An auxiliary tool for studying geological sedimentary facies
An auxiliary tool and sedimentary facies technology, applied in the field of learning tools, can solve problems such as potential safety hazards, splashing of gravel, damage to rock and mine specimens, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the efficiency of chiseling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
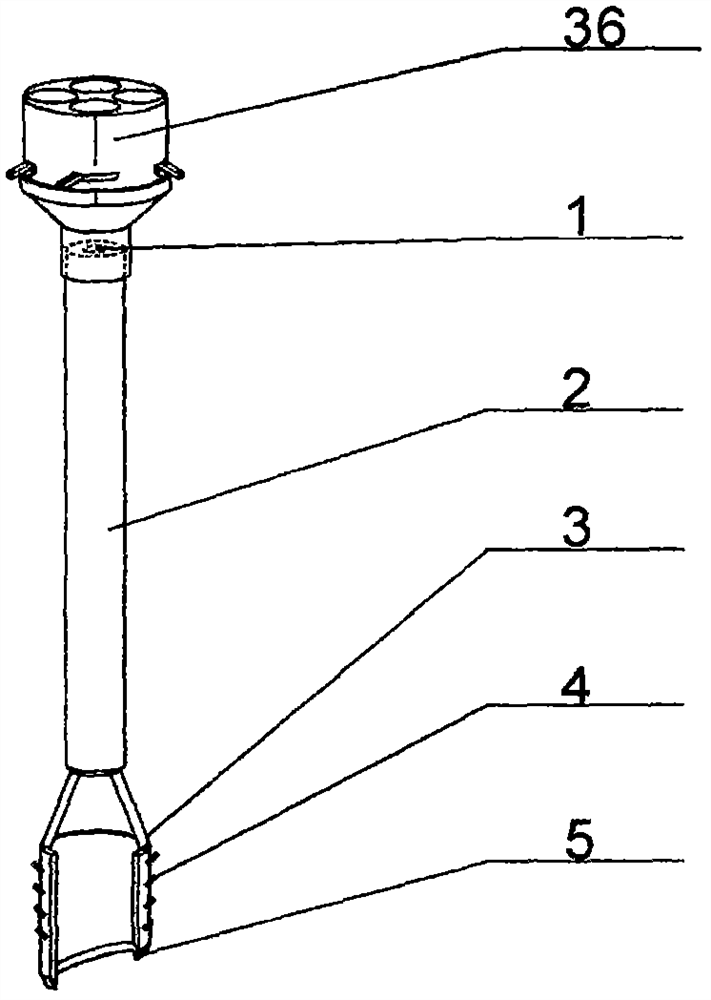
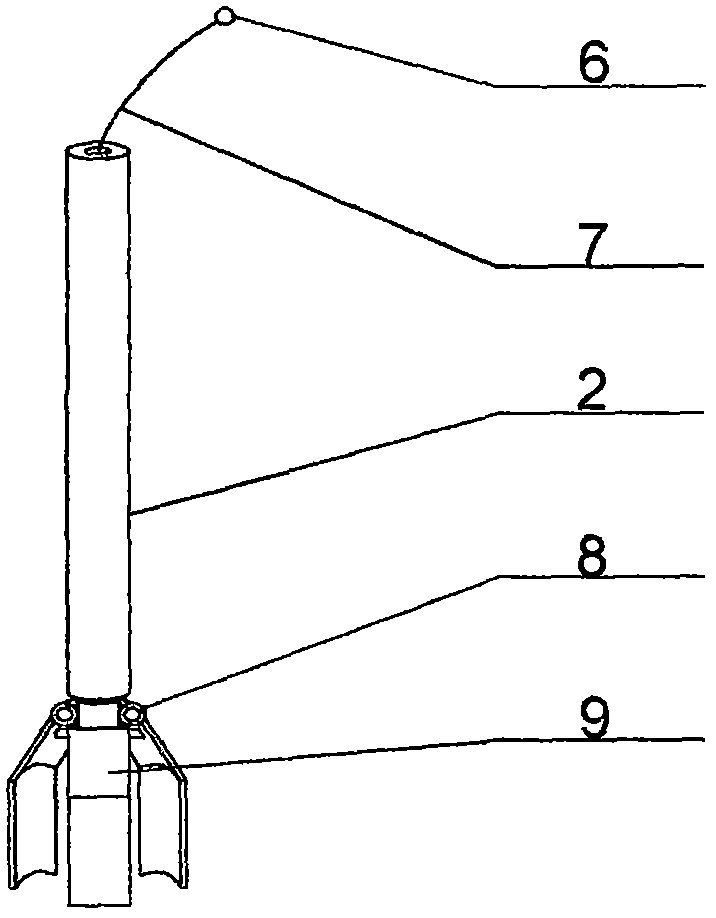
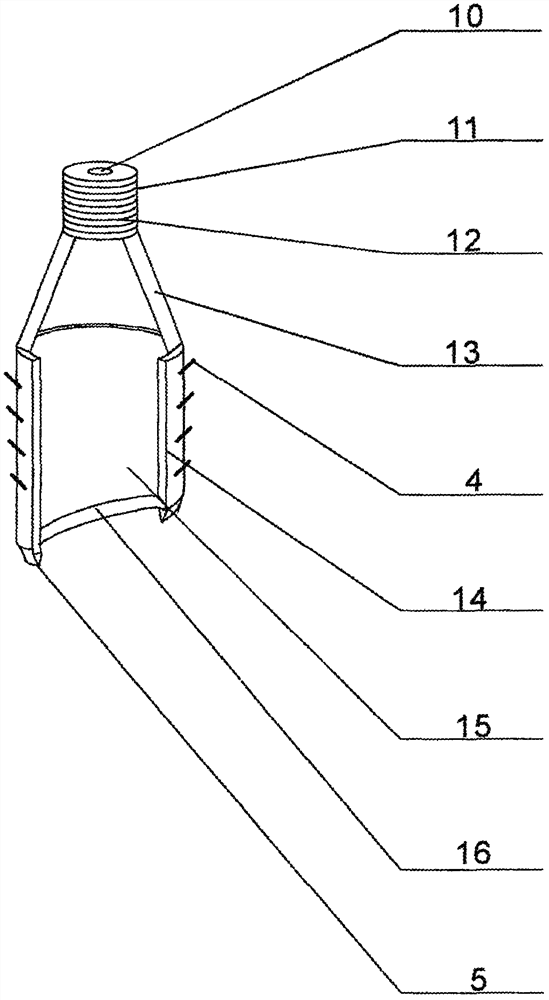
[0031] The present invention is described in further detail now in conjunction with accompanying drawing. These drawings are all simplified schematic diagrams, which only illustrate the basic structure of the present invention in a schematic manner, so they only show the configurations related to the present invention.
[0032] combined with Figure 1-8 The given auxiliary tool for studying geological sedimentary facies is provided with a chemical reagent introduction device 36 at the upper end of the handle 2, and the chemical reagent introduction device 36 is composed of a chemical reagent introduction box 39 and a snap joint 46. The upper surface of the chemical reagent introduction box 39 is provided with several card openings 38 that run through the chemical reagent introduction box 39, and a reagent holding box 37 is respectively stuck in the several card openings 38. The reagent holding box The bottom of 37 is an open structure, and the upper end of the reagent storage...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com