Method for fast identification of dominant oscillation mode based on random subspace
A technology of random subspace and oscillation mode, applied in the direction of reducing/preventing power oscillation, circuit devices, AC network circuits, etc., can solve the problems of reducing efficiency, reducing the real-time performance of online monitoring of power system dynamic stability, etc., achieving fast calculation efficiency, The effect of accurate power grid dynamic stability information and improved response speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
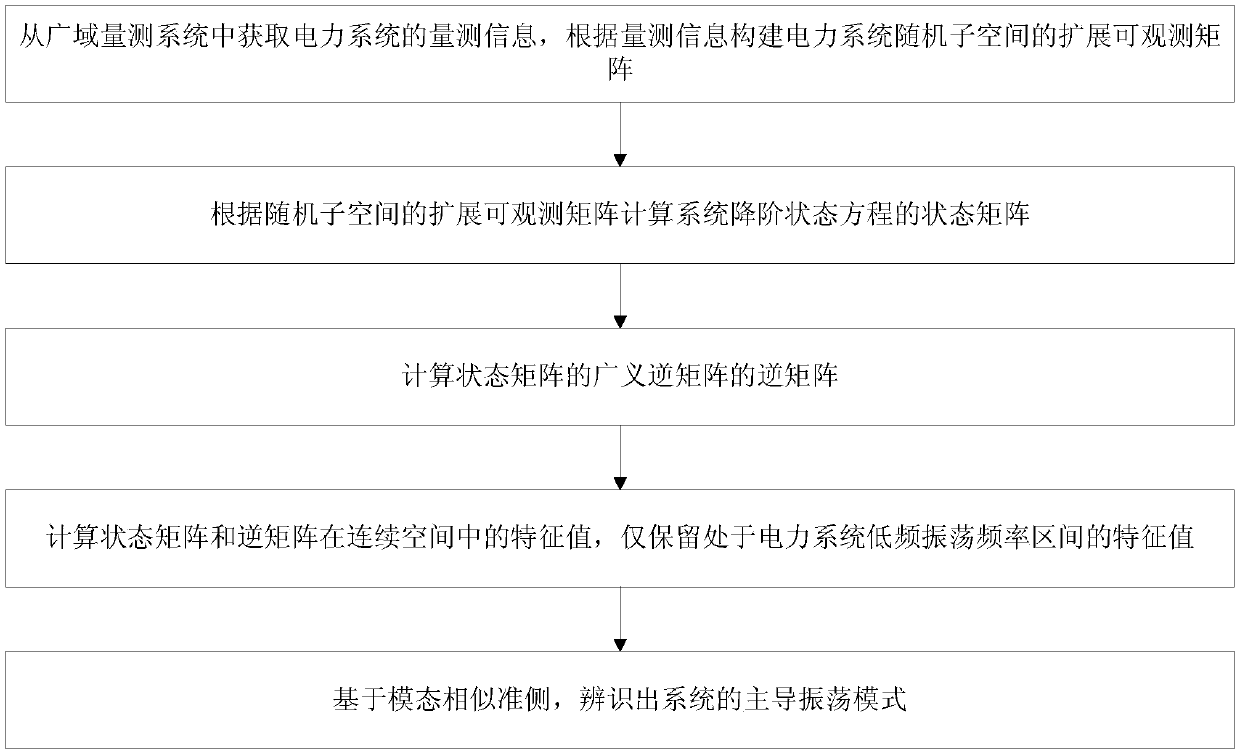
[0050] A fast identification method for dominant oscillation modes based on stochastic subspace, see figure 1 , the method includes the following steps:
[0051] 101: Obtain the measurement information of the power system from the wide-area measurement system, and construct the extended observable matrix of the random subspace of the power system according to the measurement information;
[0052] 102: Calculate the state matrix of the reduced-order state equation of the system according to the extended observable matrix of the random subspace;
[0053] 103: Calculate the inverse matrix of the generalized inverse matrix of the state matrix;
[0054] 104: Calculate the eigenvalues of the state matrix and the inverse matrix in the continuous space, and only retain the eigenvalues in the low-frequency oscillation frequency interval of the power system;
[0055] 105: Identify the dominant oscillation mode of the system based on the mode similarity criterion.
[0056] Among t...
Embodiment 2
[0065] The scheme in embodiment 1 is further introduced below in conjunction with specific calculation formulas and examples, see the following description for details:
[0066] 201: Obtain the measurement information of the power system from the wide-area measurement system (a technical term known to those skilled in the art, so I won’t repeat it here), and use the wide-area measurement information to construct the extended observable matrix of the random subspace of the power system O, including:
[0067] 1) Use the wide-area measurement signal y(t) to construct the Hankel matrix H of the random subspace of the power system:
[0068]
[0069] In the formula, Y P and Y F The expressions are:
[0070]
[0071]
[0072] In the formula, n is the maximum dimension of the pre-set reduced-order state equation of the system; b is the length of the wide-area measurement signal y(t).
[0073] 2) LQ decomposition of the Hankel matrix H:
[0074]
[0075] Wherein, the H...
Embodiment 3
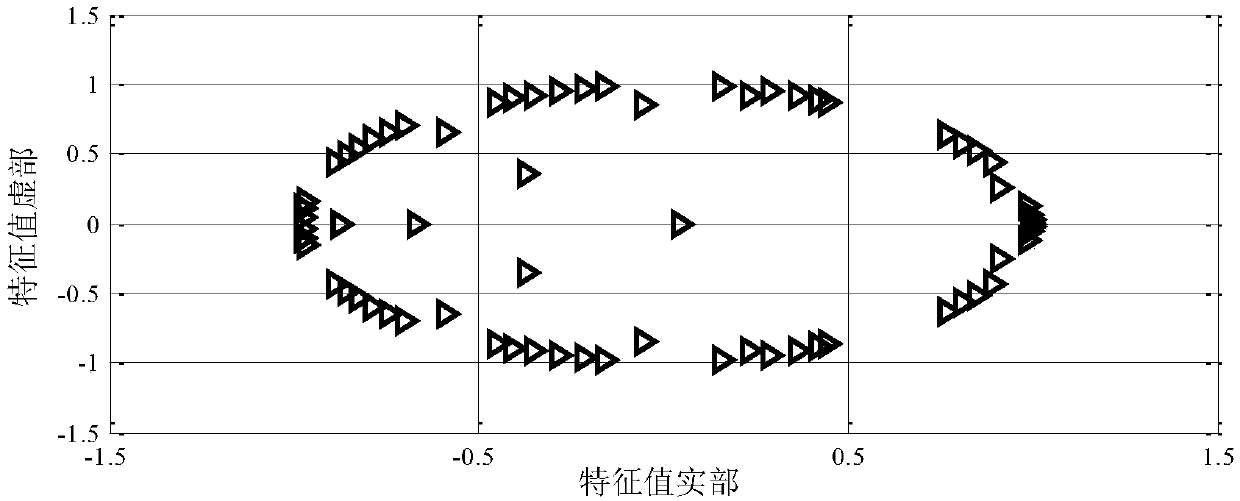
[0122] The following combined with specific examples, Figure 2-Figure 8 , and Table 1-Table 3, carry out feasibility verification to the scheme in embodiment 1 and 2, see the following description for details:
[0123] This example takes the rapid identification of the dominant oscillation mode of the China Southern Power Grid as an example to verify the effectiveness of Embodiments 1 and 2 of the present invention.
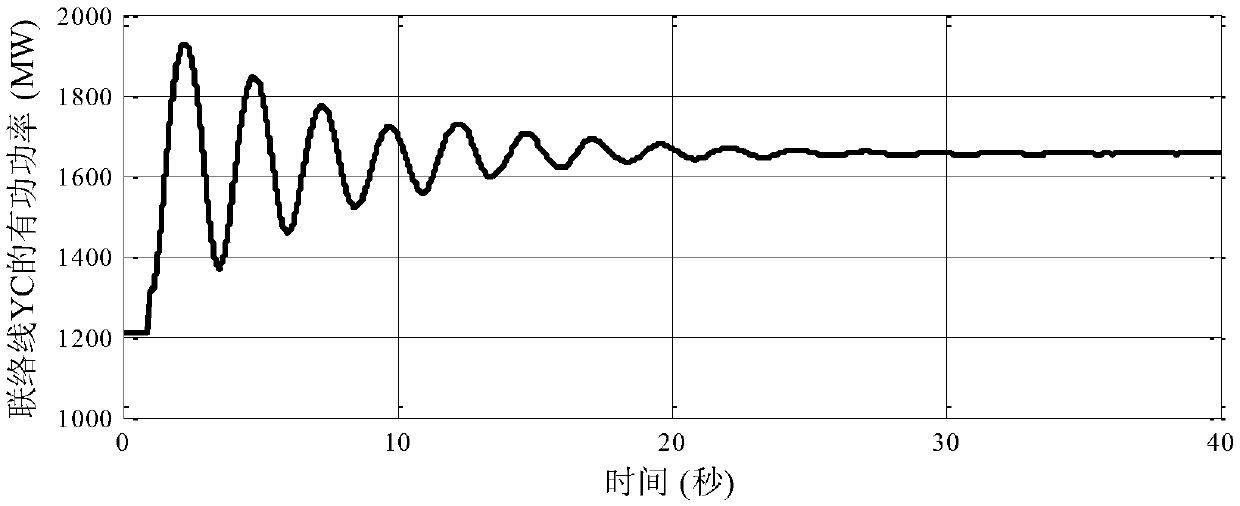
[0124] Based on the operation mode data of China Southern Power Grid in 2013, in the time domain simulation process, the Chusui DC single-pole blocking fault is set, and the duration is 0.1s. After 0.1s, the single-pole in the blocking fault exits the operation. The active power of the tie line YC between Yunnan and Guangxi power grids is selected as the research object of this method. After being disturbed, the active power of the tie line YC changes as follows: figure 2 shown.
[0125] Using the active power simulation data of 1s to 20s on the tie line YC a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com