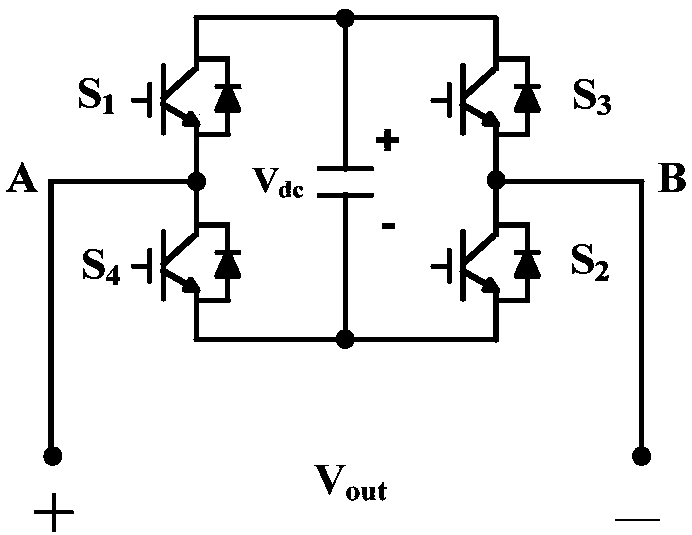
Method for driving power semiconductor switches in H-bridge circuit
A technology of power semiconductor and driving method, which is applied to the conversion device of output power, the conversion of AC power input to DC power output, electrical components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
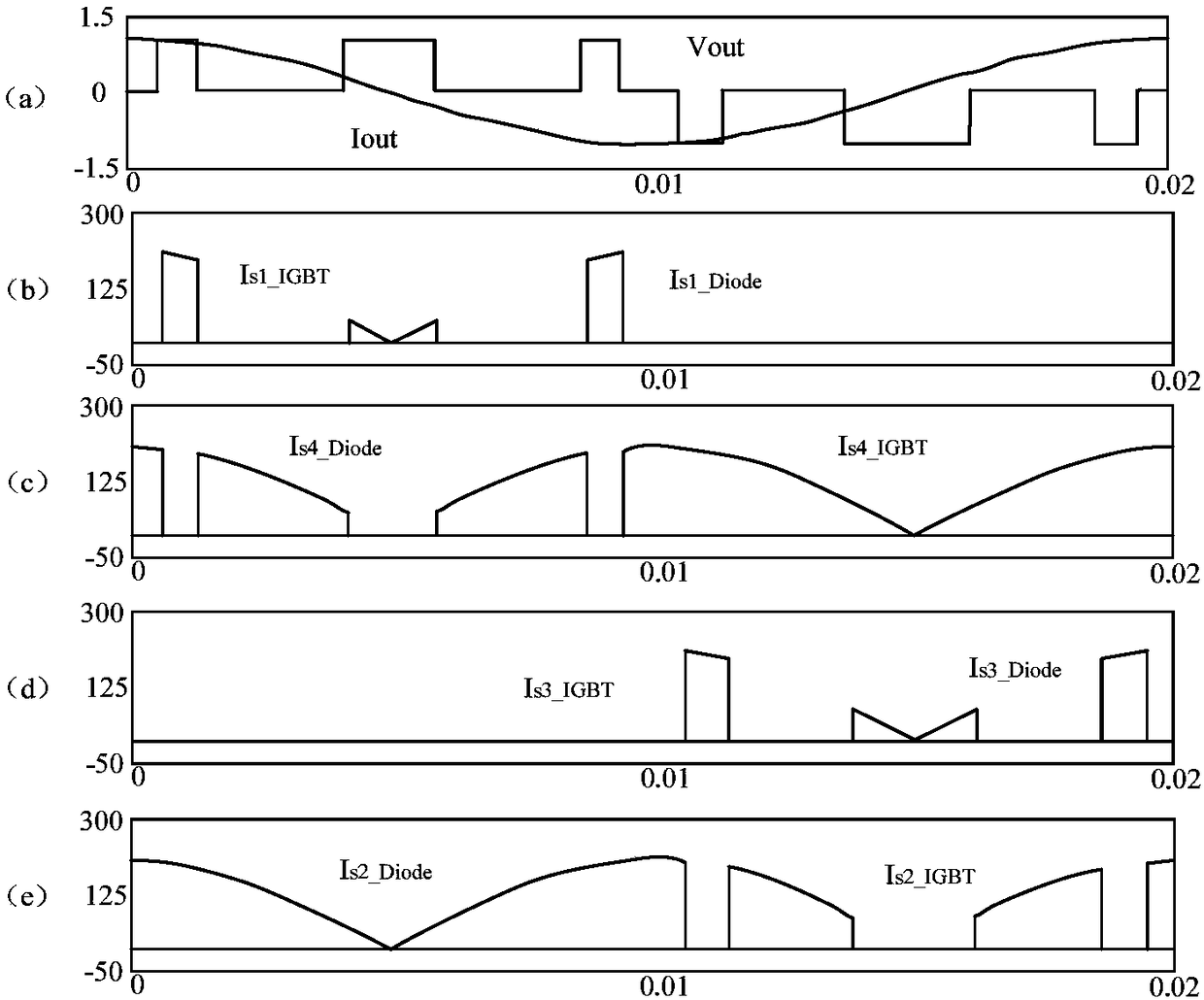
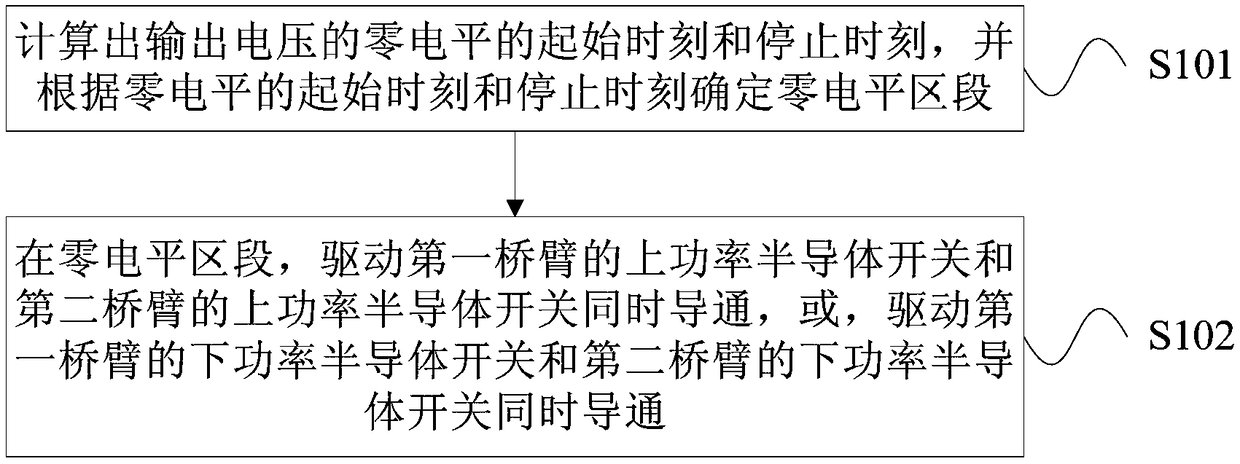
[0074] Example 1: Figure 7 The conduction diagram of the power semiconductor switch in the H bridge circuit provided by the present invention Figure 1 . Such as Figure 7 As shown, it is assumed that the control circuit 11 calculates the start time and stop time of the zero level of the output voltage Vout in every T / 2 work cycle, and determines that each T / 2 work cycle includes 3 Zero-level segments, that is, an odd number of zero-level segments. In this embodiment, Vout is a waveform diagram of the output voltage of the H-bridge circuit, and |Vout| is a waveform diagram of the absolute value of the output voltage of the H-bridge circuit. COM is the waveform diagram of the polarity of the output voltage of the H-bridge circuit. When the polarity of the output voltage Vout of the H-bridge circuit is positive (the positive pole comes from the modulation wave of the H-bridge circuit in the control circuit, when the modulation wave>0, the When the polarity of the H-bridge o...
example 2
[0080] Example 2: Figure 8 The conduction diagram of the power semiconductor switch in the H bridge circuit provided by the present invention Figure II . Such as Figure 8 As shown, it is assumed that the control circuit 11 calculates the start time and stop time of the zero level of the output voltage Vout in every T / 2 work cycle, and determines that each T / 2 work cycle includes 4 Zero-level segments, that is, an even number of zero-level segments. In this embodiment, Vout is a waveform diagram of the output voltage of the H-bridge circuit, and |Vout| is a waveform diagram of the absolute value of the output voltage of the H-bridge circuit. COM is a waveform diagram of the polarity of the output voltage of the H-bridge circuit. When the polarity of the output voltage Vout of the H-bridge circuit is positive, COM=1. When the polarity of the H-bridge output voltage is negative, COM=0. QS1 is the control signal waveform diagram of the upper power semiconductor switch S1 o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com