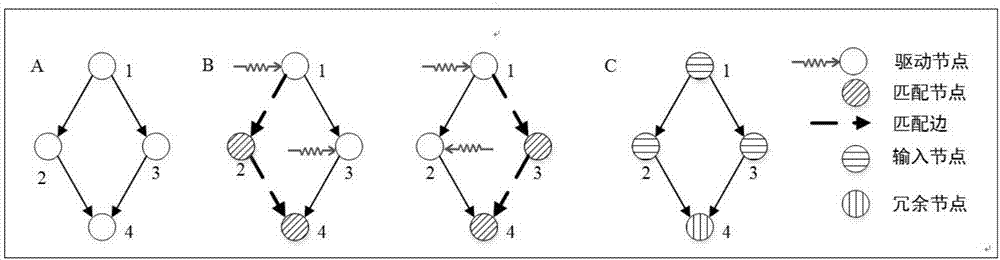
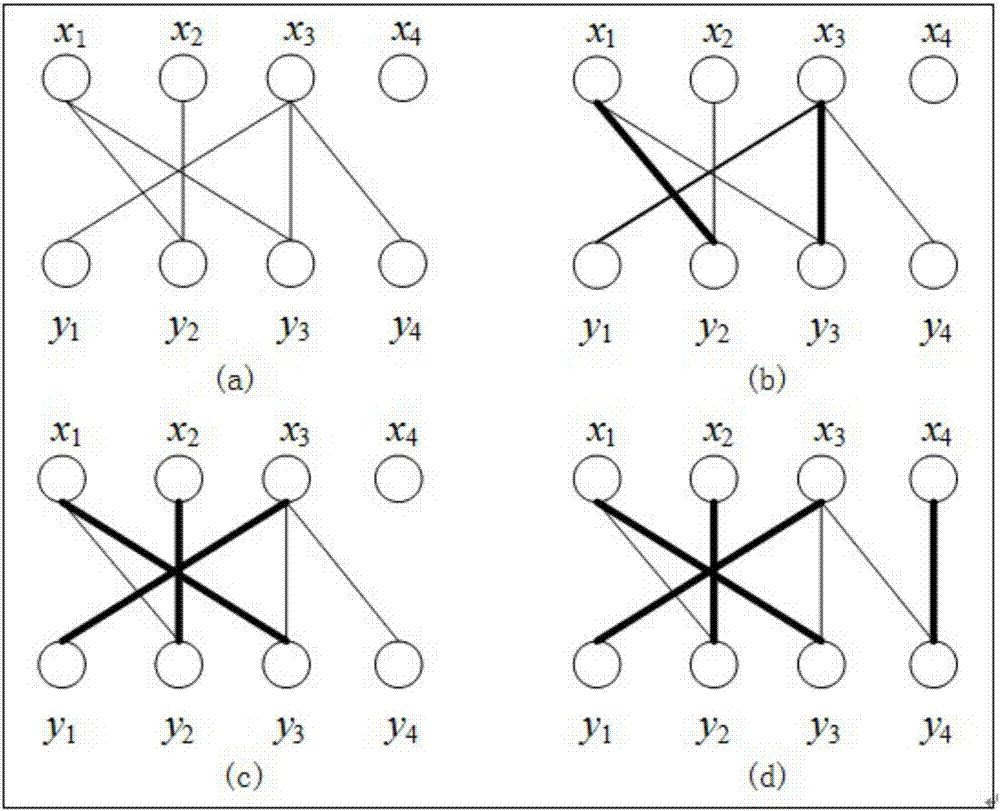
Method for changing node control category in complex network
A technology of node control and complex network, applied in the network field, it can solve the problems of large number of nodes that cannot be converted into a single node, and achieve the effect of enhancing controllability, reducing conversion cost and high efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] like Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for changing the node control category in a complex network, and the method of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0089] Step 101 , for the redundant node n to be processed, obtain all unsaturated nodes in the network that can reach the redundant node n through an interleaving path.
[0090] For example, step 101 of this embodiment may include the following sub-steps not shown in the figure:
[0091] 1011. For the redundant node n, obtain all non-matching incoming edges of the redundant node n in the network, and add nodes corresponding to all non-matching incoming edges to the first queue C;
[0092] 1012. Traverse the nodes in the first queue C, and if the traversed nodes belong to unsaturated nodes that have not been visited, then update the unsaturated node set U, the edge set E', and the node set V';
[0093] 1013. If the traversed node has not been visited and is not an unsaturated node, obtai...
Embodiment 2
[0128] For the network (G, M, n), the specific process of the method in this embodiment is as follows:
[0129] Step1: For the redundant node n, let the queue Q=Q+{n}, find the matching incoming edge e(s,n) of n, V'={s}.
[0130] Step2: Take a node v from the queue Q, Q=Q-{v}, its matching incoming edge is e(m,v); find the non-matching incoming edge {e(c1,v,),...,e(ci, v)}, join the queue C=C+{c1,...,ci}.
[0131] Step3: Take a node c that is not s from the queue C, C=C-{c};
[0132] If c has been visited, then E'=E'+{e(m,c)}, turn to Step3;
[0133] If all outgoing edges of c are not in the maximum matching M, then U'=U'+{c}, E'=E'+{e(m,c)}, V'=V'+{c}, go to Step3 .
[0134] Otherwise, find the matching edge e(c,k) of c, let Q=Q+{k}, E'=E'+{e(m,c)}, V'=V'+{c}, c mark is visited. Repeat Step3 until C is empty.
[0135] Step4: Repeat Step2 and Step3 until Q is empty.
[0136] Step5: Add virtual node t, let V'=V'+{t};
[0137] For nodes {u1,u2,…,ui} in U’,
[0138] Add...
Embodiment 3
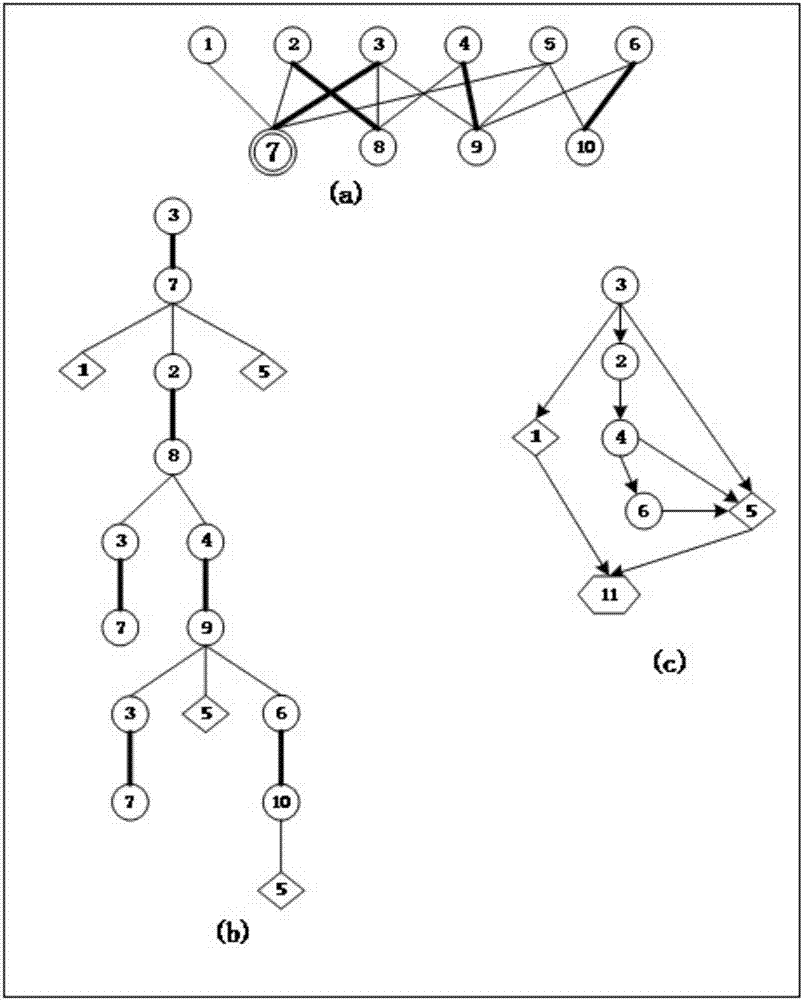
[0152] In the embodiment of the present invention, in order to illustrate the process of converting redundant nodes into driving node algorithms, this embodiment provides a simple network ( image 3 ) in the transformation process of nodes.
[0153] Step S1, first use the maximum matching HK algorithm to find a maximum matching, image 3 Medium-thick edges represent matching edges, thin edges represent non-matching edges, double-circle nodes represent target nodes, diamond-shaped nodes represent unsaturated nodes, and hexagonal-shaped nodes represent newly added virtual nodes t. Edge weight defaults to 1. For the target node 7, add 7 to the queue Q, and its matching incoming edge is e(3,7), V'={3}, M=3. In this embodiment, the target node is the redundant node 7, and its corresponding node corresponding to the matching incoming edge is denoted as s.
[0154] Step S2, take out node 7 from Q, its matching incoming edge is e(3,7), find all non-matching incoming edges e(1,7), e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com