Field mouse babesia RPA molecular detection method
A technology of Babesia and detection methods, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of high detection costs, achieve fast and time-saving effects, prevent background noise, and have flexible volumes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
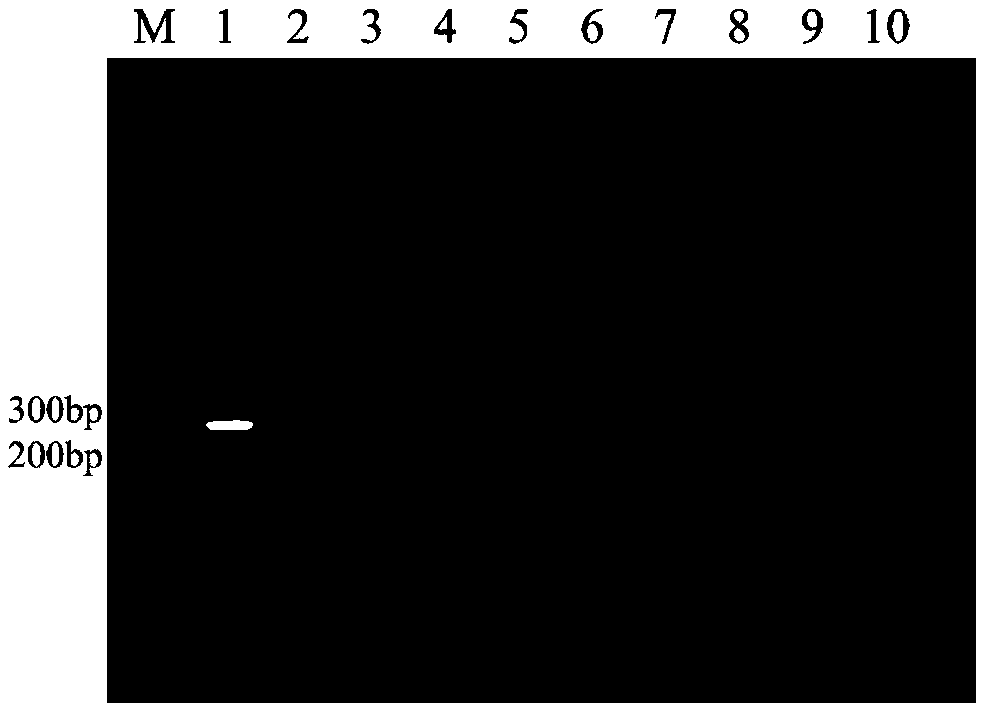
[0030] Embodiment 1: Carry out the detection of Babesia microti to blood sample
[0031] 1. Extraction of total DNA from blood samples of BALB / c mice: The total DNA in blood samples was extracted using QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Germany) according to the instructions of the kit.
[0032] 2. Gene selection
[0033] Analyzing more than 10 articles on the detection of Babesia microti, it was found that most of them used 18S rRNA as the target sequence for detection, but it was difficult to synthesize RPA primers because of its short specific region. We selected the mitochondrial gene and compared the full-length mitochondrial length (11109bp) of different strains published in GenBank, and then compared the sequences with Bioedit software. gene) showed high specificity to protozoa and various hosts. Therefore, the highly specific segment of the COX I gene of Babesia microti was selected as a candidate template for primer design.
[0034] 3. Determining the target sequence
...
Embodiment 2
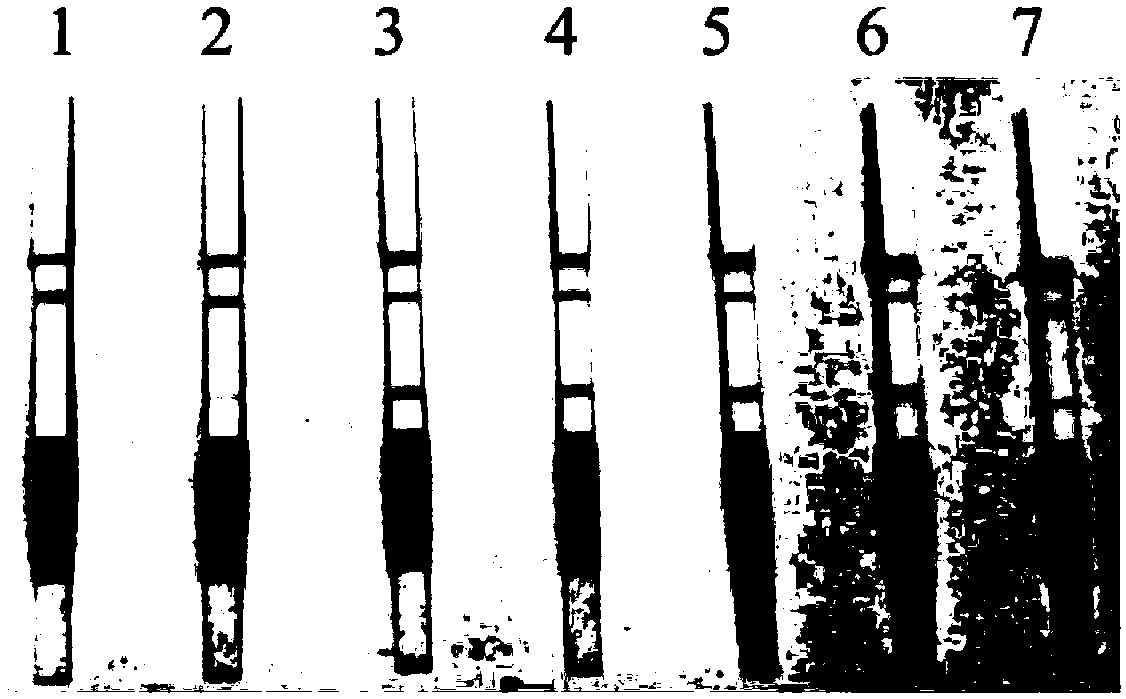
[0045] Embodiment 2: Babesia vole RPA detection method specificity test
[0046] As shown in Table 1, the Theileria buffalo, Babesia canis, Babesia orientalis and Toxoplasma gondii strains used in the specificity test were isolated and preserved by the animal parasite laboratory where the applicant works Insect strain. Plasmodium falciparum DNA was donated by Chongqing Third Military Medical University. All strains were preserved in frozen anticoagulated form. In addition, human, dog, buffalo and BALB / c mouse gDNA were all provided by the applicant's animal parasite laboratory.
[0047] Table 1 Specificity test for RPA detection of Babesia vole
[0048]
[0049] Explanation of Table 1: "+" indicates that the detection line of the test strip develops color, and "-" indicates that the detection line of the test strip does not develop color.
[0050] Extraction of total DNA: Extract the total DNA of the above ten samples according to the method described in Blood / Cell / Tiss...
Embodiment 3
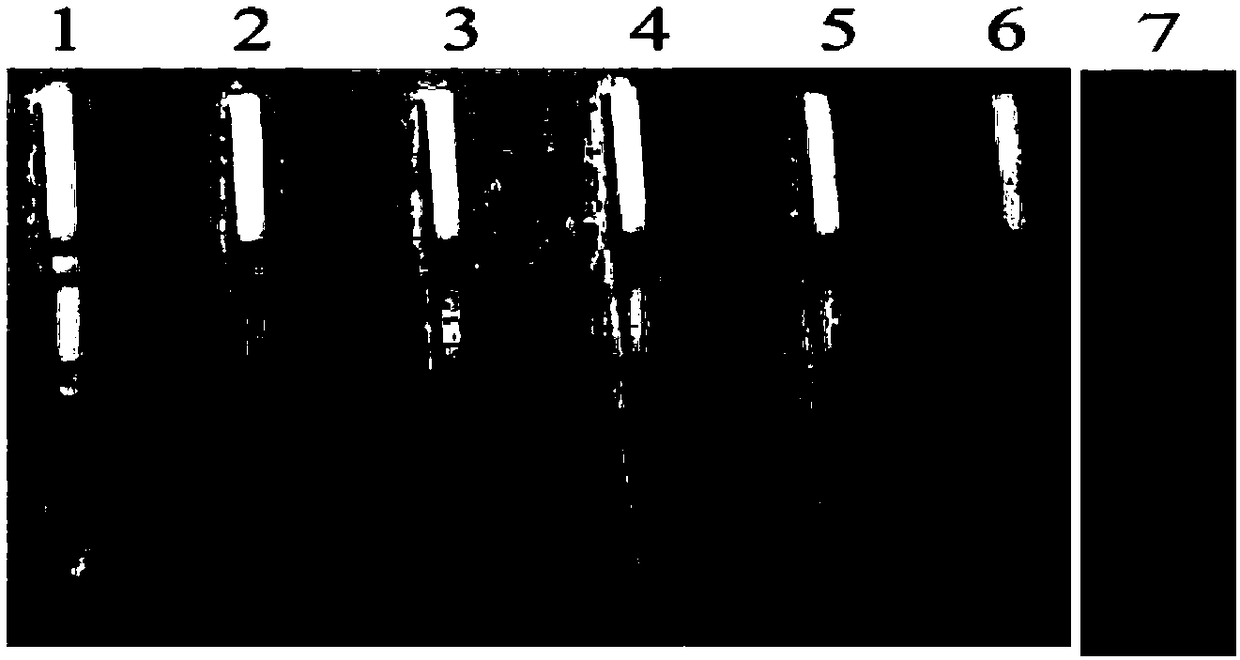
[0056] Embodiment 3: Sensitivity test of Babesia vole RPA detection method
[0057] The sensitivity of the RPA method for Babesia microti was tested using COX I gene-positive gDNA as a template. Methods as below:
[0058] 1. The method of embodiment 1 extracts blood total DNA template from BALB / c mouse blood sample.
[0059] 2. Amplify the target fragment by common PCR method: amplify the 18S rRNA gene of Babesia microti with the total blood DNA of infected BALB / c mice, and the nucleotide sequence of the primer pair is as follows.
[0060] Upstream primer F2: 5'-AACCTGGTTGATCCTGCCAGTAGTCAT-3';
[0061] Downstream primer R2: 5'-GATCCTTCTGCAGGTTCACCTAC-3';
[0062] The reaction system is: TaKaRa Taq enzyme (5U / μl) 0.3ul, 10×PCR Buffer (Mg 2+ Plus) 2.5ul, dNTPMixture (2.5mM each) ul, template DNA 2ul, ddH 2 O 16.2ul, 1ul each of upstream and downstream primers. The total reaction system is 25ul.
[0063] 3. PCR product analysis: 10 μl of the final PCR product above was add...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com