City water supply pipe network-based artificial water quality monitoring point addressing method
A technology for water quality monitoring and urban water supply, applied in general water supply conservation, forecasting, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as weak rationalization, obvious randomness, and insufficient scientific basis for the distribution of monitoring points, and achieve the goal of ensuring representativeness and optimizing operation and management. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] A method for site selection of artificial water quality monitoring points based on urban water supply pipe network, comprising the following steps:
[0051] A. Use the hydraulic model of the pipe network to simulate the hydraulic operation of the urban water supply pipe network, and combine the road network to realize the grid division of the entire water supply pipe network;
[0052] B. Calculate the water consumption of residents in each grid;
[0053] C. Determine the number of artificial water quality monitoring points in the pipe network in each grid;
[0054] D. Determine the distribution status of online users in each corresponding block through the geographic information system;
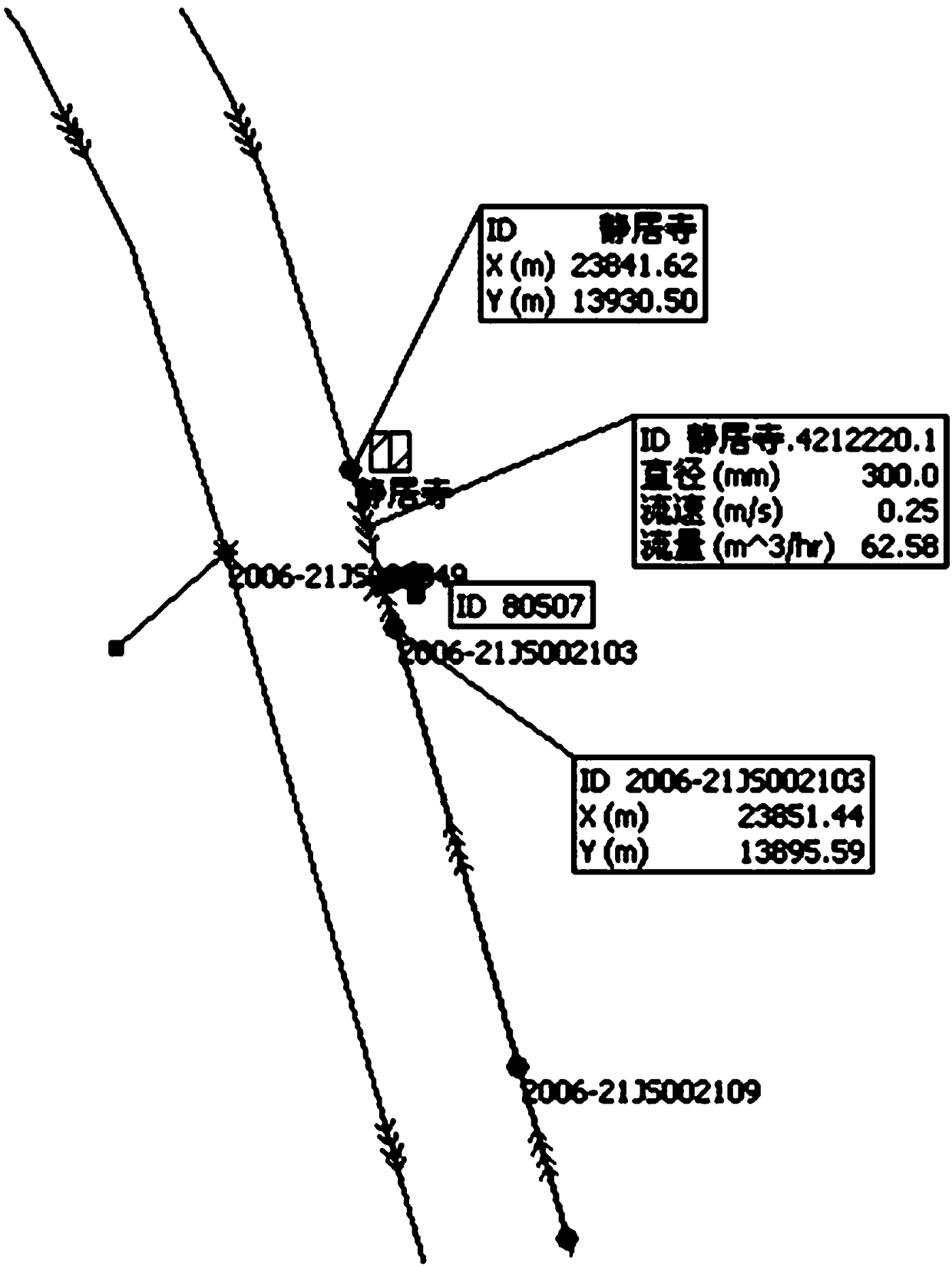
[0055] E. According to the data acquisition and monitoring control system, the hydraulic model of the pipe network and the information obtained in step D, calculate the water age of different locations in the urban water supply area and the water age of the internal network users in e...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Based on the principles of the foregoing embodiments, this embodiment discloses a specific implementation manner.
[0061] A. Use the pipe network hydraulic model InfoWorksWS to simulate the hydraulic operation of the urban water supply network. The simulation process includes: the main water pipelines, ring pipe networks, branch pipelines, and important pipelines of the urban water supply network. Combing; combing of flow velocity, flow rate, water age, water flow direction, and coverage in the pipe network; simulation of the operating status of the pipe network. Urban water supply is delivered from the water plant, through the water transmission and distribution network, through the main pipelines, and delivered to users. The urban pipe network completes the whole process of tap water from raw water, process water, factory water to pipe network water. Water pipelines are generally laid according to the distribution of urban roads, so as to match the water supply pipeli...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Based on the principles of the foregoing embodiments, this embodiment takes Chengdu as an example to illustrate the method.
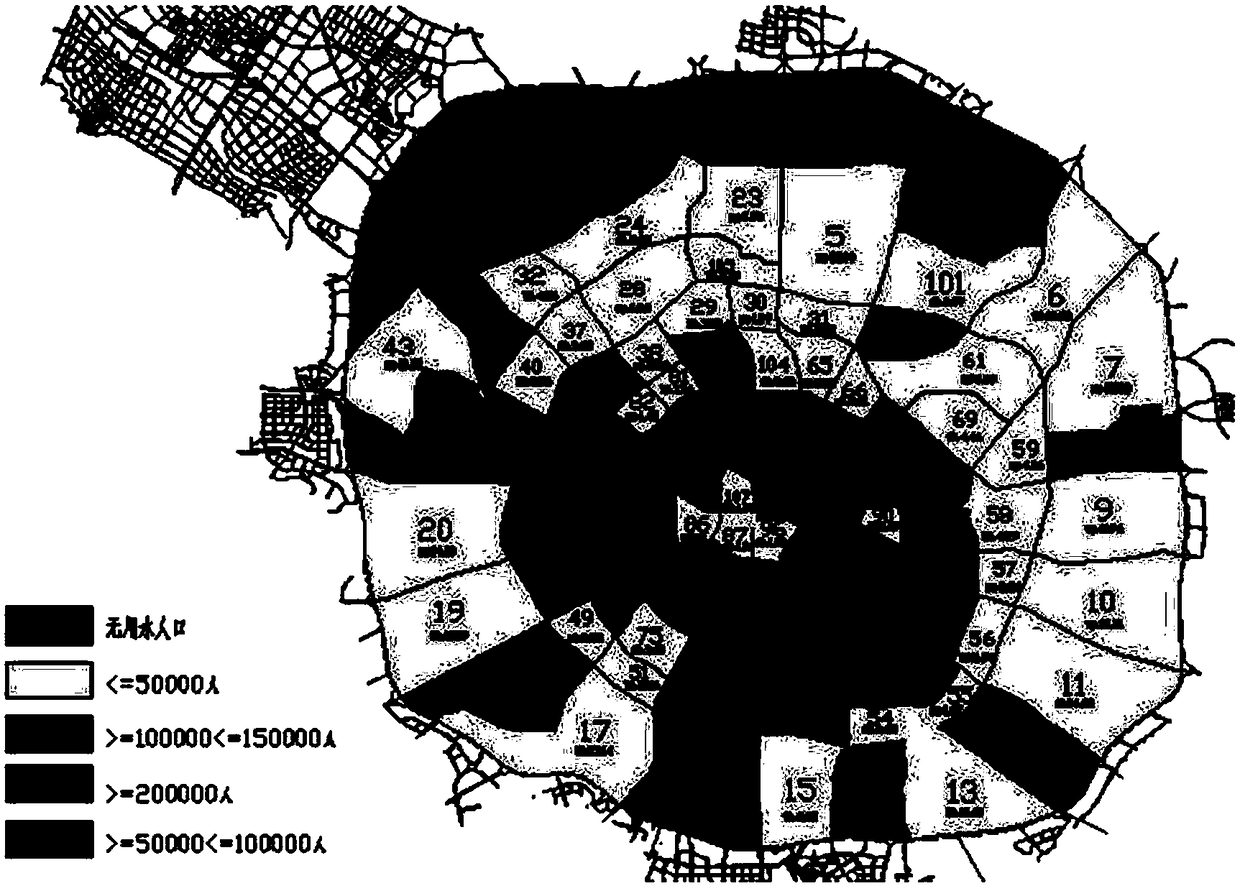
[0082] According to the distribution of road network and water supply pipelines in Chengdu, the main urban area of Chengdu is divided into 109 representative user areas, and the population and population density of the area are calculated by using the sales volume of residential water, as shown in figure 1 shown.
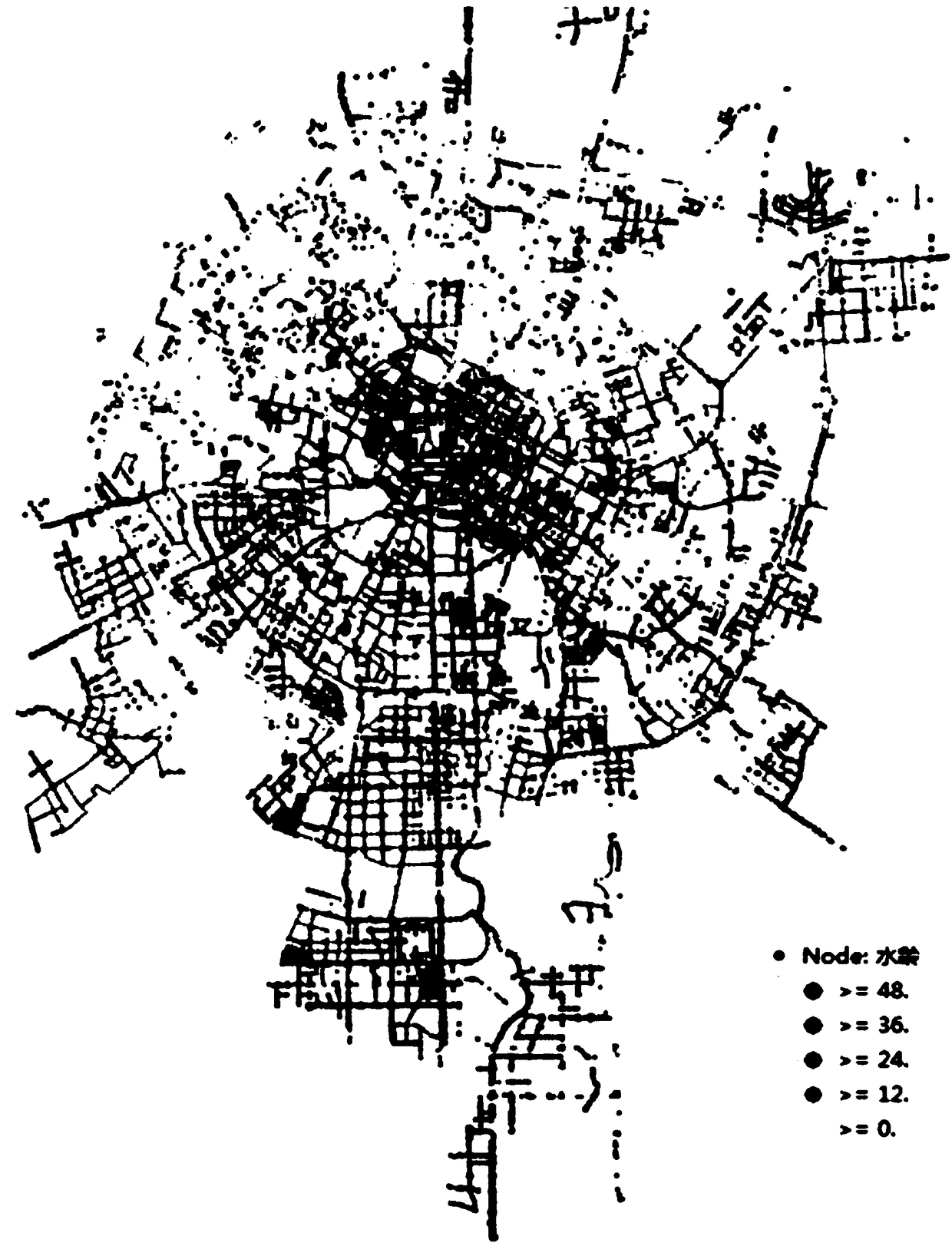
[0083] Combining the geographic information system with the hydraulic model data of the pipe network, the high-density user area in the water supply area of the main urban area of Chengdu is calculated and constructed.
[0084] Water age is an important indicator for evaluating water quality. The research team conducts water age model calculations on the pipe network in the main urban area, such as figure 2 .
[0085] according to figure 1 Based on the grid coverage layout results, the user areas, streets, water meter users a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com