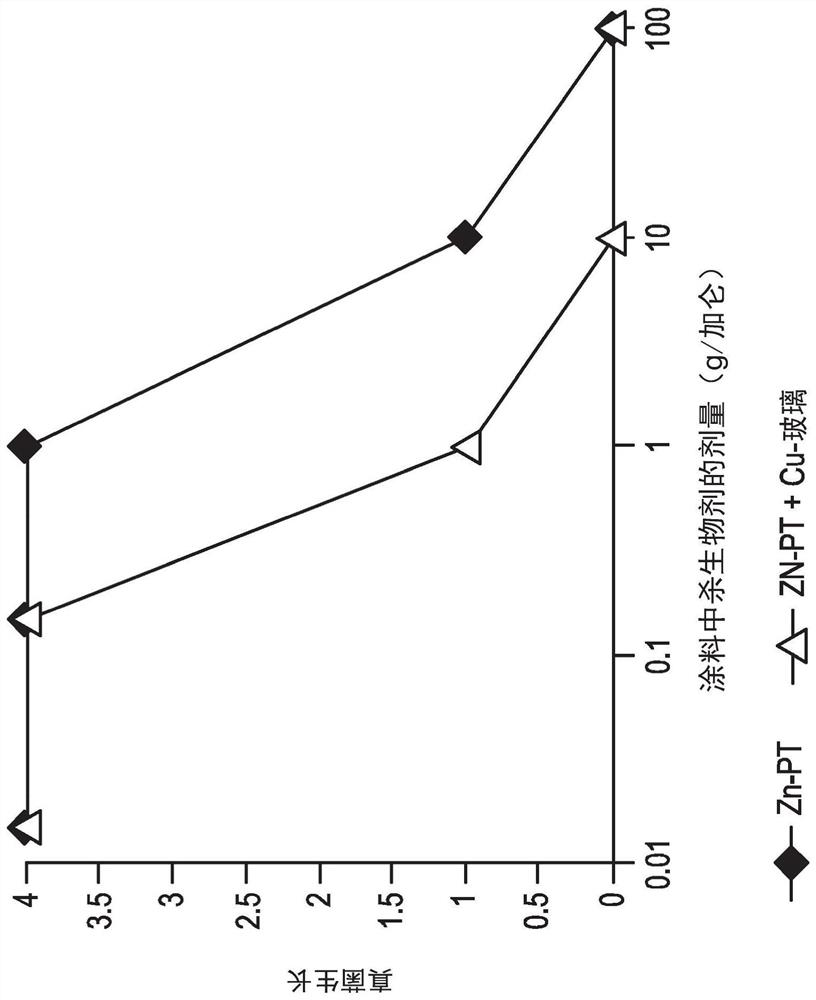
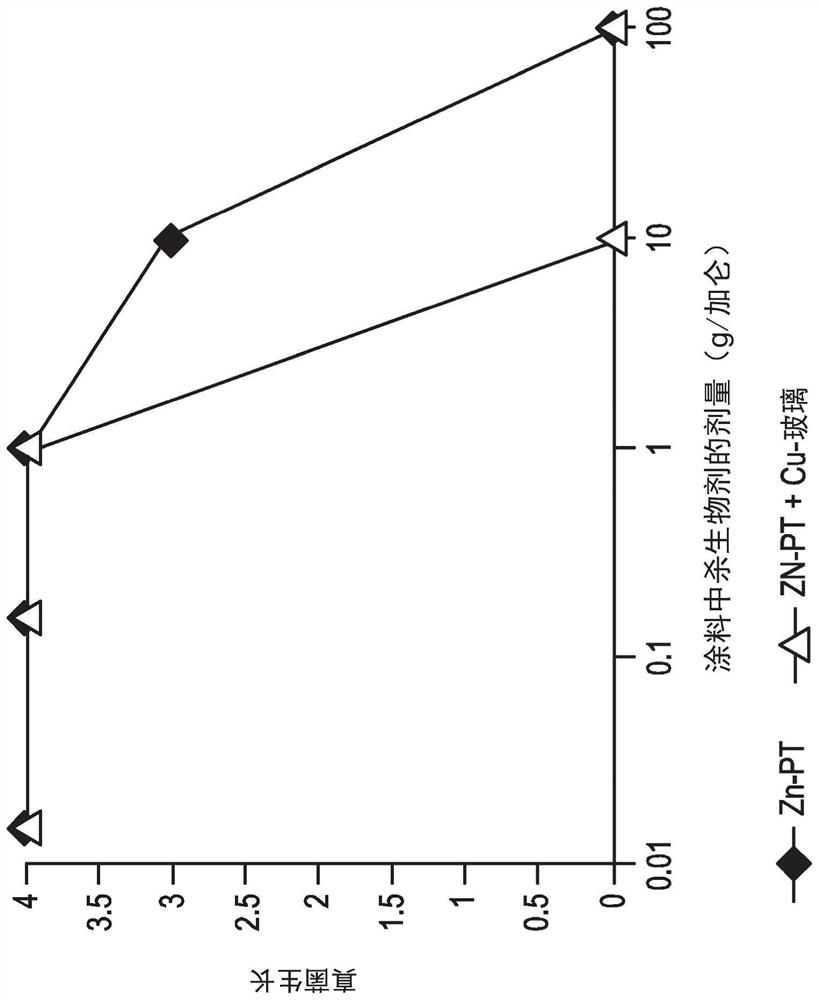
[0104] Evaluation of the amount of ZnPT and copper-containing glass required to inhibit fungal growth. The copper-containing glass had the same composition as used in Examples 1A-1F. like figure 1 and 2 As shown, the combination of ZnPT and copper-containing glass inhibited fungal growth at a lower amount than ZnPT alone. figure 1 showed that only 1 g / gallon of ZnPT and copper-containing glass was needed to reduce mold growth (10 g / gallon for ZnPT alone). figure 2 showed that only 10 g / gallon of ZnPT and copper-containing glass was needed to reduce mildew growth (100 g / gallon for ZnPT alone).
Embodiment 3
[0106] Evaluation of the color of coatings containing ZnPT and copper-containing glass. Examples 3A-3D contained the same biocide-free Control Paint A as used in Example 1 . Example 3A did not contain any ZnPT or copper-containing glass particles. Examples 3B-3D contained 1 g / gallon, 5 g / gallon, and 10 g / gallon of copper-containing glass particles, respectively. None of Examples 3A-3D contained ZnPT. As shown in Table 3, minimal color change was observed at concentrations up to 10 g / gallon. ΔE in Table 3 is the color coordinate relative to Example 3A. Specifically, for embodiments 3B-3D, the equation √(((L*-L* 实施例3A ) 2 +(a*-a* 实施例3A ) 2 +(b*-b* 实施例3A ) 2 ) to determine the ΔE of Examples 3B-3D.
[0107] Table 3: L*, a*, b* and ΔE values for Examples 3A-3D relative to Example 3A
[0108] Example L* a* b* ΔE Comparative Example 3A 96.46 -0.03 1.58 Example 3B 96.53 0.08 2.03 0.47 Example 3C 95.86 0.44 2.79 1.43 Example...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com