Prognosis and treatment of squamous cell carcinomas
A squamous cell carcinoma and cell technology, applied in the direction of cytokines/lymphokines/interferons, antibody medical components, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of poor understanding of molecular mechanisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
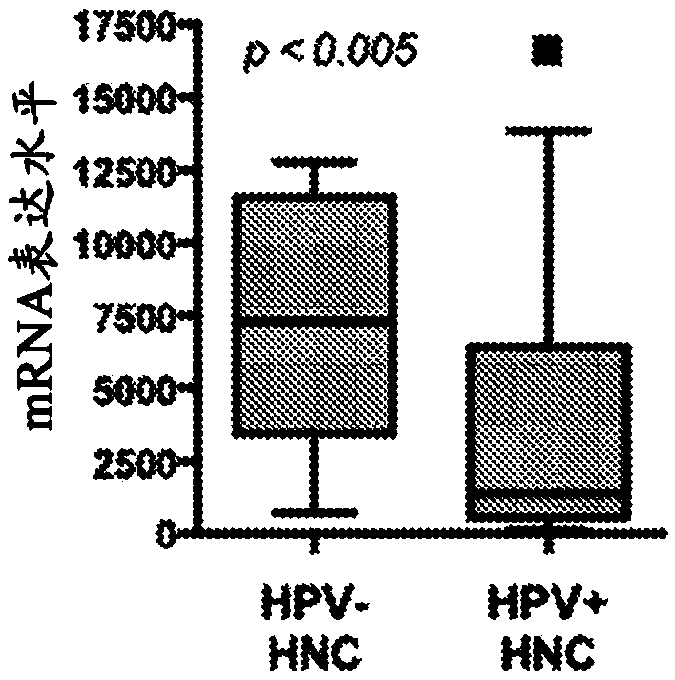
[0090] Example 1: Analyze the global gene expression profile of 84 fresh frozen human cervical and head / neck tissue samples to compare HPV + And HPV-cancer.
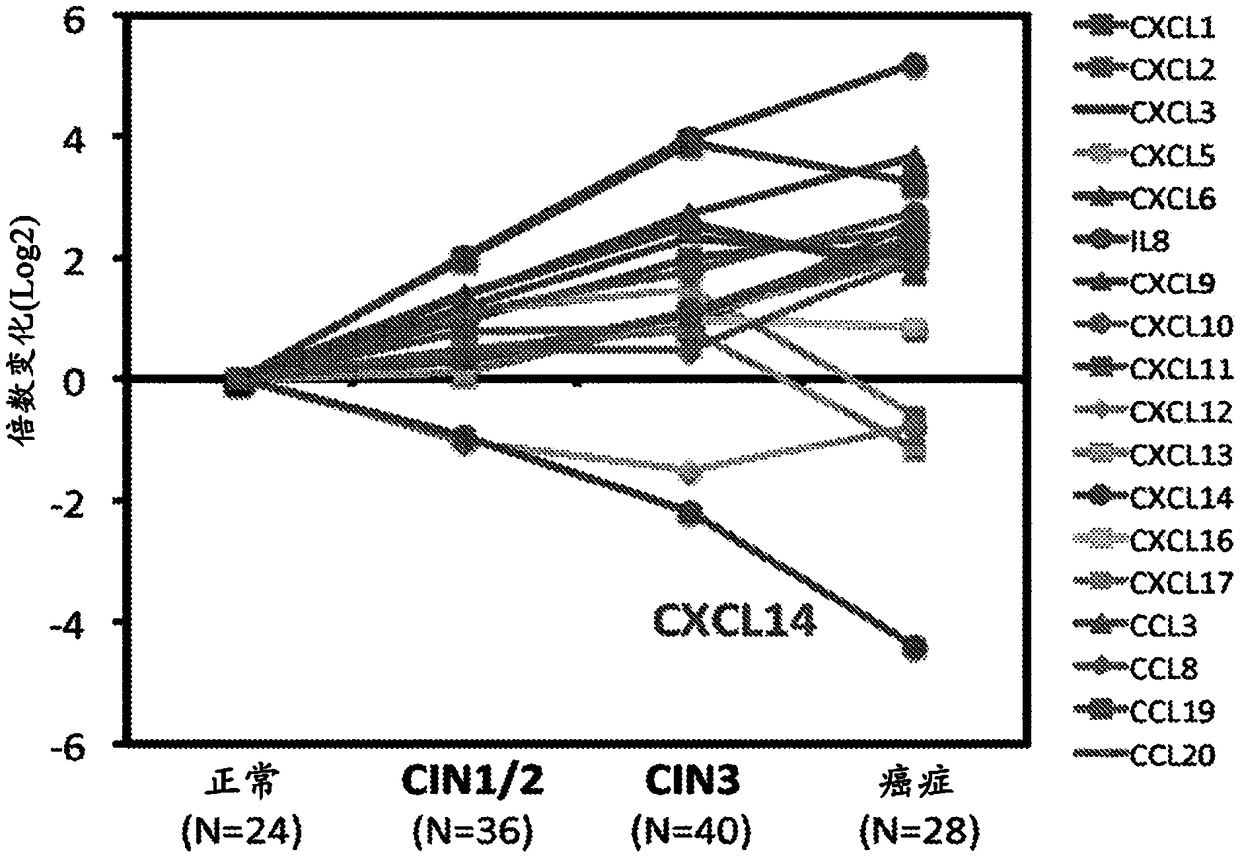
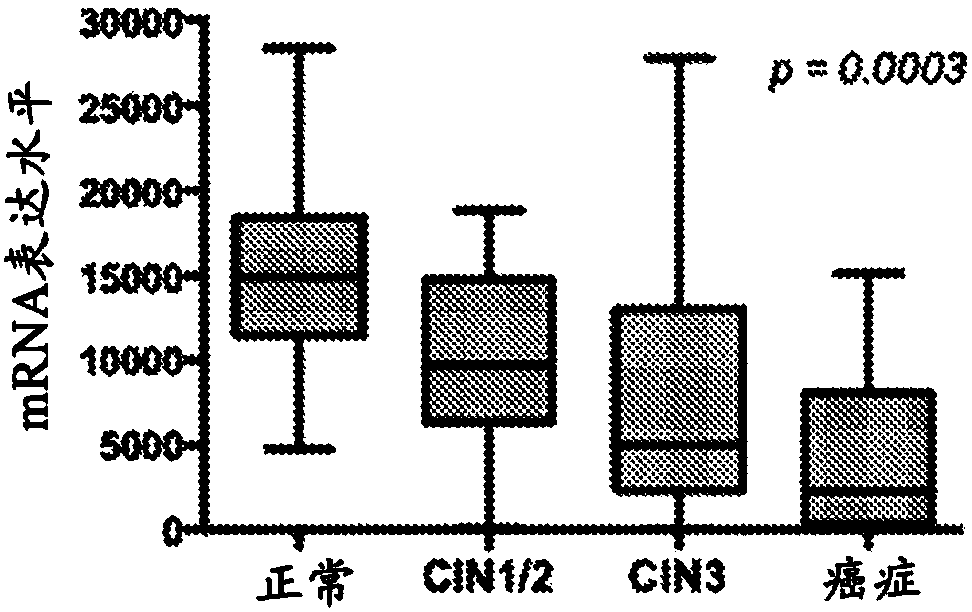
[0091] The previous results revealed a significant HPV-specific gene expression signature that allows distinguishing HPV+ HNSCC and cervical cancer (CxCa) from HPV-HNSCC. These findings clearly indicate that HPV plays a key role in the development of HPV-related cancers. The inventors further analyzed the global gene expression profiles of 128 cervical tissue samples in different disease stages, including normal, early and late malignant preepithelial lesions, and squamous carcinoma. The results reveal a cascade of molecular changes that culminates in changes in the expression of multiple genes when it eventually transforms into invasive epithelial cancer. In order to understand the immune regulation of HPV in the local microenvironment during the progression of HPV-related cancers, the inventors used gene expression dat...
Embodiment 2
[0096] Example 2: CXCL14 promoter hypermethylation in HPV+ cells
[0097] Previous studies have shown that promoter hypermethylation can inhibit the expression of CXCL14. In order to determine whether reduced CXCL14 expression is associated with promoter hypermethylation, the inventors performed methylation-specific PCR (MSP) using NIKS and W12 cell lines. The methylation of the CXCL14 promoter was inversely correlated with the expression of CXCL14, and the hypermethylation of the CXCL14 promoter was significantly increased in HPV+keratinocytes and HNSCC cells (Figure 4). CXCL14 promoter hypermethylation disappeared in NIKS-16ΔE7 cells. These results indicate that CXCL14 promoter hypermethylation is induced by high-risk HPV and accumulates throughout cancer progression. Previous studies have shown that HPV oncoprotein E7 activates the methyltransferase activity of DNMT1. In addition, epigenetic silencing of many genes has been shown in HPV+ cells and CxCa. The inventor's dat...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Example 3: Re-expression of CXCL14 in HNSCC cells clears tumors through adaptive immunity:
[0099] CXCL14 is an evolutionarily conserved chemokine, showing 98% homology between human CXCL14 and mouse Cxcl14. To determine whether CXCL14 affects tumor growth in vivo, the inventors studied mouse oropharyngeal epithelial cells (MOE / E6E7) that form tumors in immunocompetent, syngeneic C57BL / 6 (B6) mice. Consistent with human cell lines and patient tissues, it was found that MOE / E6E7 cells expressed significantly less Cxcl14 than syngeneic HPV-MOE cells and showed a highly methylated Cxcl14 promoter ( Figure 7 ). In order to test the tumor suppressor function of CXCL14, the inventors established the MOE / E6E7 cell line, which then expressed its physiological level of Cxcl14. Strikingly, most B6 mice injected with MOE / E6E7 cells expressing Cxcl14 cleared their tumors, while all mice injected with control MOE / E6E7 cells died of tumor burden within 21 days ( Figure 8A ). Howev...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com