A mems microstructure four-axis excitation device driven by piezoelectric ceramics
A piezoelectric ceramic drive and excitation device technology, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, machine/structural component testing, vibration testing, etc., can solve the problem of inaccurate pre-tightening force or piezoelectric ceramic output force, large parallelism error, and insufficient Flexibility and other issues to achieve the effect of avoiding the interference of the pressure sensor, accurate pre-tightening force data, and smooth adjustment process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
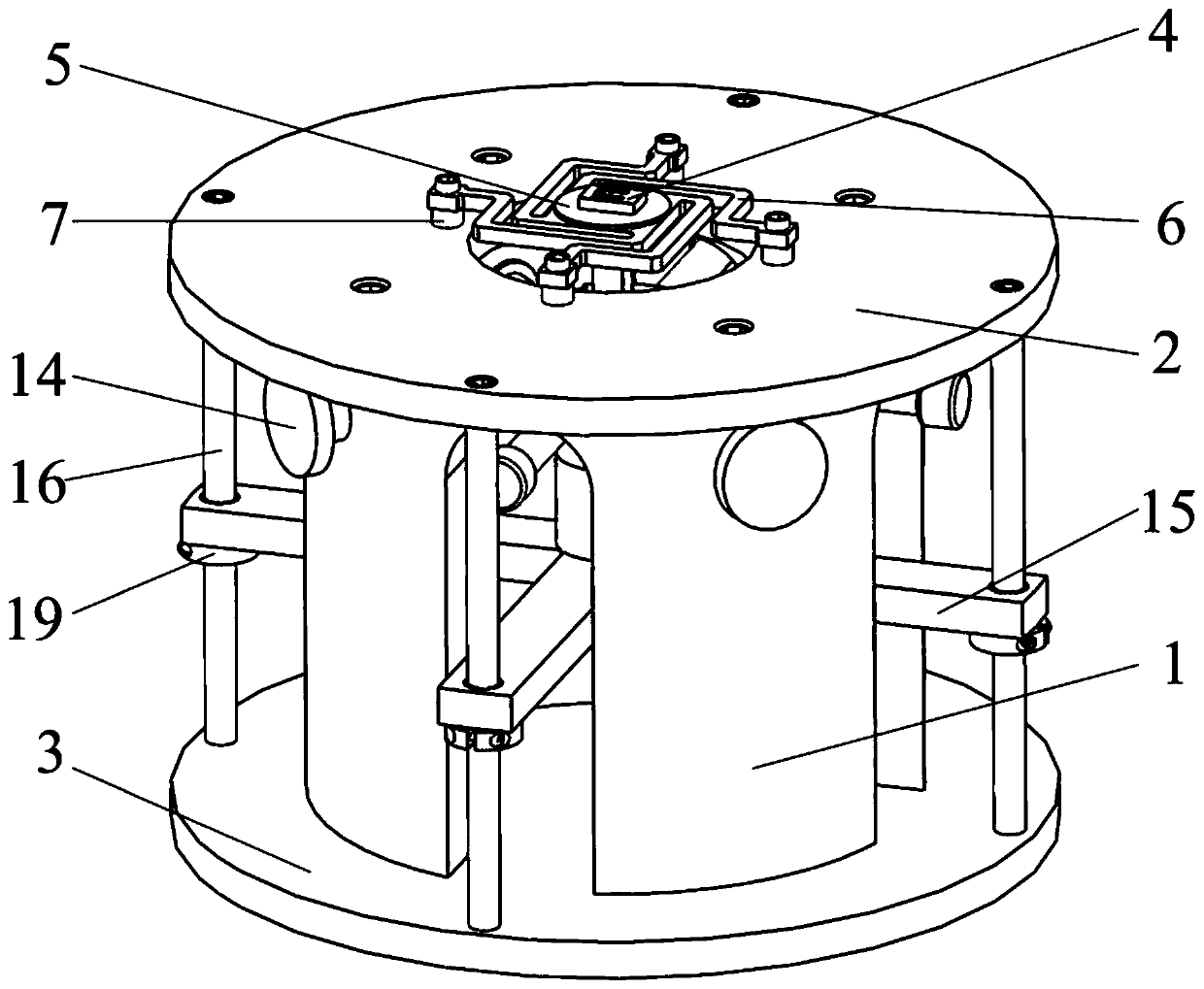
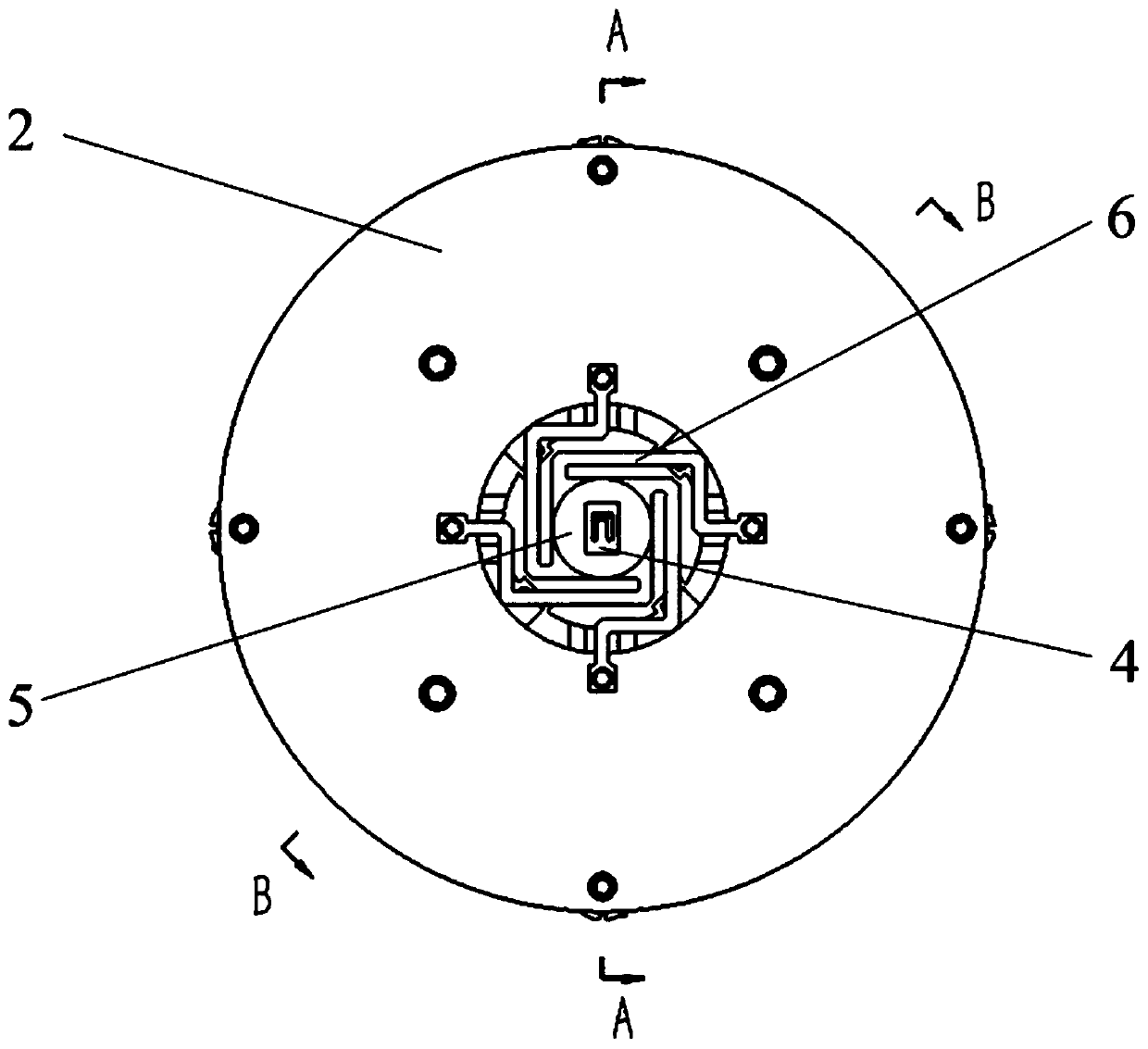
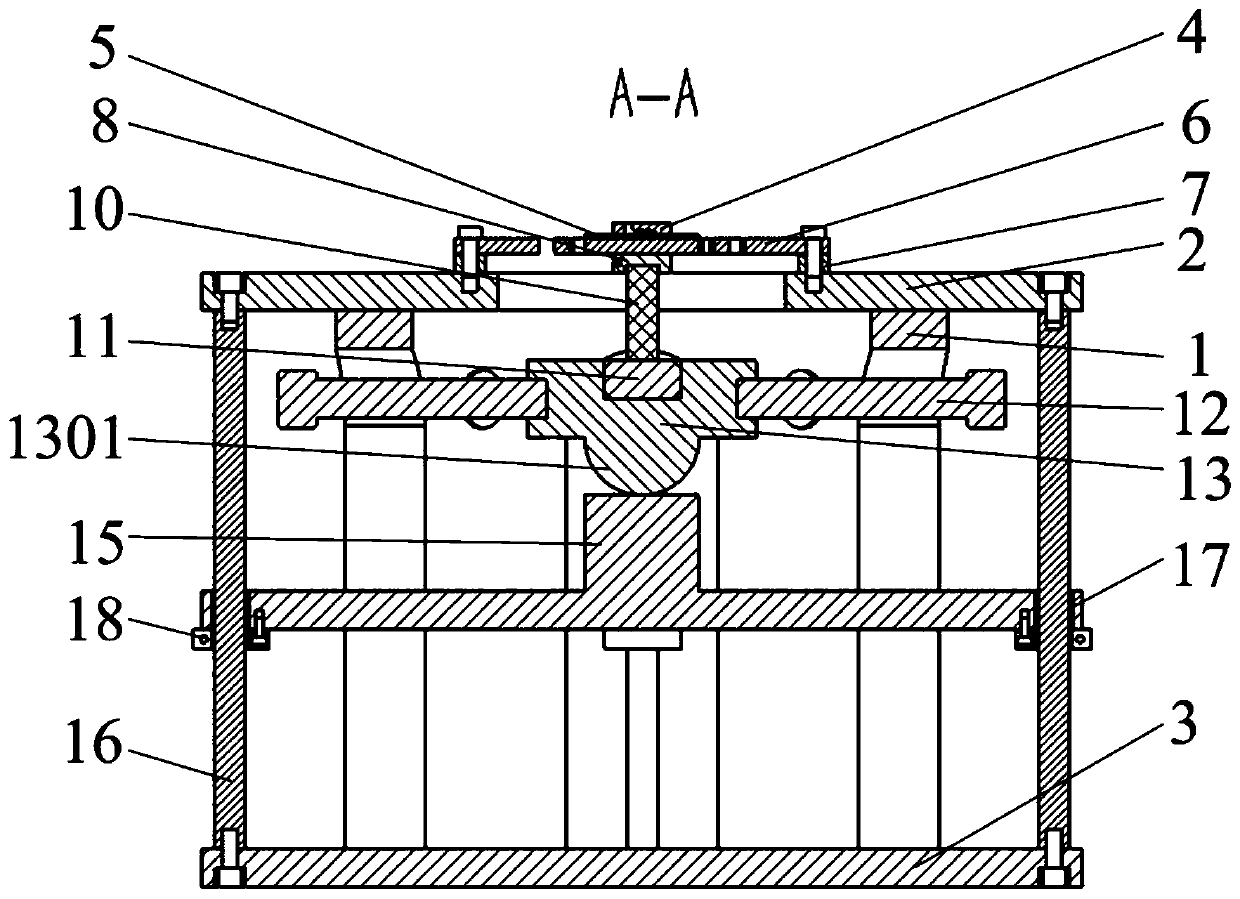
[0041] like Figure 1 to Figure 8 As shown, the present invention relates to a MEMS microstructure four-axis excitation device driven by piezoelectric ceramics, comprising a hollow sleeve 1, in which a stacked piezoelectric ceramic 10, a pressure sensor 11 and a The movable base formed by the upper coupling block 13 and the lower coupling block 15 is provided with an elastic support 6 and a MEMS microstructure 4 on the sleeve 1 .
[0042] An annular top plate 2 and a bottom plate 3 are respectively fixed on the upper surface and the bottom surface of the sleeve 1 by screws, and the MEMS microstructure 4 is mounted on the annular top plate 2 through an elastic support 6 . The elastic support includes a square base plate 602 and four support arms 601 uniformly distributed around the circumference, each support arm 601 is composed of a first connecting arm 6011, a second connecting arm 6012, and a third connecting arm 6013 which are vertically connected in sequence. Composed of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com