Imaging polarimetry
An imaging and polarization technology, applied in chipless transponders, information reading at high temperature, and the system field that implements this method, can solve the problems of difficult radar system boundaries or classifications, and achieve simple and reliable identification and classification, high data capacity, avoiding the effects of wave switching
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
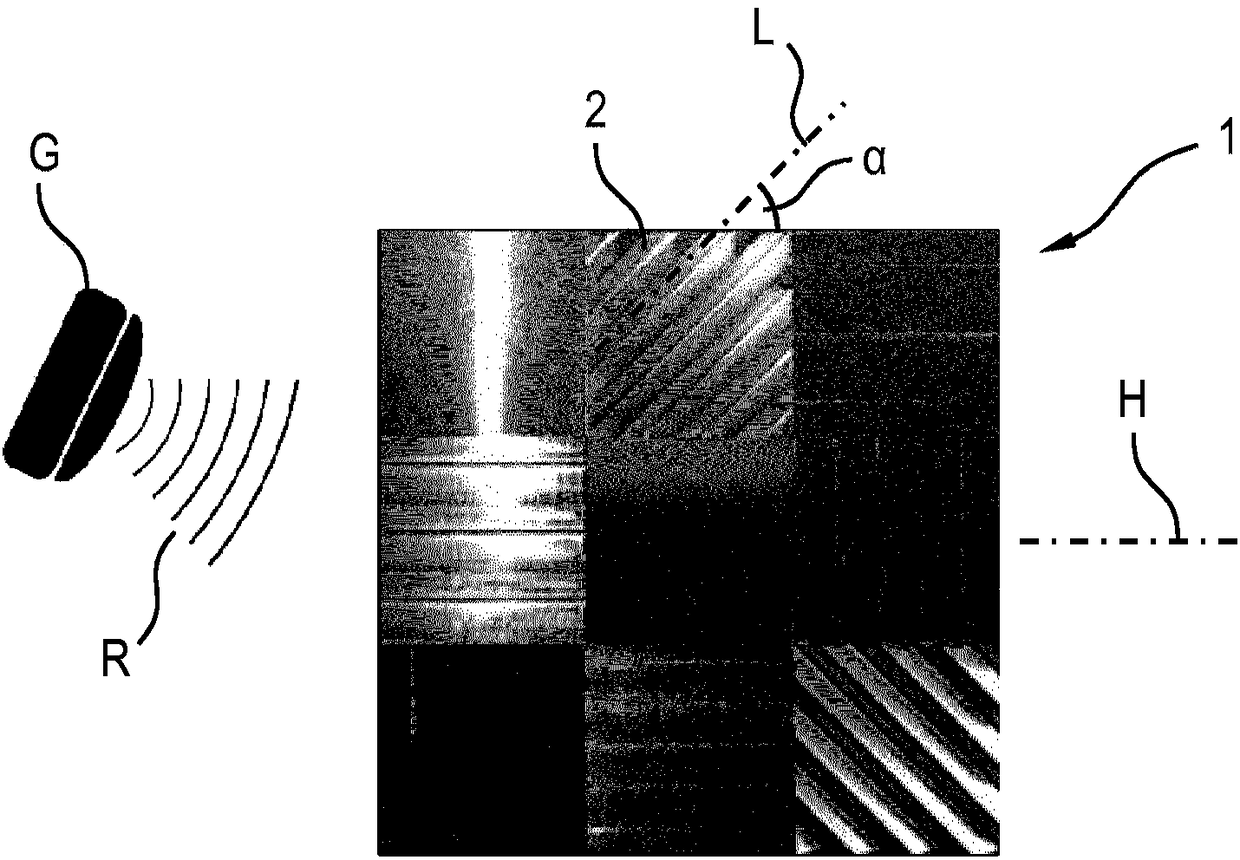
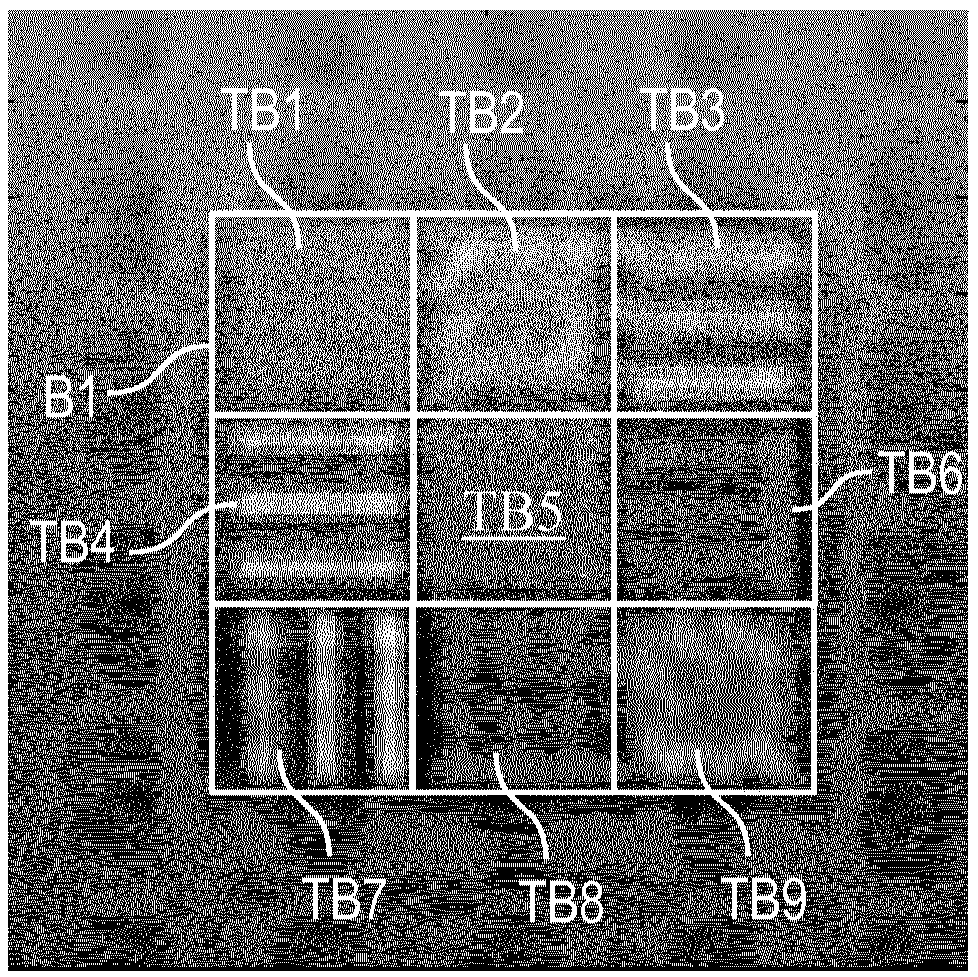
[0059] figure 1 A transponder 1 is shown which is designed as a sheet-shaped aluminum part with a square contour in plan view. The side length can be, for example, approximately 10 cm. The transponder 1 can be illuminated with fully polarized radio waves, in particular radar radiation R, by means of a reading device G. The reflected or backscattered radiation at the transponder 1 can be detected by the reading device G and evaluated there or in a separate evaluation device (above). In particular at least one image B1 to B3 can be produced by means of the detected backscattered radiation (see for example Figure 3 to Figure 5 ), whose image points carry polarization information.
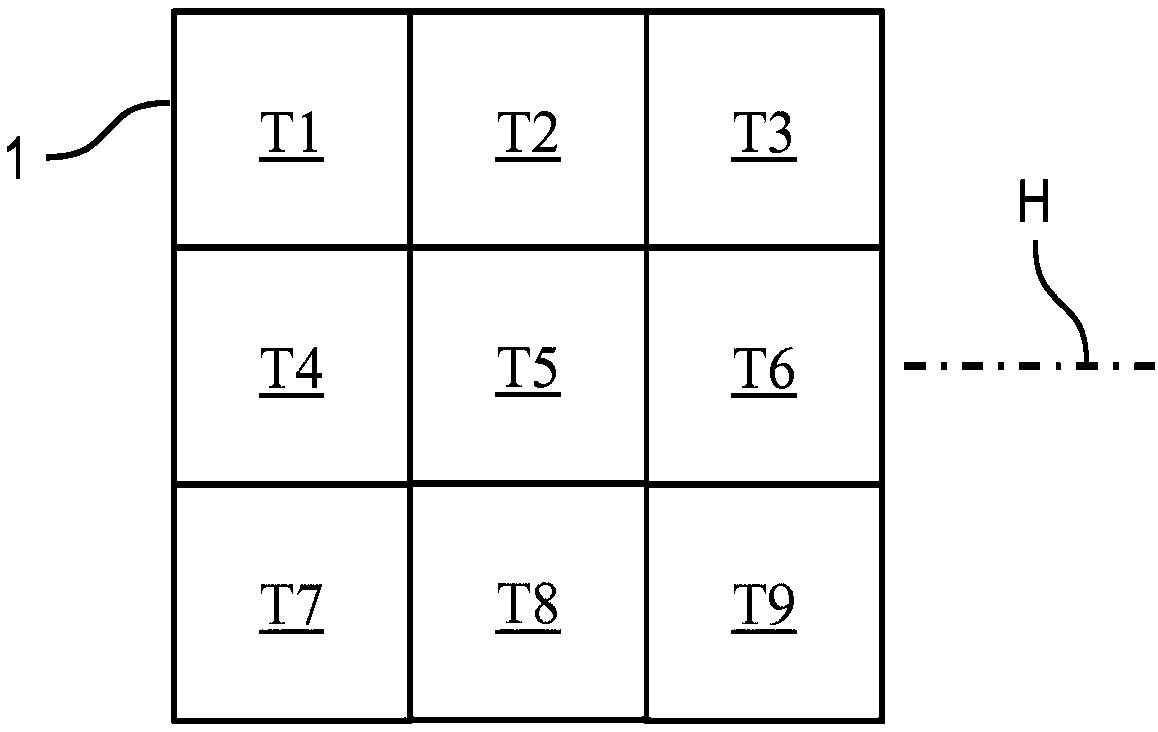
[0060] figure 2 A simplified view of the new fields or partial areas T1 to T9 of the transponder 1 is shown. The partial areas T1 to T9 likewise have a square shape and are of the same size.
[0061] The polarization behavior of the subsurfaces T1 to T9 can be distinguished by means of the meas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com