A demand calculation method for smart meters
A calculation method, smart meter technology, applied in the direction of measuring electrical variables, measuring devices, complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve problems such as processing, and achieve the effect of reasonable and accurate calculation method and convenient calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
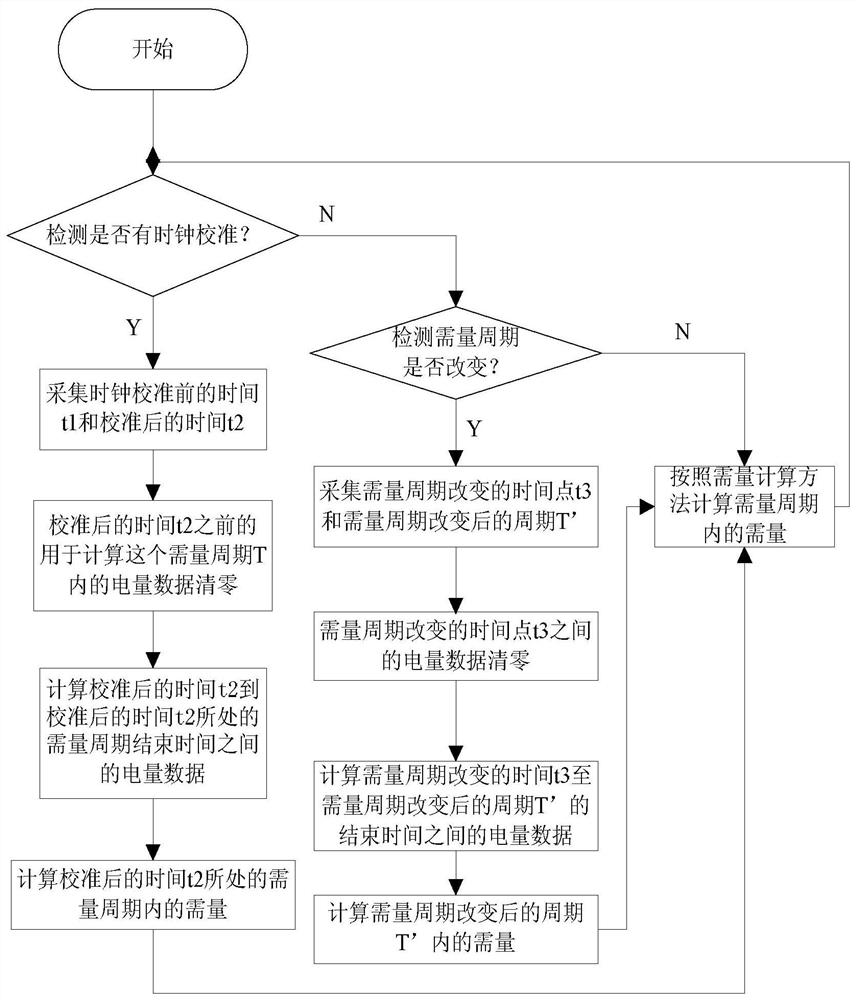
[0055] The demand calculation after clock calibration and demand period change using the interval-based demand calculation method is as follows:
[0056] Time calibration within the demand period T:
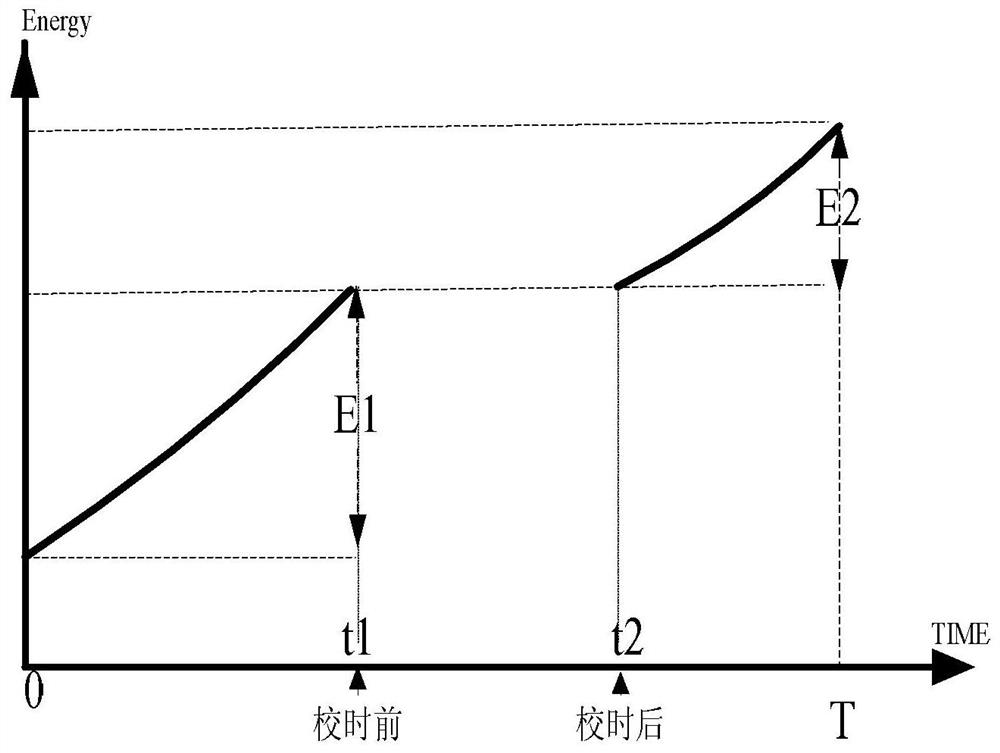
[0057] Such as figure 2 As shown, the demand cycle is [0, T), the time t1 before clock calibration is less than the time t2 after calibration, that is, the clock is adjusted backwards, t1 and t2 are both within the demand cycle T, and in [0, T) The electricity accumulated in the period is E1, and the electricity accumulated in [t2, T) is E2, then the demand period is [0, T) and the demand P=E2 / T.
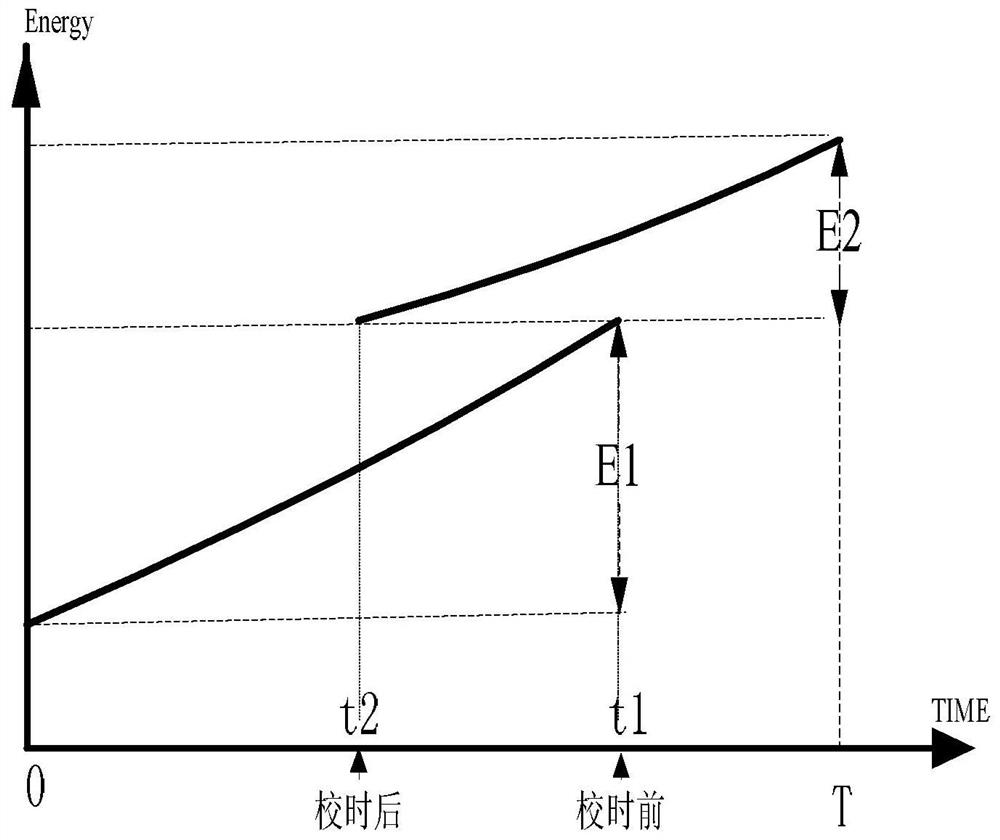
[0058] Such as image 3 As shown, the demand period is [0, T), the time t1 before clock calibration is greater than the time t2 after calibration, that is, the clock is adjusted forward, and both t1 and t2 are within the demand period T, in [0, t1 ) is E1, and the accumulated electricity in [t2, T) is E2, then the demand period is [0, T) and the demand P=E2 / T.
[0059] Time calibr...
Embodiment 2
[0068] The demand calculation after clock calibration and demand period change using the slipping demand calculation method is as follows:
[0069] Time calibration within slip cycle T1:
[0070] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the slip cycle is T1, the number of slips is N=2, then the second demand cycle is T2=2T1, the time t1 before the clock calibration is less than the time t2 after the calibration, that is, the clock is adjusted backwards, and t1 and t2 are both in the slip cycle [2T1, 3T1), the accumulated electricity in [0, T1) is E1, the accumulated electricity in [T1, 2T1) is E2, and the accumulated electricity in [2T1, t1) is E3, the accumulated electricity in [t2, 3T1) is E4, and the accumulated electricity in [3T1, 4T1) is E5, then the demand P1 of the second demand cycle [0, 2T1) = 0; the second demand The demand P2 of the quantity period [T1, 3T1) = E4 / 2T1; the demand P3 of the second demand period [2T1, 4T1] = (E4+E5) / 2T1;
[0071] Such as Figure 9 As shown, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com