Quantitative survey device for submerged plants in lakes and reservoirs and survey method
A technology for submerged plants and lakes, which is applied to measurement devices, sampling devices, and test plants/trees, etc., can solve problems such as inapplicability to deep-water areas and inability to quantitatively collect submerged plants, and achieves that it is not easy to malfunction, is easy to maintain, and is suitable for wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
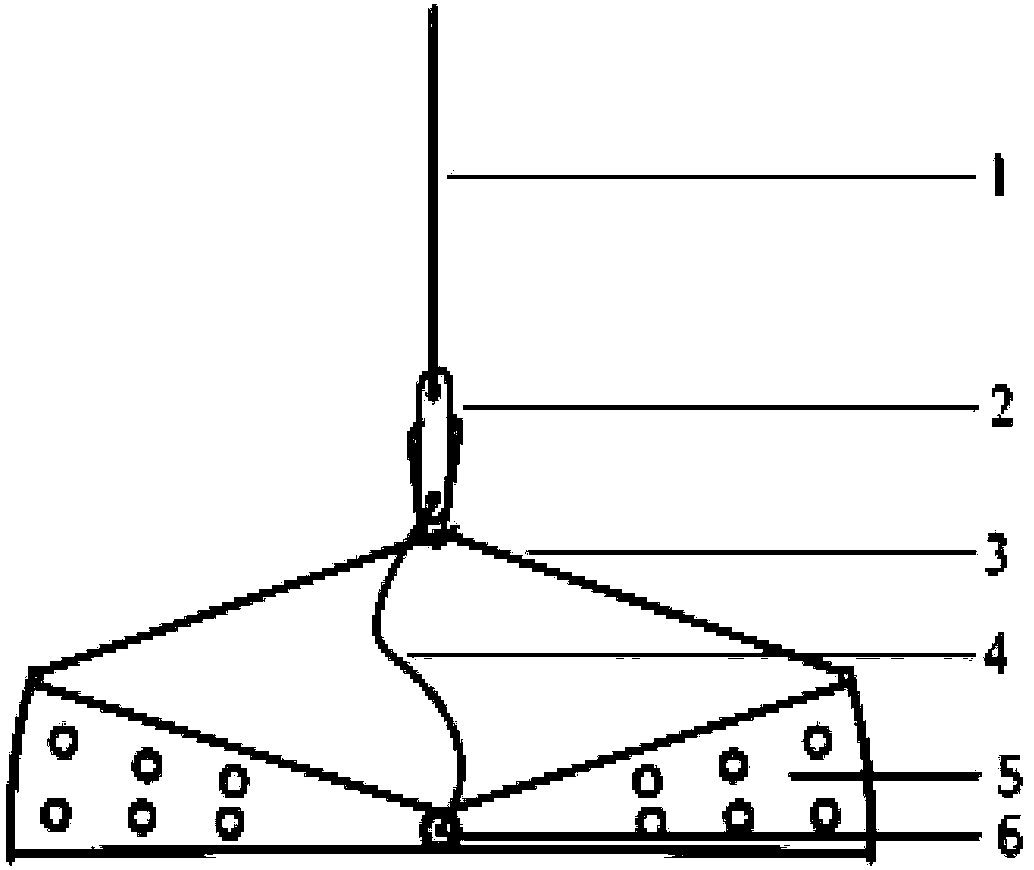
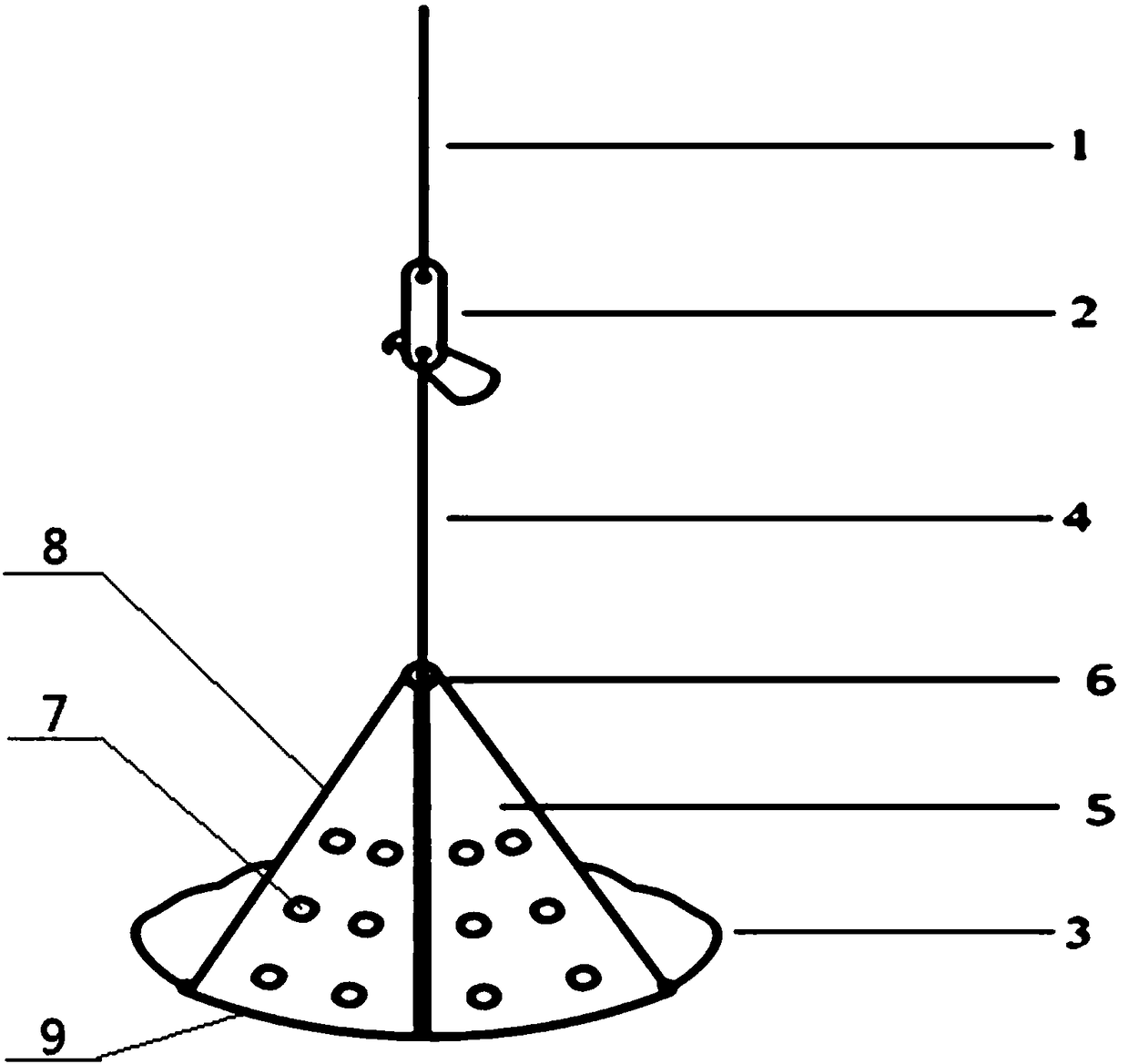
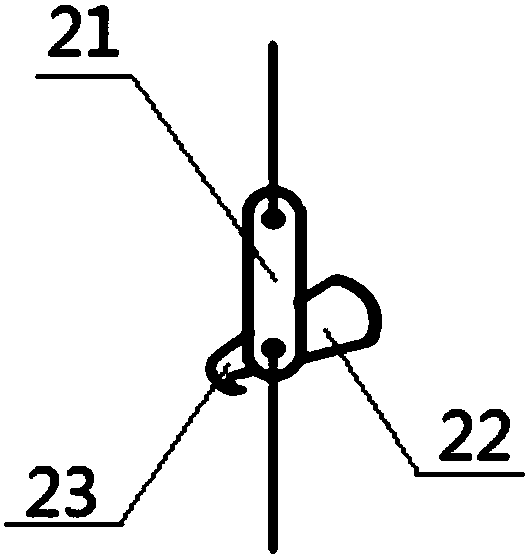
[0043]A quantitative investigation device for submerged plants in lakes and reservoirs, including a traction rope, an automatic rope release hook and a grass grabbing bucket; the automatic rope release hook includes a flat plate and a hook plate, each end of the flat plate is provided with a connection port, and the traction rope passes through a connection port Connected with the flat plate; one end of the hook plate is provided with a hook head, and the hook plate is hinged to the flat plate; the grass grabbing bucket includes two grabs, which are used to grab aquatic plants, and the opposite ends of the two grabs are hingedly connected, and a steel wire rope is provided at the hinge The grabbing bucket is connected to the other connection port of the flat plate through the steel wire rope at the hinge; the ends of the two grab buckets are connected together through the steel wire rope.
Embodiment 2
[0045] A quantitative investigation device for submerged plants in lakes and reservoirs, the structure of which is as described in Example 1, the difference is that the grab bucket includes two grab jaw plates, and a bucket wall is connected between the two grab bucket jaw plates. One end of the two grab jaw plates is connected with a bucket bottom. Two grapples each are so composed.
Embodiment 3
[0047] A quantitative investigation device for submerged plants in lakes and reservoirs, its structure is as described in Example 2, the difference is that the jaw plate of the grab bucket is a fan-shaped plate with a cross-sectional area of one-eighth, and the arc of the two fan-shaped plates The ends are connected with a bucket bottom, and the respective diameter sides of the two fan-shaped plates are connected with a bucket wall. Two grab jaw plates, a bucket wall, and a bucket bottom are combined to form a grab bucket with a cavity that can grab and place plants. The fan-shaped plate has two diameter sides, and the bucket wall is only set at one diameter side. The two fan-shaped The other diameter side of the plate is open to serve as the opening of the grab cavity.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com