Uncut chip substrate
A technology for cutting chips and substrates, used in lighting and heating equipment, light source fixing, electric solid devices, etc., can solve problems such as reduced productivity, degradation of heat dissipation characteristics, burr generation, etc., to achieve uniform heat dissipation characteristics, improve heat dissipation performance, and reduce the possibility of sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0045] Hereinafter, preferred exemplary embodiments of a method of manufacturing an optical device, and an optical device manufactured thereby will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
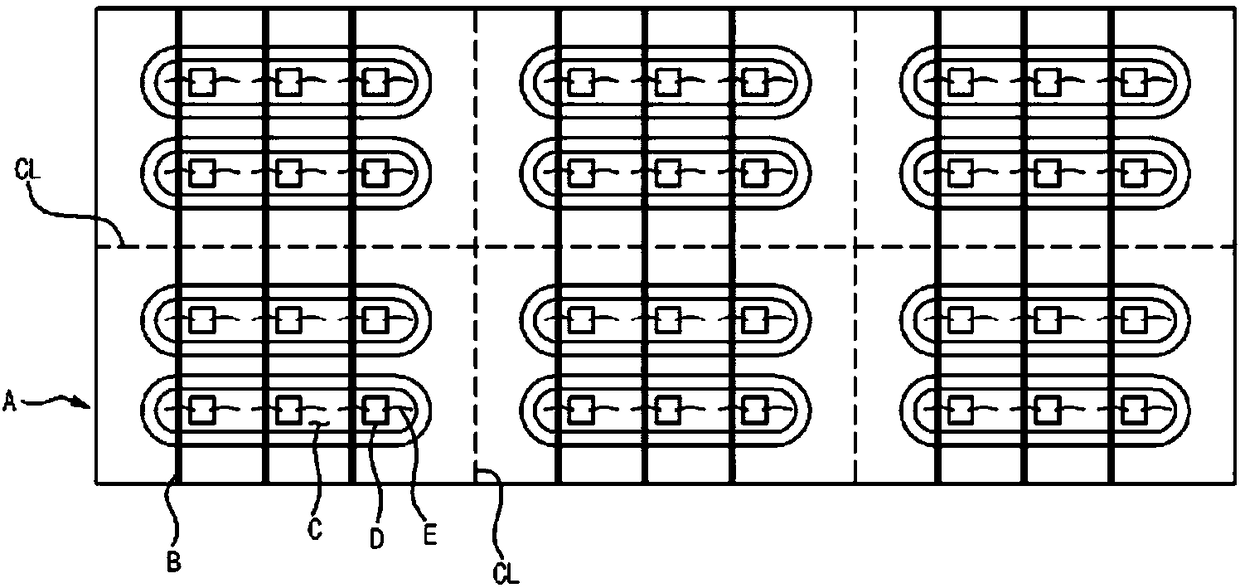
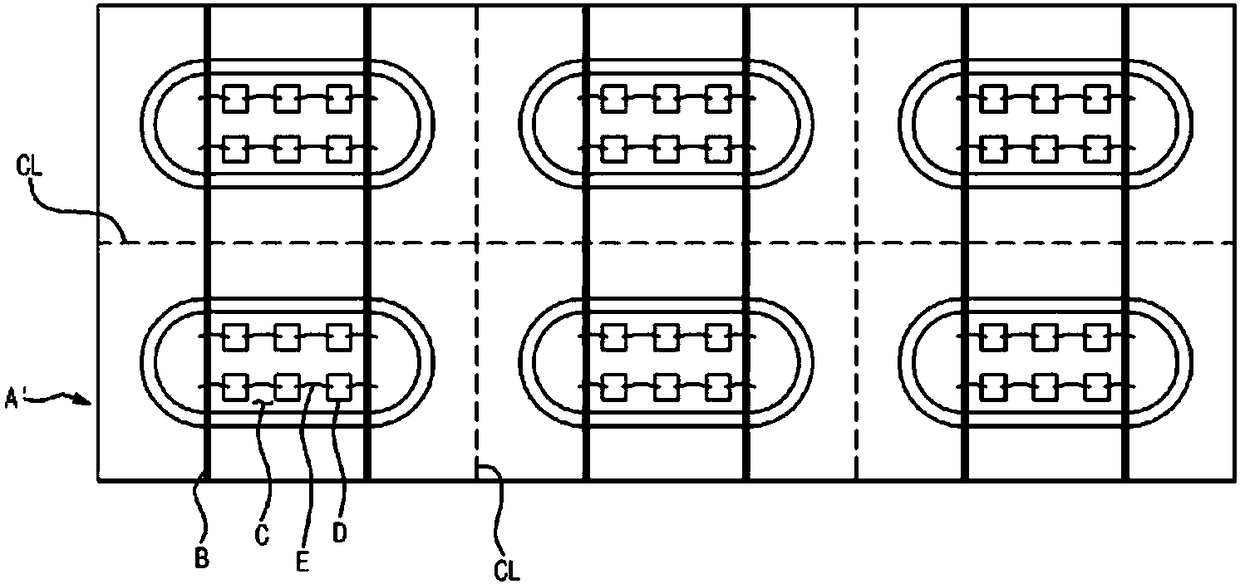
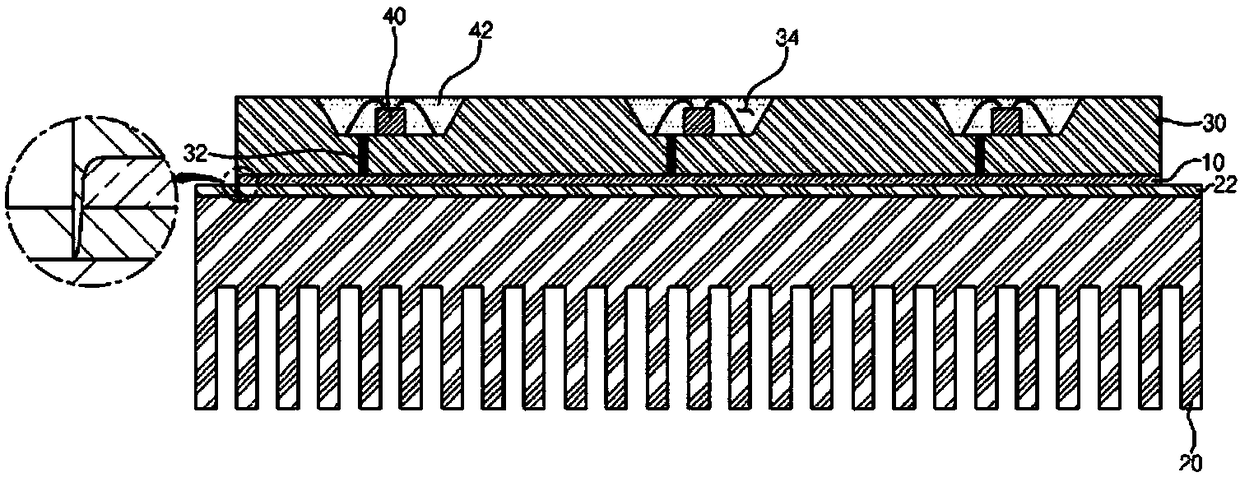
[0046] image 3 is a flowchart describing a method for manufacturing an optical device according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention. Figures 4a to 4e is used to manufacture such as figure 2 The perspective view of the process in the main steps of the method of the optical device shown, and its cross-sectional view along the line A-A.
[0047] Such as image 3 As shown, according to the method for manufacturing an optical device according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, first, in step S10, a base substrate 100 for an optical device having at least one vertical insulating layer 110 (hereinafter referred to as " base substrate"), such as Figure 4a shown. exist Figure 4a and in subsequent figures, 120 denotes an optical...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com