A Design Method of Large Girth Type II Quasi-Cyclic LDPC Codes Based on Sidon Sequence
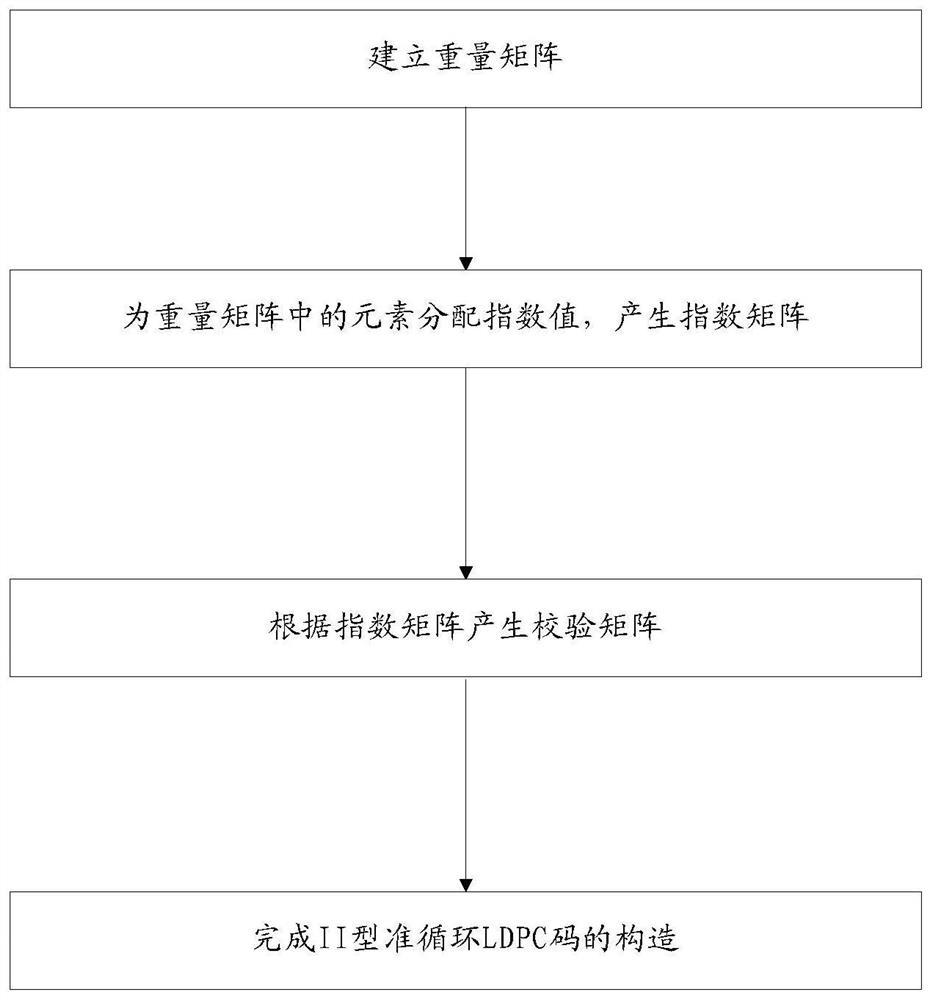
An LDPC code and quasi-cyclic technology, which is applied in the design field of large girth II type quasi-cyclic LDPC codes, can solve the problems of inflexible code rate, inability to meet the coding requirements of various code rates, and inability to guarantee the girth length, etc., so as to improve flexibility sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
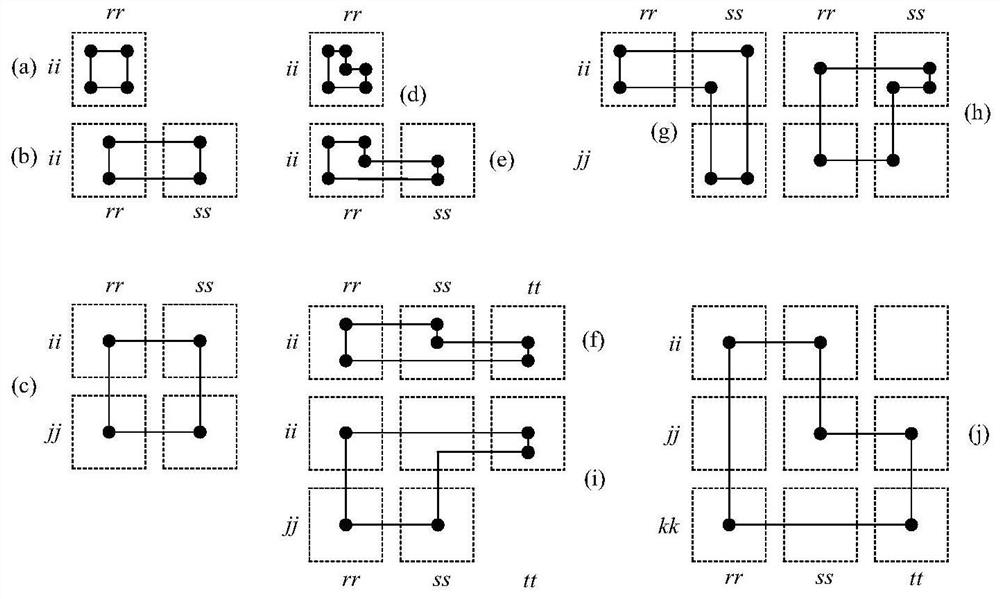
[0080] The code rate of II type QC-LDPC code in embodiment 1 and embodiment 2 is 1 / 2, and the method that adopts computer detection shows figure 2The 6-ring shown in (j) does not exist. The code rate of Type II QC-LDPC codes in Embodiments 3 and 4 is 2 / 3, which is directly eliminated without computer detection. figure 2 The 6-ring shown in (j).
[0081] Example 1:
[0082] It is assumed that a type II QC-LDPC code with a code length of 1680 and a code rate R of 1 / 2 needs to be designed. Since R=(L-1) / L in the present invention, L=2 is taken. Since the code length in the present invention is NLP, NP is 1680 / L=840. N cannot be too large, otherwise P will be small, which will result in no Sidon sequence with many elements. Might as well take N=5, then P=840 / N=168.
[0083] (Step 1) Build a weight matrix. in satisfying a 0 ≠a 1 and mod(a 0 +a 1 , N)≠0, select the (a) that maximizes the upper bound of the minimum distance 0 ,a 1 ). (a 0 ,a 1 ) = (1, 2), it can be ...
Embodiment 2
[0090] It is assumed that a type II QC-LDPC code with a code length of 3456 and a code rate R of 1 / 2 needs to be designed. Since R=(L-1) / L in the present invention, L=2 is taken. Since the code length in the present invention is NLP, NP is 3456 / L=1728. Might as well take N=6, then P=1728 / N=288.
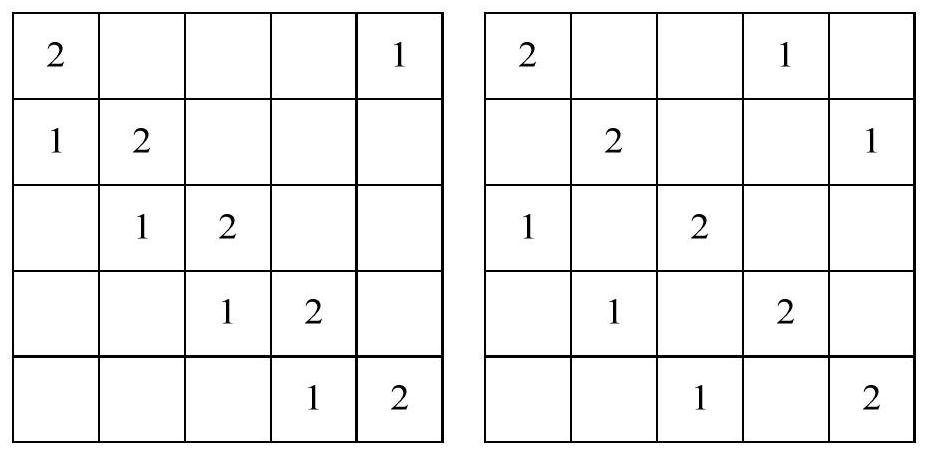
[0091] (Step 1) Select the weight matrix. in satisfying a 0 ≠a 1 and mod(a 0 +a 1 , N)≠0, select the (a) that maximizes the upper bound of the minimum distance 0 ,a 1 ). (a 0 ,a 1 )=(1,4), it can be known that the upper bound of the minimum distance is 66 by the S-V method. Actually 66 is the maximum value of the upper bound on the minimum distance that can be reached by any two blocks (either circular or acyclic) for N=6. by (a 0 ,a 1 ) to get the weight matrix, such as Figure 4 shown.
[0092] (Step 2) Assign parity pairs to each element 2 in the weight matrix. For P=288, use the Bose construction method to obtain a Sidon sequence, and divide the sequence into pari...
Embodiment 3
[0098] It is assumed that a type II QC-LDPC code with a code length of 3600 and a code rate R of 2 / 3 needs to be designed. Since R=(L-1) / L in the present invention, L=3 is taken. Since the code length in the present invention is NLP, NP is 3600 / L=1200. Might as well take N=10, then P=1200 / N=120.
[0099] (Step 1) Select the weight matrix. In satisfying mod(a i +a j ,N)≠0(0≤i,j≤L-1) and mod(a 0 +a 1 +a 2 , N)≠0, choose (a 0 ,a 1 ,a 2 ). Since it is very difficult to use the S-V method to calculate the upper bound of the minimum distance when N = 10, we choose the local optimal value and determine (a 0 ,a 1 ,a 2 )=(1, 4, 7), the weight matrix is obtained.
[0100] (Step 2) Assign parity pairs to each element 2 in the weight matrix. For P=120, use the Bose construction method to obtain a Sidon sequence, and divide the sequence into parity to obtain S=S 1 ∪S 2 , where S 1 ={0,54,64,68,70,98}, S 2 ={29,37,55,75,117}. use S 1 All 6 even numbers and S in 2 All...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com