A mems microstructure four-axis base excitation device driven by stacked piezoelectric ceramics
A piezoelectric ceramic drive and excitation device technology, which is used in measurement devices, machine/structural component testing, vibration testing, etc., can solve problems such as inflexibility, increased error in measurement results, and complex adjustment processes, and achieve smooth adjustment processes. , The effect of reducing shear force and accurate measurement value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
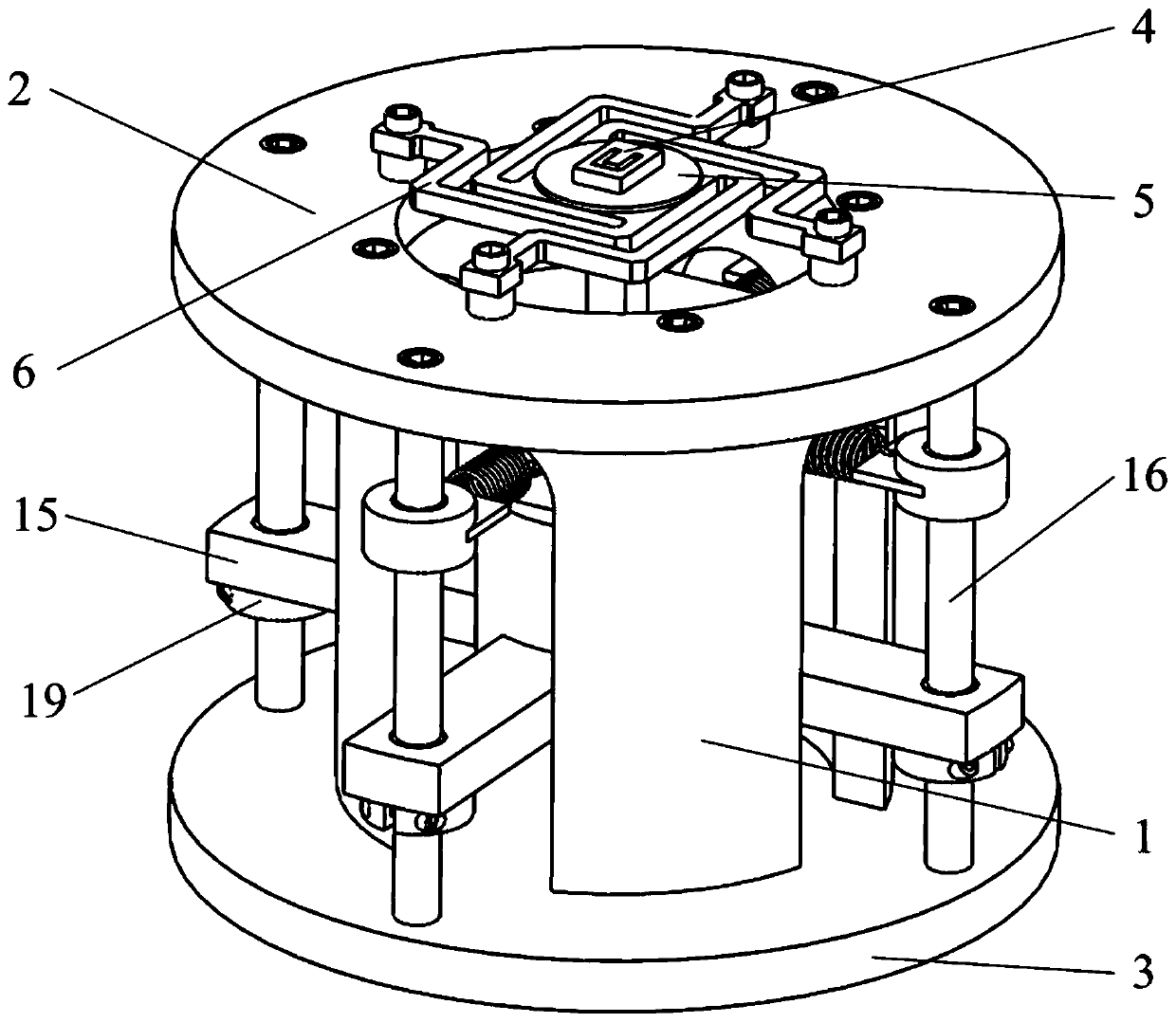
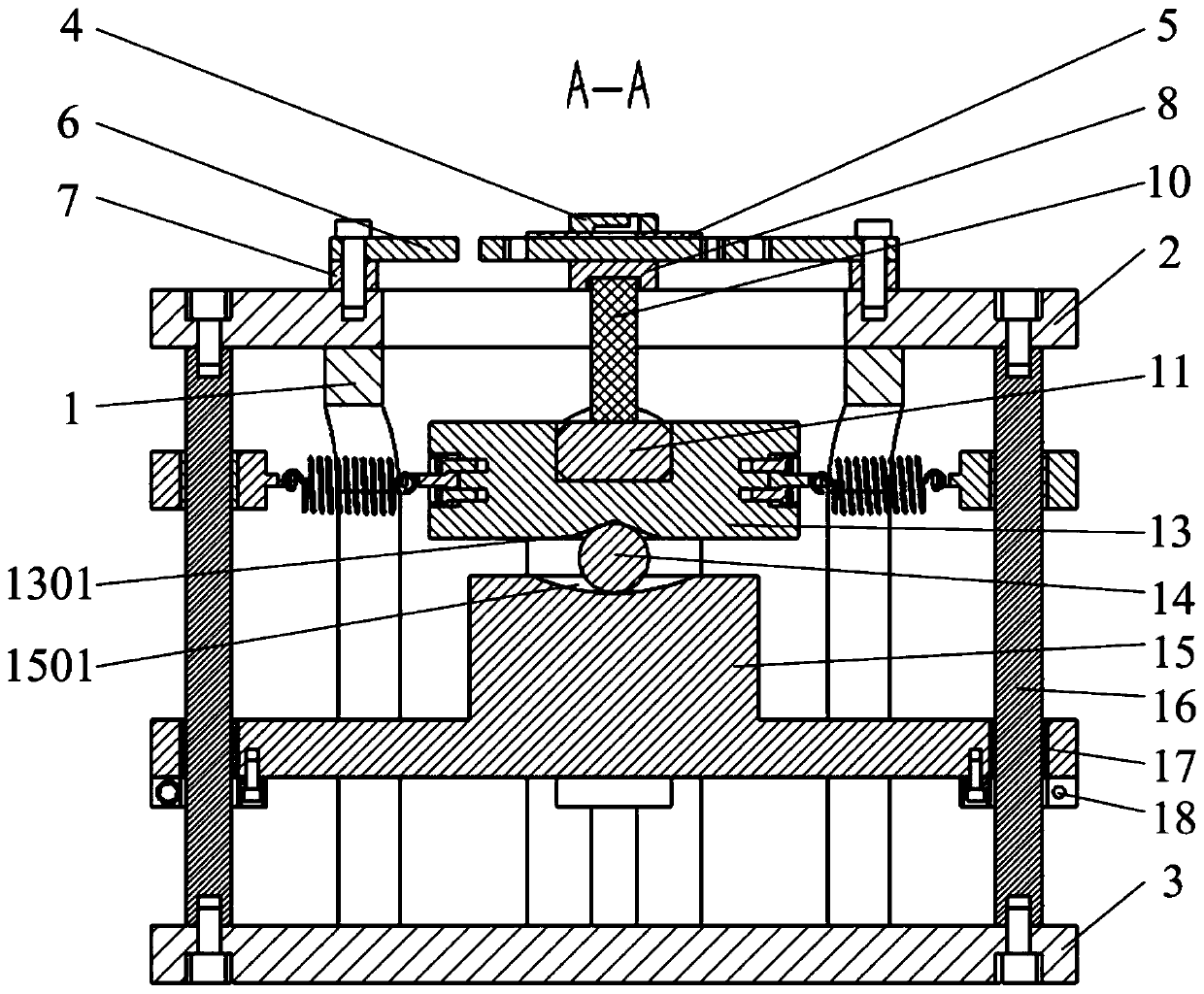
[0038] like Figure 1 to Figure 7 As shown, the present invention relates to a MEMS microstructure four-axis base excitation device driven by stacked piezoelectric ceramics, comprising a hollow sleeve 1, in which stacked piezoelectric ceramics 10, a pressure sensor 11 and a movable base composed of an upper coupling block 13, a steel ball 14 and a lower coupling block 15, and an elastic support 6 and a MEMS microstructure 4 are arranged on the sleeve 1.
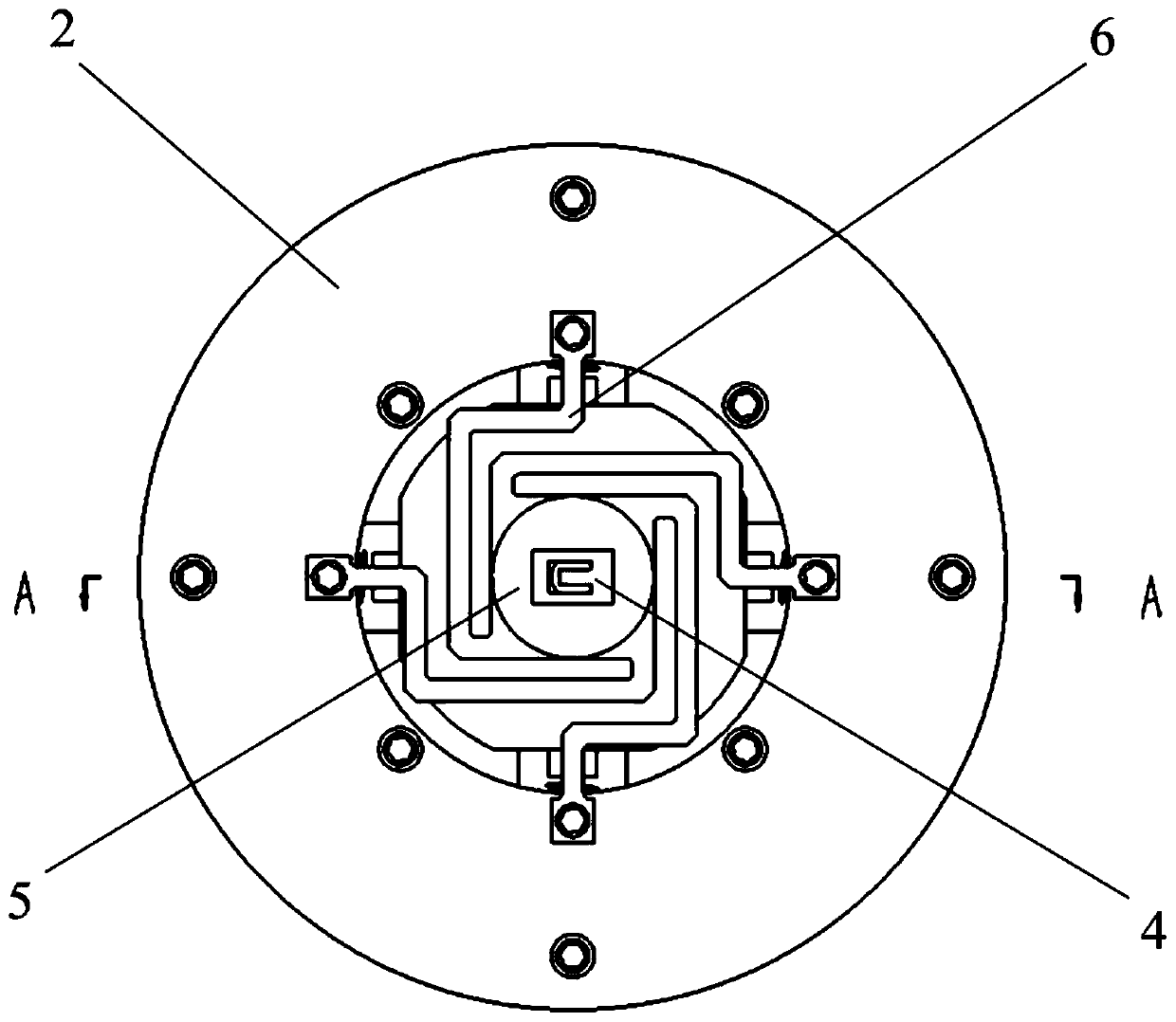
[0039] An annular top plate 2 and a bottom plate 3 are respectively fixed on the upper surface and the bottom surface of the sleeve 1 by screws, and the MEMS microstructure 4 is mounted on the annular top plate 2 through an elastic support 6 . The elastic supporting member 6 includes a square base plate 602 and four support arms 601 uniformly distributed on the circumference, each support arm 601 is composed of a first connecting arm 6011, a second connecting arm 6012, and a third connecting arm that are vertically connected ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com