A complex terrain humanoid robot adaptive balance control method, device and system
A humanoid robot and balance control technology, applied in the direction of program control manipulators, manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as extensive limitations, achieve the effects of reducing hardware loss, wide application range, and strengthening self-adaptive ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
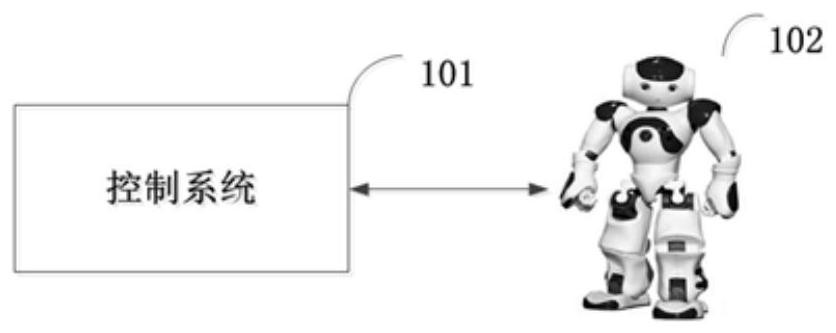
[0070] figure 1 It is an application environment diagram of a complex terrain humanoid robot adaptive balance control method provided in one embodiment, such as figure 1 As shown, in this application environment, a control system 101 and a humanoid robot 102 are included.
[0071] The control system 101 can be a tablet computer, a notebook computer, or a desktop computer, but is not limited to this. The control system can be combined by one or more of the above-mentioned devices, and the completed function is to realize the operation of the humanoid robot, Including programming, starting and stopping, receiving, storing, sending data and instructions, motion analysis, etc., but not limited to this, that is, devices that can complete the above functions fall within the protection scope of this application.
[0072] The humanoid robot 102 can be a Nao robot or other similar types of bipedal or quadrupedal robots, mainly for tasks in different motion states. The tasks of the ro...
Embodiment 2
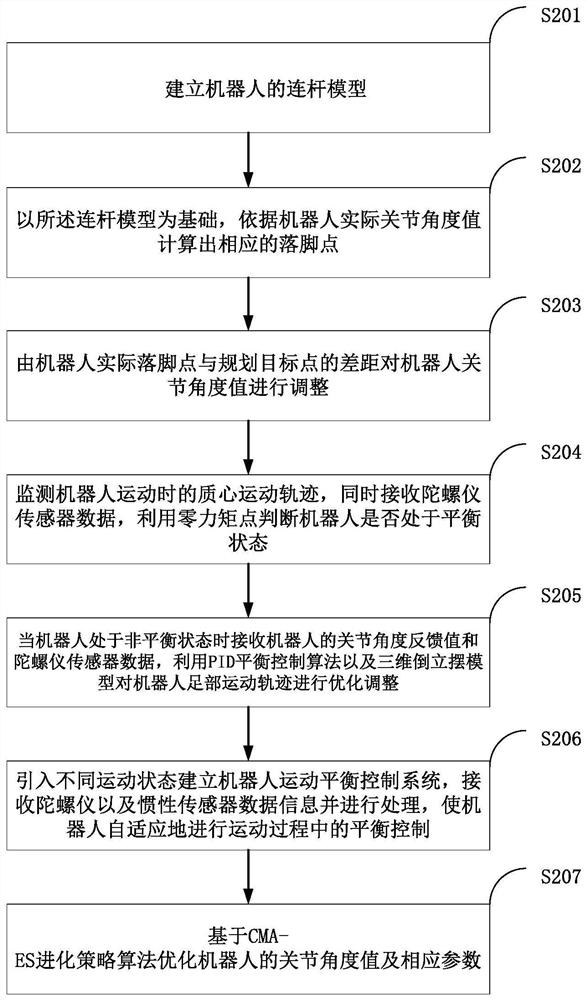
[0074] like figure 2 As shown, in one embodiment, a method for adaptive balance control of a humanoid robot with complex terrain is provided, and this embodiment is mainly applied to the above-mentioned method. figure 1 The control system 101 in (of course, the control system can also be integrated into the humanoid robot 102 ) as an example. Specifically, the following steps can be included:
[0075] Step S201, establishing a connecting rod model of the robot;
[0076] Step S202, based on the connecting rod model, calculate the corresponding foothold according to the actual joint angle value of the robot;
[0077] Step S203, adjusting the joint angle value of the robot according to the difference between the actual landing point of the robot and the planned target point;
[0078] Step S204, monitoring the movement trajectory of the center of mass of the robot during movement, simultaneously receiving data from the gyroscope sensor, and using the zero moment point to deter...
Embodiment 3
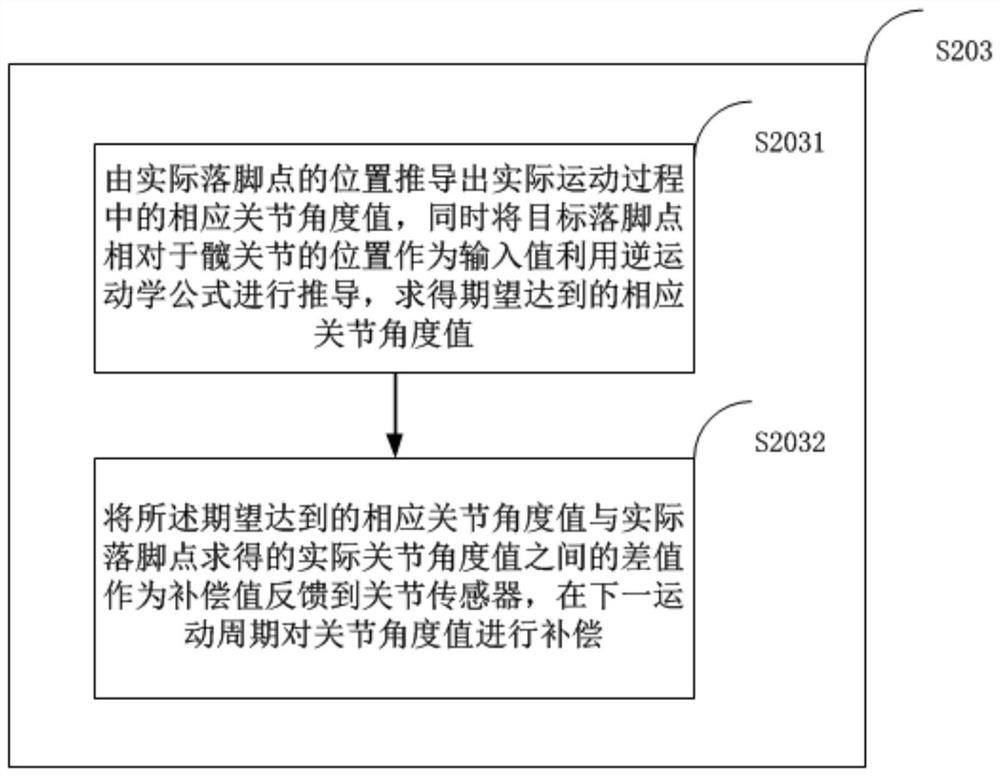
[0102] like image 3 As shown, in one embodiment, an adaptive balance control method for a humanoid robot with complex terrain is given. For the convenience of description, only the parts related to the embodiment of the present invention are shown. Compared with the second embodiment, the The difference is that in step S203, the robot joint angle value is adjusted by the difference between the actual landing point of the robot and the planned target point, including:
[0103] Step S2031, derive the corresponding joint angle value in the actual movement process from the position of the actual foothold, and at the same time deduce the position of the target foothold relative to the hip joint as the input value to obtain the desired corresponding joint angle value;
[0104] Step S2032, the difference between the expected corresponding joint angle value and the actual joint angle value obtained from the actual foothold is fed back to the joint sensor as a compensation value, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com